PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851873

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851873
Levulinic Acid - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Levulinic Acid Market size is estimated at 22.29 kilotons in 2025, and is expected to reach 30.01 kilotons by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.13% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
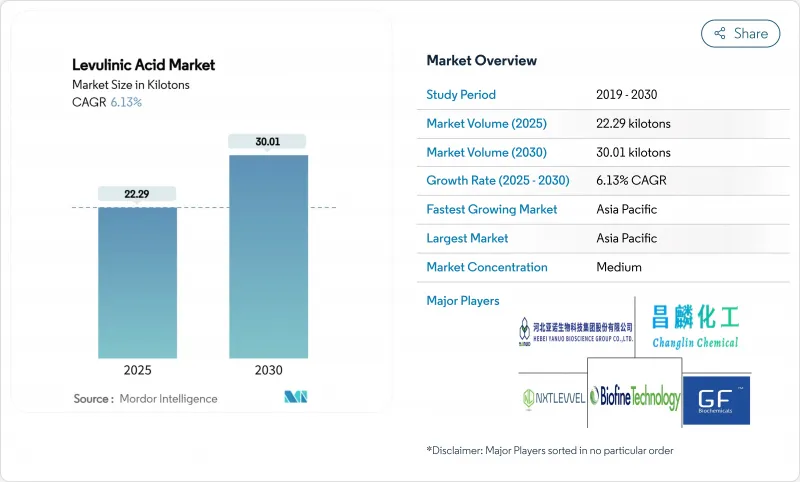
Demand grows as regulatory programs such as the EU Chemicals Strategy for Sustainability and the US Federal Sustainable Chemistry Plan press manufacturers to adopt bio-based intermediates that help decarbonize value chains. Cosmetics and personal care remain the largest outlet because levulinic acid serves as a naturally sourced preservative that satisfies clean-label preferences. Fuel and fuel-additive manufacturers are scaling purchases fastest as the compound underpins gamma-valerolactone pathways for sustainable aviation fuel. Acid hydrolysis technology continues to dominate installed capacity, yet enzymatic and microbial routes are attracting new investment to cut unit costs and ease catalyst deactivation issues. Asia-Pacific keeps its lead on both volume and growth thanks to abundant biomass, supportive policy, and a dense chemical manufacturing base, while new projects in Italy and North America signal gradual capacity consolidation across the levulinic acid market.
Global Levulinic Acid Market Trends and Insights
Rising Demand for Bio-Based Solvents and Plasticizers
Regulatory pressure to replace phthalate plasticizers is propelling levulinic acid esters into polymer films and rigid packaging. Recent trials achieved 546% elongation at break in polylactic acid when 20 wt% levulinic acid ester replaced traditional citrate plasticizers, matching performance while raising bio-conetent. The EU Chemicals Strategy frames bio-based plasticizers as preferred under essential-use criteria, encouraging brand owners to specify levulinic acid derivatives. Established catalyst suppliers have lowered esterification energy demand by almost 20%, narrowing the price gap with petro-routes. Consumer packaged goods firms aim to lift bio-sourced inputs to at least 25% by 2030, creating forward purchasing commitments that anchor new capacity agreements across the levulinic acid market.
Growing Use of Levulinic Acid Derivatives as Low-Carbon Fuel Additives
Conversion of levulinic acid into gamma-valerolactone provides an intermediate for sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) that can reach breakeven production costs near USD 3.15 per gasoline-equivalent gallon in integrated biorefineries. Catalysts developed in 2024 delivered 87.6% yield of 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, a blending component that upgrades octane and lowers lifecycle carbon intensity. Global biofuel consumption rose to 107 Mtoe in 2023 and investments topped USD 13 billion, while aviation stakeholders pledge 35% SAF penetration by 2070, sharpening long-term offtake agreements for levulinic acid derivatives. Pilot enzymatic routes now claim a tenfold increase in precursor yield from identical biomass inputs, signalling further cost reduction potential.
High Production Cost versus Petro-Substitutes
Levulinic acid remains pricier than incumbent petrochemical intermediates because biomass yields are modest and downstream purification is capital intensive. Weak chemical sector recovery-US output grew only 1.5% in 2024-limits the capacity of buyers to pay bio-premiums. In polymers and solvents the levulinic acid market competes with raw materials produced at megascale crackers that long ago depreciated assets, widening the cost gap. Catalyst fouling in acid hydrolysis plants adds maintenance expense and downtime that erode margins. As a result, some bulk users defer substitution plans until second-generation processes deliver lower variable costs.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Increasing Adoption in Cosmetics and Personal Care as Natural Preservative
- Increasing Usage as a Substitute in Traditional Fertilizers
- Limited Commercial-Scale Manufacturing Capacity
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Acid hydrolysis retained 54.65% share of the levulinic acid market in 2024 by leveraging decades of commercial experience and the Biofine process that attains 70-80% theoretical yield. Most current plants use dilute sulfuric acid to convert cellulose into intermediate sugars and then levulinic acid, a route viewed as low risk by investors. However, catalyst decay and humin disposal impose recurring costs that pressure margins, especially when feedstock moisture fluctuates. Emerging enzymatic and microbial methods post a 6.81% CAGR as developers showcase tenfold higher precursor yields per unit biomass and reduced utility demand. Start-ups in the Netherlands and Canada secured Series B funding in 2025 to scale demo units that bolt onto pulp-mill side streams, signaling confidence in biotechnological cost-down potential for the levulinic acid market.
Acid hydrolysis players are investing in continuous-flow reactors equipped with inline separation to cut residence time and limit humin buildup. Meanwhile, catalytic hydrogenation units next door upgrade in-house levulinic acid to gamma-valerolactone or 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, capturing margin in drop-in fuel additives. Enzymatic routes still face enzyme cost and stability hurdles, yet platform suppliers report double-digit reductions in enzyme loading after protein-engineering breakthroughs. The technology mix reflects a transition era where established processes secure present volumes while biotech innovation charts the next productivity leap for the levulinic acid market.
The Levulinic Acid Market Report is Segmented by Production Technology (Acid Hydrolysis, Biofine Process, and More), Grade (Industrial Grade, Pharma Grade, and Food Grade), End-User Industry (Cosmetics and Personal Care, Pharmaceuticals, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (tons).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific constitutes the demand epicenter at 41.29% volume share in 2024 and a projected 6.58% CAGR to 2030, supported by China's biomass surpluses and national carbon-neutrality targets. Provincial grants cover up to 30% of capital expenditure for bio-chemical projects, spurring new plants in Shandong and Guangxi. Japan's commercial woody-ethanol scheme underpins co-production of levulinic acid, while India's specialty-chemicals capacity expansion-notably in Gujarat-creates fresh downstream pull. Regional supply tightness keeps pricing firm, encouraging local investors to shorten import routes.
North America holds a mature yet opportunity-rich base where federal tax credits and loan guarantees spur biorefinery retrofits. Canada's Clean Fuel Standard compels refiners to adopt low-carbon feedstock, boosting contracts for gamma-valerolactone derived from levulinic acid. Mexican chemical clusters in Veracruz eye corn stover as an affordable feedstock, though logistics and agronomic residue management still limit scale. The market exhibits mid-single-digit growth as producers enhance process efficiency and secure long-term biomass offtake.
Europe preserves a strong foothold owing to rigorous sustainable-chemistry legislation. Italy hosts the world's largest single levulinic acid unit at 10,000 t/a, demonstrating industrial feasibility, while German and French firms pilot enzyme-enabled variants. The EU Fit-for-55 package accelerates demand in transport fuels and plastics, and Horizon Europe grants finance catalyst research that aims to outpace Asia on cost. South America and the Middle-East and Africa remain emerging pockets; Brazil's sugarcane bagasse and South Africa's forest residues present ample feedstock, yet investment decisions hinge on political stability and infrastructure to tap these reserves for the levulinic acid market.
- AK Scientific Inc.
- Avantium
- Biofine Technology, llc.
- GFBiochemicals
- GODAVARI BIOREFINERIES LTD.
- Hangzhou Aromalake Tech Co., Ltd.
- Hebei Yanuo Bioscience Group Co., Ltd
- LangFang Hawk Technology and Development Co,Ltd.
- Merck KGaA (Sigma-Aldrich)
- NXTLEVVEL Biochem
- Shandong Xinhua Pharma
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Tokyo Chemical Industry Co,. Ltd.
- Zibo Changlin Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Demand for Bio-Based Solvents and Plasticizers
- 4.2.2 Growing Use of Derivatives
- 4.2.3 Increasing Adoption in Cosmetics and Personal Care as Natural Preservative
- 4.2.4 Increasing Usage as a Substitute in Traditional Fertilizers
- 4.2.5 Circular-Economy Partnerships with Pulp and Paper Mills
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Production Cost Vs Petro- Substitutes
- 4.3.2 Limited Commercial-Scale Manufacturing Capacity
- 4.3.3 Catalyst Deactivation from Humin Build-Up in Continuous Reactors
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Volume)
- 5.1 By Production Technology
- 5.1.1 Acid Hydrolysis
- 5.1.2 Biofine Process
- 5.1.3 Catalytic Hydrogenation Route
- 5.1.4 Emerging Biotechnological Routes
- 5.2 By Grade
- 5.2.1 Industrial Grade
- 5.2.2 Pharma Grade
- 5.2.3 Food Grade
- 5.3 By End-user Industry
- 5.3.1 Cosmetics and Personal Care
- 5.3.2 Pharmaceuticals
- 5.3.3 Polymers and Plasticizers
- 5.3.4 Fuel and Fuel Additives
- 5.3.5 Flavors and Fragrances
- 5.3.6 Other End-users Industries (Agriculture and Fertilizers, etc.)
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.1.1 China
- 5.4.1.2 Japan
- 5.4.1.3 India
- 5.4.1.4 South Korea
- 5.4.1.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.4.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.2 North America
- 5.4.2.1 United States
- 5.4.2.2 Canada
- 5.4.2.3 Mexico
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.4.3.6 Russia
- 5.4.3.7 NORDIC Countries
- 5.4.3.8 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.4.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share(%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 AK Scientific Inc.
- 6.4.2 Avantium
- 6.4.3 Biofine Technology, llc.
- 6.4.4 GFBiochemicals
- 6.4.5 GODAVARI BIOREFINERIES LTD.
- 6.4.6 Hangzhou Aromalake Tech Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Hebei Yanuo Bioscience Group Co., Ltd
- 6.4.8 LangFang Hawk Technology and Development Co,Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Merck KGaA (Sigma-Aldrich)
- 6.4.10 NXTLEVVEL Biochem
- 6.4.11 Shandong Xinhua Pharma
- 6.4.12 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.4.13 Tokyo Chemical Industry Co,. Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Zibo Changlin Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment
- 7.2 Growing Prevalence of Bio-based Levulinic Acid




