PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851454

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851454
Gas Turbine - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Gas Turbine Market size is estimated at USD 62.54 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 88.06 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 7.08% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
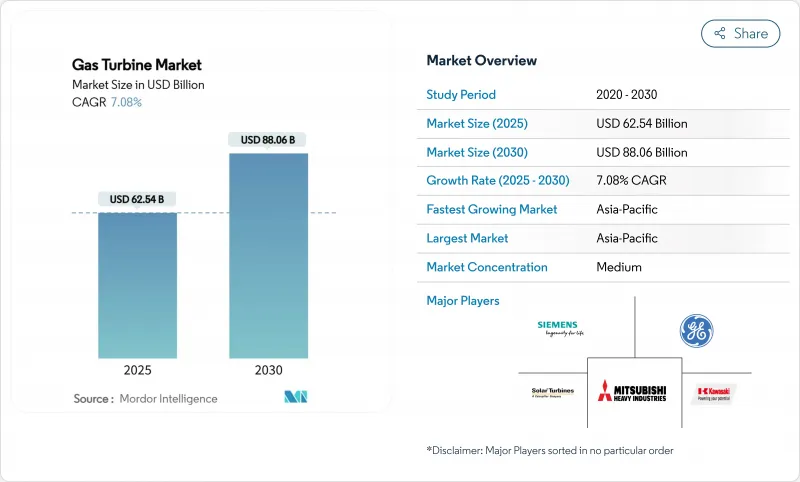
Momentum comes from energy-security concerns, stricter carbon-reduction policies, and the need for flexible assets that stabilize grids with rising renewable penetration. Rapid growth in data-center electricity demand, spurred by artificial-intelligence workloads, is prompting utilities such as Duke Energy to secure additional turbines that can start quickly and run efficiently. Manufacturers prioritize hydrogen-ready designs, higher combined-cycle efficiencies, and modular construction techniques to lower installation times and cost. Supply-chain constraints for superalloy hot-gas-path parts and financing hurdles linked to ESG taxonomies temper the overall outlook yet have not slowed new-build backlogs.
Global Gas Turbine Market Trends and Insights
Asia-Pacific Coal-to-Gas Transition Accelerating Utility Orders
With coal fleets facing tighter emissions limits, utilities across China, India, and Vietnam are turning to high-efficiency turbines pre-engineered for hydrogen co-firing. China's rollout of a high-capacity hydrogen unit demonstrates national intent to pair clean fuel with dispatchable power. Vietnam is already installing 9HA.02 systems to secure a low-carbon baseload. Singapore plans to run hydrogen-ready units before 2030, highlighting how the gas turbine market bridges renewables and decarbonization goals. Regional procurement pipelines exceed 42 GW of potential capacity additions by 2030.
LNG-Linked Island Grids in Southeast Asia Driving Mobile Aeroderivative Demand
Island economies depend on seasonal tourism and must manage variable renewables on small grids. Portable TM2500 packages, now delivering 34 MW within minutes and operating without water, supply flexible peaking and emergency power. Operators tap floating LNG storage for fuel, enabling quick installation and relocation. Enhanced dry-low-NOx combustion trims emissions, while multi-fuel capability underpins resilience against supply disruptions. As such, aeroderivative suppliers see a distinct niche emerging across archipelagic Southeast Asia and certain Caribbean states.
Gas-Price Volatility Post-Ukraine War Curtailing EU Projects
Russian pipeline flows to Europe dropped 80%, sending spot gas prices to unprecedented highs and undermining project financing for simple-cycle units. Developers now prioritize combined-cycle plants with long-term LNG contracts, while some peaking projects pivot to battery storage. Germany accelerates regasification terminals to secure supply, yet lenders remain cautious until prices stabilize, slowing the gas turbine market in several EU states.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Petro-Chemical Cogeneration Build-out in the Middle East
- Disaster-Relief Leasing Surge for Aeroderivative Sets in the Caribbean
- Utility-Scale Battery Storage Displacing Peaking Turbines
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Large frames exceeding 120 MW captured 58% of 2024 sales, confirming utility preference for high-output, high-efficiency equipment in baseload and combined-cycle duty. Their heavy construction favors thermal stability and endures more viscous fuel blends, a key trait for future hydrogen. The gas turbine market size allocated to this class is forecast to expand steadily at the overall industry pace, given persistent retirements of coal assets.
Mid-range units between 31 MW and 120 MW represent the fastest growing slice at 7.44% CAGR. They balance efficiency with cycling capability, making them attractive for renewables-firming. Enhanced turndown ratios and quick cold starts suit markets with volatile solar or wind profiles. The gas turbine market benefits as data centers deploy dedicated mid-range plants that can match variable computational loads while ensuring local reliability.
Combined-cycle configurations held 75% of 2024 shipments thanks to greater than 64% net efficiencies that cut fuel cost and CO2 per MWh. Integration advances, such as modular heat-recovery steam generators, lower construction timelines, further widening their appeal. The gas turbine market share for combined-cycle designs should increase as new national emissions rules discount simple-cycle projects without carbon-capture provisions.
Simple/open-cycle sets retain importance for peaking and emergency duty, especially in grids needing fast-ramp assets. Cogeneration plants also prosper where industrial hosts value steam output. With overall process-energy utilizations reaching 80%, cogeneration supports petrochemical expansion in the Middle East and Southeast Asia.
The Gas Turbine Market Report is Segmented by Capacity (Below 30 MW, 31 To 120 MW, Above 120 MW), Operating Cycle (Combined Cycle, Simple/Open Cycle, and Cogeneration/CHP), Fuel Type (Natural Gas, Liquid Fuels, and Other Fuel Types), Service (OEM and MRO), End-User Industry (Power, Oil and Gas, and Other End-User Industries), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific generated 59.1% of 2024 revenue and is set for a 7.96% CAGR through 2030. Combined with industrial expansion, coal-to-gas switching underpins growth in China, India, Vietnam, and Indonesia. Government policies favor hydrogen-capable turbines as a medium-term decarbonization step, reinforcing regional equipment orders.
North America ranks second. Decommissioning coal plants, rejuvenating aging combined-cycle fleets, and powering AI-driven data centers all support volume. Asset consolidation continues with independent power producers acquiring portfolios to capture capacity payments and ancillary-service revenues.
Europe faces gas-price volatility, yet still invests in reserve peaking units and back-up capacity markets. New regasification terminals and strategic LNG contracts restore fuel security, while simple-cycle peakers equipped with fast-shutdown features stand ready to complement large offshore-wind additions.
- General Electric Company
- Siemens Energy AG
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd.
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd.
- Ansaldo Energia SpA
- MAN Energy Solutions SE
- Wartsila Oyj Abp
- Rolls-Royce Holdings plc
- Solar Turbines Incorporated
- Capstone Green Energy Corporation
- Doosan Skoda Power
- IHI Corporation
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
- Harbin Electric Co. Ltd.
- Shanghai Electric Group Co. Ltd.
- OPRA Turbines BV
- Baker Hughes Company
- Vericor Power Systems LLC
- Zorya-Mashproekt
- Nanjing Turbine & Electric Machinery Group
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 LNG-linked Island Grids in SEA Driving Mobile Aeroderivative Demand
- 4.2.2 Petro-chemical Cogeneration Build-out in Middle East
- 4.2.3 Disaster-Relief Leasing Surge for Aeroderivative Sets in Caribbeans
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Gas-price Volatility Post-Ukraine War Curtailing EU Projects
- 4.3.2 Utility-scale Battery Storage Displacing Peaking Turbines (US/Australia)
- 4.3.3 ESG-driven Financing Restrictions under EU Taxonomy
- 4.3.4 Super-alloy Supply-Chain Shortages for Large-Frame Hot-gas-path Parts
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Capacity
- 5.1.1 Below 30 MW
- 5.1.2 31 to 120 MW
- 5.1.3 Above 120 MW
- 5.2 By Type
- 5.2.1 Combined Cycle
- 5.2.2 Simple/Open Cycle
- 5.2.3 Cogeneration/CHP
- 5.3 By Fuel Type
- 5.3.1 Natural Gas
- 5.3.2 Liquid Fuels (Diesel/Kerosene/LPG)
- 5.3.3 Other Fuel Types (Hydrogen, Biogas)
- 5.4 By Service
- 5.4.1 OEM
- 5.4.2 Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul (MRO)
- 5.5 By End-User Industry
- 5.5.1 Power
- 5.5.2 Oil and Gas
- 5.5.3 Other End-user Indutries (Industrial, Marine)
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.2 Germany
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Russia
- 5.6.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 India
- 5.6.3.3 Japan
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Argentina
- 5.6.4.3 Chile
- 5.6.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.3 South Africa
- 5.6.5.4 Egypt
- 5.6.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 General Electric Company
- 6.4.2 Siemens Energy AG
- 6.4.3 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd.
- 6.4.4 Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd.
- 6.4.5 Ansaldo Energia SpA
- 6.4.6 MAN Energy Solutions SE
- 6.4.7 Wartsila Oyj Abp
- 6.4.8 Rolls-Royce Holdings plc
- 6.4.9 Solar Turbines Incorporated
- 6.4.10 Capstone Green Energy Corporation
- 6.4.11 Doosan Skoda Power
- 6.4.12 IHI Corporation
- 6.4.13 Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
- 6.4.14 Harbin Electric Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Shanghai Electric Group Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.16 OPRA Turbines BV
- 6.4.17 Baker Hughes Company
- 6.4.18 Vericor Power Systems LLC
- 6.4.19 Zorya-Mashproekt
- 6.4.20 Nanjing Turbine & Electric Machinery Group
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




