PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851624

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851624
Global Nanocellulose - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
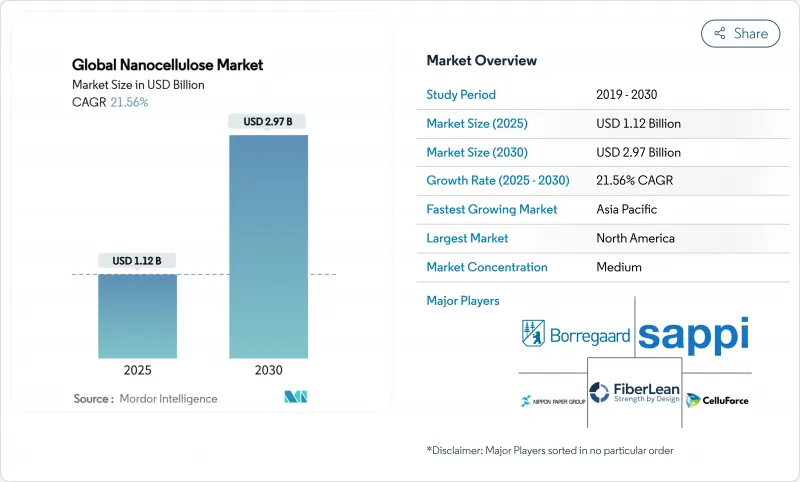
The Global Nanocellulose Market size is estimated at USD 1.12 Billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 2.97 Billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 21.56% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Escalating sustainability mandates, volatile petrochemical prices, and rapid material science breakthroughs converge to create a clear runway for double-digit expansion. Automotive lightweighting, recyclable barrier films, and biomedical scaffolds headline near-term demand, while enzymatic low-energy processes unlock future cost competitiveness. North American incumbents leverage mature pilot lines and close original equipment manufacturer (OEM) ties, yet Asian producers narrow the gap through lower conversion costs and proximity to electronics and packaging clusters. Raw-material flexibility shifting from wood pulp to agricultural residues further de-risks supply chains and anchors circular-economy business models. Established pulp majors expand tonnage on the competitive front, whereas biotech start-ups chase premium therapeutic niches, resulting in an active partnership and licensing landscape that accelerates application rollout.
Global Nanocellulose Market Trends and Insights
Superior Mechanical and Barrier Properties
Nanocellulose's tensile strength of 4.9-7.5 GPa (Gigapascals) and elastic modulus of 100-200 GPa position it close to carbon fiber in weight-sensitive components, making it attractive for automotive body panels and aircraft interiors. Oak Ridge National Laboratory validated this potential in 2025 by showing 50% higher tensile strength and nearly double toughness in carbon-nanofiber-enhanced nanocellulose composites versus conventional glass-fiber alternatives. The high aspect ratio and surface area foster tight bonding with polymer matrices, minimizing delamination risk and boosting fatigue life. Japanese automakers project a 20 kg per-vehicle weight cut when nanocellulose substitutes selected metal and plastic parts, translating into meaningful fuel savings and lower lifecycle emissions. Beyond load-bearing parts, ultrathin nanocellulose films block oxygen and water vapor better than Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol (EVOH) or Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC), yet remain recyclable and compostable. These dual mechanical and barrier advantages underpin the material's broad addressable market, from consumer electronics casings to pharmaceutical blister packs.
Sustainable Packaging Demand Surge
Retail, e-commerce, and food brands rush to replace petroleum films, driving a steep demand curve for bio-based barriers. European chains in Belgium, France, and Luxembourg replaced pilot-scale plastic trays with cellulose packs in the 2024 R3PACK trial, eliminating thousands of tonnes of single-use plastics. European Union (EU) directives mandate that all packaging be reusable or recyclable by 2030, prompting converters to qualify nanocellulose coatings that upgrade ordinary paperboard. Bacterial cellulose films show superior ultraviolet (UV) shielding and tensile strength, reducing spoilage in light-sensitive foods while holding up under cold-chain logistics. Swedish start-up lines achieved cost parity with Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) wrap by optimizing drying energy and roll-to-roll coating speeds, removing the final economic roadblock. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)'s Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) nod for fibrillated cellulose in food contact further derisks adoption for North American suppliers . As brand owners lock in multi-year supply contracts, the nanocellulose market secures a predictable revenue base for capacity expansions.
High Production Cost and Scale-up Risk
Even with hydrolysis optimization, minimum selling prices hover at USD 10,031 per dry tonne for acid routes, and USD 65,740 per dry tonne for current enzymatic yields, dwarfing commodity polymer benchmarks. Continuous papermaking pilots halve capex per output kilogram, yet sustained quality control remains elusive as retention tops out at 73%. Capex intensity restricts large-scale units to pulp majors and state-backed entities, marginalizing innovators in emerging markets that lack patient capital. Life-cycle assessments show a 6.5-fold environmental win once plants exceed 20,000 tpa, but financing such nameplates requires off-take certainty that few downstream users can underwrite today. This chicken-and-egg dynamic tempers otherwise strong demand signals and prompts phased debottlenecking rather than greenfield mega-mills.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Regulatory Push to Replace Single-use Plastics
- Rising R&D Pilot Facilities and Funding
- Competition From Other Bio-nanomaterials
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Nanofibrillated Cellulose (NFC) commands 41.93% market share in 2024, reflecting its established production infrastructure and broad applicability across paper processing and composites applications. However, Bacterial Cellulose is the fastest-growing segment with 37.02% CAGR through 2030, driven by its ultra-pure properties and premium positioning in pharmaceuticals and biomedical applications. The production dichotomy reveals strategic positioning where NFC leverages mechanical processing scalability, while bacterial cellulose targets high-value applications, justifying fermentation costs.
Nanocrystalline Cellulose (NCC) maintains steady growth through its crystalline structure advantages in reinforcement applications, particularly where dimensional stability and thermal resistance prove critical. Microfibrillated Cellulose (MFC) is a bridge technology, offering enhanced properties over conventional cellulose while remaining cost-competitive with traditional additives in paper and packaging applications.
Wood Pulp maintains its dominant position with 58.36% market share in 2024, leveraging established supply chains and processing infrastructure developed over decades of pulp and paper industry evolution. Yet, Agricultural Residues as a source demonstrate the strongest growth trajectory at 23.68% CAGR, fundamentally challenging wood pulp's long-term dominance through cost advantages and circular economy alignment. The shift toward agricultural residues reflects economic optimization and sustainability mandates favoring waste valorization over virgin resource consumption.
Micro-algae, seaweed, and bacterial hosts supply specialty volumes for cosmetic serums and ophthalmic solutions where absolute purity trumps cost. These bio-sources allow closed-loop cultivation, minimizing pesticide carry-over and easing Genetically Modified Organism (GMO)-free certification. European consortiums study hemp hurd and flax shive feedstocks, leveraging regional fiber crops to offset pulpwood shortages. However, residue logistics remain complex: seasonal availability demands wet-storage silos or densification pellets, adding hidden capex. Wood pulp producers counter with chain-of-custody certification and guaranteed year-round supply, arguing reliability for mass-market packaging volumes. The competitive dance ensures continuous innovation and locks the nanocellulose market into a multi-feedstock future.
The Nanocellulose Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Nanofibrillated Cellulose, Bacterial Cellulose, and More), Source (Wood Pulp, Agricultural Residues, and More), Form (Dry, Gel, and Suspension), End-Use Industry (Paper Processing, Oil and Gas, Composites, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD)
Geography Analysis
North America leads the Nanocellulose market with a 43.92% revenue share in 2024, backed by early USDA and DOE grants that underwrote pilot lines and strong pull from automotive and aerospace original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). The region enjoys deeply integrated pulp-and-paper logistics, letting mills quickly pivot digesters toward cellulose nanofibrils without greenfield capital expenditure (CAPEX). Tier-1 suppliers collaborate with state universities to optimize automotive sheet-molding compounds that meet Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) crash standards. Regulatory frameworks on sustainable packaging are less stringent than in the European Union (EU), yet brand commitments by big box retailers ensure stable offtake. As a result, the nanocellulose market size across North America remains the anchor against which global producers benchmark pricing.
Asia-Pacific records a 24.36% CAGR that challenges North America's leadership by 2030. Japanese corporations commercialized cellulose nanofiber years ahead of rivals by repurposing depreciated paper machines, while Chinese start-ups deploy low-cost, high-pressure homogenizers built domestically to evade import duties. Electronics assemblers in Shenzhen specify nanocellulose barrier films to protect Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) modules from oxygen ingress, creating captive demand and shortening supplier qualification cycles. Agricultural residue abundance in India and Thailand cuts feedstock bills by 40%, and enzyme licensing deals accelerate adoption. Consequently, the Nanocellulose market attracts continuous plant announcements around ASEAN ports where export logistics converge.
Europe secures mid-teen growth on the back of the world's strictest single-use-plastic bans. Converters in Belgium and the Nordics qualify Nanocellulose coatings to meet 95% paper recyclability thresholds. While higher energy prices squeeze margins, EU innovation grants de-risk pilot investments that showcase circular-bioeconomy leadership. South America, buoyed by sugarcane bagasse supplies, emerges as a low-cost export hub once CelOCE enzyme plants go commercial. Middle East and Africa start from a small base yet eye nanocellulose enhanced cement composites to curb desert construction dust, with multinational cement majors funding test pours near Gulf megaprojects. This geographic mosaic mirrors differing policy, resource, and industrial profiles, underpinning a balanced global growth picture for the nanocellulose market.
- Axcelon Biopolymers Corporation
- Borregaard AS
- CelluComp
- CelluForce
- Chuetsu Pulp & Paper Co., Ltd.
- Daicel Corporation
- FiberLean
- GranBio Technologies
- Melodea
- NIPPON PAPER INDUSTRIES CO., LTD.
- Norske Skog ASA
- Oji Holdings Corporation
- Sappi Ltd
- Stora Enso
- UPM
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Superior Mechanical and Barrier Properties
- 4.2.2 Sustainable Packaging Demand Surge
- 4.2.3 Regulatory Push to Replace Single-use Plastics
- 4.2.4 Rising R&D Pilot Facilities and Funding
- 4.2.5 Enzymatic Low-energy Production Breakthroughs
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Production Cost and Scale-up Risk
- 4.3.2 Competition From Other Bio-nanomaterials
- 4.3.3 Food-contact Safety and Inhalation Concerns
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Nanofibrillated Cellulose (NFC)
- 5.1.2 Nanocrystalline Cellulose (NCC)
- 5.1.3 Bacterial Cellulose
- 5.1.4 Microfibrillated Cellulose (MFC)
- 5.1.5 Others
- 5.2 By Source
- 5.2.1 Wood Pulp
- 5.2.2 Agricultural Residues
- 5.2.3 Micro-algae & Other Bio-sources
- 5.2.4 Others
- 5.3 By Form
- 5.3.1 Dry (Powder)
- 5.3.2 Gel
- 5.3.3 Suspension
- 5.4 By End-use Industry
- 5.4.1 Paper Processing
- 5.4.2 Paints and Coatings
- 5.4.3 Oil and Gas
- 5.4.4 Food and Beverage
- 5.4.5 Composites
- 5.4.6 Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics
- 5.4.7 Other End-user Industries
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 China
- 5.5.1.2 India
- 5.5.1.3 Japan
- 5.5.1.4 South Korea
- 5.5.1.5 Malaysia
- 5.5.1.6 Thailand
- 5.5.1.7 Indonesia
- 5.5.1.8 Vietnam
- 5.5.1.9 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 North America
- 5.5.2.1 United States
- 5.5.2.2 Canada
- 5.5.2.3 Mexico
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 NORDIC Countries
- 5.5.3.7 Turkey
- 5.5.3.8 Russia
- 5.5.3.9 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Colombia
- 5.5.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.4 Qatar
- 5.5.5.5 Egypt
- 5.5.5.6 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.7 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Axcelon Biopolymers Corporation
- 6.4.2 Borregaard AS
- 6.4.3 CelluComp
- 6.4.4 CelluForce
- 6.4.5 Chuetsu Pulp & Paper Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Daicel Corporation
- 6.4.7 FiberLean
- 6.4.8 GranBio Technologies
- 6.4.9 Melodea
- 6.4.10 NIPPON PAPER INDUSTRIES CO., LTD.
- 6.4.11 Norske Skog ASA
- 6.4.12 Oji Holdings Corporation
- 6.4.13 Sappi Ltd
- 6.4.14 Stora Enso
- 6.4.15 UPM
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment
- 7.2 Enzymatic and Biological Methods for Nanocellulose Production




