PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851783

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851783
Food Processing Automation - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Food processing automation market size was valued at USD 27.95 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 40.12 billion by 2030, reflecting a 7.49% CAGR.
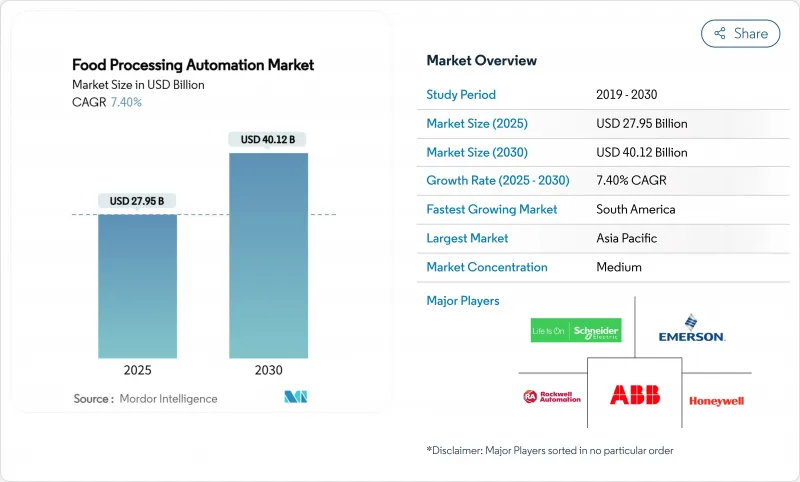
This expansion stemmed from escalating labor shortages, tighter global food-safety rules, and the push for lean, energy-efficient production. Roughly 48% of capital spending by large food manufacturers in 2025 flowed toward new or upgraded automation projects, signifying a decisive move from isolated machinery toward connected, data-driven lines. The food-grade robotics boom, the proliferation of real-time OEE dashboards, and widespread cloud adoption further accelerated uptake. Providers that bundled hardware, software, and compliance services captured rising demand for turnkey solutions.
Global Food Processing Automation Market Trends and Insights
Digitisation of HACCP-compliant traceability
Digital traceability platforms replaced manual logs by linking IoT sensors, blockchain databases, and cloud dashboards that captured cooking temperatures, lot codes, and supplier credentials in real time. These systems cut average recall response from weeks to hours and prepared processors for FDA traceability mandates effective January 2026. Large buyers adopted them to lower insurance premiums and protect brand equity, creating new revenue streams for automation integrators that offered end-to-end compliance packages.
Adoption of hygienic, wash-down-ready robotics
Food-grade robots equipped with IP69K housings, corrosion-proof surfaces, and food-safe lubricants enabled automation of moist, chilled, or high-pressure wash-down zones previously deemed off-limits. Leading deployments in cheese and dairy cutting showed 83% waste reductions, while ROI periods often stayed below 18 months for medium-size plants.
High up-front CAPEX for retrofit brown-field sites
Retrofits often cost 40-60% more than new-build installations because lines must stay partially operational, utilities must be relocated, and legacy PLCs need custom gateways. RaaS contracts and modular cells that slide into existing layouts began to ease the burden, yet finance teams in small plants still viewed payback windows cautiously.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Surge in ready-to-eat (RTE) meal demand
- Workforce shortages accelerating "lights-out" plants
- Cybersecurity vulnerabilities in legacy SCADA
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Industrial Robotics contributed USD 8.22 billion to the Food processing automation market size in 2024 and is projected to grow at a 13.8% CAGR. Installations spanned primary cutting, pick-and-place, and case packing. AI-vision upgrades allowed grippers to adjust in milliseconds to irregular produce, boosting first-pass yield. Distributed Control Systems remained essential for dairy pasteurization and brewing, providing deterministic control over temperature-sensitive stages. MES adoption climbed as processors synchronized shop-floor data with ERP suites to streamline audit queries and allergen control. Meanwhile, VFD retrofits cut conveyor energy draw by up to 25%, prompting utility rebate programs in Europe. Continuous sensor miniaturization pushed decision logic to the edge, letting production cells self-optimize without waiting for cloud feedback.
Even with robotics dominance, manufacturers layered multiple technologies to maximize uptime. A protein plant might feed vision-guided robots through a DCS buffer, log KPIs into MES, and fine-tune motor torque via VFDs, illustrating platform convergence across the Food processing automation market.
Hardware retained 67.3% revenue share in 2024 because processors still needed stainless servo actuators, wash-down robots, and sealed motors before digital analytics could add value. However, software and services grew 12.5% annually as users demanded predictive maintenance dashboards, cloud MES subscriptions, and 24/7 cyber-monitoring. Smart cameras embedded neural inference chips, while robotics OEMs bundled SaaS licenses that delivered firmware updates and AI models over-the-air.
Managed cybersecurity, regulatory reporting, and energy-optimization contracts expanded margins beyond the one-time equipment sale. As a result, integrated offerings blurred the line between physical assets and code, reshaping vendor revenue streams throughout the Food processing automation market.
The Food Processing Automation Market Report is Segmented by Operational Technology and Software (Distributed Control Systems, Manufacturing Execution Systems, and More), Component (Hardware, Software and Services), End-User (Dairy Processing, Bakery and Confectionery, and More), Application (Packaging and Re-Packaging, and More), Automation Level (Fully-Automatic Lines, and Semi-Automatic Lines), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific maintained leadership with 38.7% revenue share in 2024, underpinned by China's food-safety rule tightening and wage inflation that accelerated robotics adoption in meat deboning, dairy filling, and snack packaging. Japanese OEMs exported food-grade robots across the region, reinforcing a dense support ecosystem. Indian processors modernized fruit sorting and spice grinding lines through government automation incentives.
South America registered an 11.9% CAGR outlook. Brazilian meatpackers retrofitted chilled rooms with hygienic robots to meet EU import standards, while sugar mills installed MES and VFDs to cut energy consumption. Investments rippled into Argentina and Chile where produce exporters automated washing and grading to secure new shelf-life-sensitive markets.
North America's mature installed base focused on AI retrofits and cybersecurity hardening. RTE meal producers in urban corridors adopted cobots to meet convenience-food demand spikes. European processors pushed ESG goals, adding high-efficiency drives and water-recapture skid packages. The Middle East and parts of Africa initiated palm-date and dairy modernisation programs, showing rising but uneven penetration in the global Food processing automation market.
- ABB Ltd.
- Alfa Laval AB
- Baader Food Processing Machinery GmbH
- Bosch Rexroth AG
- Buhler Holding AG
- Endress+Hauser Group Services AG
- Emerson Electric Co.
- FANUC Corp.
- Festo SE & Co. KG
- GE A Group AG
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Ishida Co., Ltd.
- John Bean Technologies Corp.
- Key Technology Inc. (Duravant LLC)
- KUKA AG
- Marel hf
- Mitsubishi Electric Corp.
- Multivac Sepp Haggenmuller SE & Co. KG
- Omron Corp.
- Regal Rexnord Corp.
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- SPX FLOW Inc.
- Tetra Pak International S.A.
- Yaskawa Electric Corp.
- Yokogawa Electric Corp.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Digitisation of HACCP?compliant traceability
- 4.2.2 Adoption of hygienic, wash-down-ready robotics
- 4.2.3 Surge in ready-to-eat (RTE) meal demand post-pandemic
- 4.2.4 Workforce shortages accelerating "lights-out" plants
- 4.2.5 Real-time OEE analytics lowering downtime
- 4.2.6 ESG-driven energy-efficient line retrofits
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High up-front CAPEX for retrofit brown-field sites
- 4.3.2 Cyber-security vulnerabilities in legacy SCADA
- 4.3.3 Low ROI in price-sensitive emerging markets
- 4.3.4 Skills gap in OT-IT convergence
- 4.4 Evaluation of Critical Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact Assessment of Key Stakeholders
- 4.9 Key Use Cases and Case Studies
- 4.10 Impact on Macroeconomic Factors of the Market
- 4.11 Investment Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Operational Technology and Software
- 5.1.1 Distributed Control Systems (DCS)
- 5.1.2 Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
- 5.1.3 Variable-Frequency Drives (VFD)
- 5.1.4 Valves and Actuators
- 5.1.5 Electric Motors
- 5.1.6 Sensors and Transmitters
- 5.1.7 Industrial Robotics
- 5.1.8 Other Technologies
- 5.2 By Component
- 5.2.1 Hardware
- 5.2.2 Software and Services
- 5.3 By End-User
- 5.3.1 Dairy Processing
- 5.3.2 Bakery and Confectionery
- 5.3.3 Meat, Poultry and Seafood
- 5.3.4 Fruit and Vegetable Processing
- 5.3.5 Beverage Manufacturing
- 5.3.6 Other End-Users
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Packaging and Re-packaging
- 5.4.2 Palletising and Depalletising
- 5.4.3 Sorting and Grading
- 5.4.4 Primary and Secondary Processing
- 5.4.5 Other Applications
- 5.5 By Automation Level
- 5.5.1 Fully-Automatic Lines
- 5.5.2 Semi-Automatic Lines
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Russia
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 Japan
- 5.6.4.3 South Korea
- 5.6.4.4 India
- 5.6.4.5 ASEAN
- 5.6.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 ABB Ltd.
- 6.4.2 Alfa Laval AB
- 6.4.3 Baader Food Processing Machinery GmbH
- 6.4.4 Bosch Rexroth AG
- 6.4.5 Buhler Holding AG
- 6.4.6 Endress+Hauser Group Services AG
- 6.4.7 Emerson Electric Co.
- 6.4.8 FANUC Corp.
- 6.4.9 Festo SE & Co. KG
- 6.4.10 GE A Group AG
- 6.4.11 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.12 Ishida Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 John Bean Technologies Corp.
- 6.4.14 Key Technology Inc. (Duravant LLC)
- 6.4.15 KUKA AG
- 6.4.16 Marel hf
- 6.4.17 Mitsubishi Electric Corp.
- 6.4.18 Multivac Sepp Haggenmuller SE & Co. KG
- 6.4.19 Omron Corp.
- 6.4.20 Regal Rexnord Corp.
- 6.4.21 Rockwell Automation Inc.
- 6.4.22 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.4.23 Siemens AG
- 6.4.24 SPX FLOW Inc.
- 6.4.25 Tetra Pak International S.A.
- 6.4.26 Yaskawa Electric Corp.
- 6.4.27 Yokogawa Electric Corp.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




