PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851879

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851879
Glioblastoma Multiforme Treatment - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The glioblastoma multiforme treatment market is valued at USD 3.02 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 4.44 billion by 2030, reflecting an 8.01% CAGR over the period.
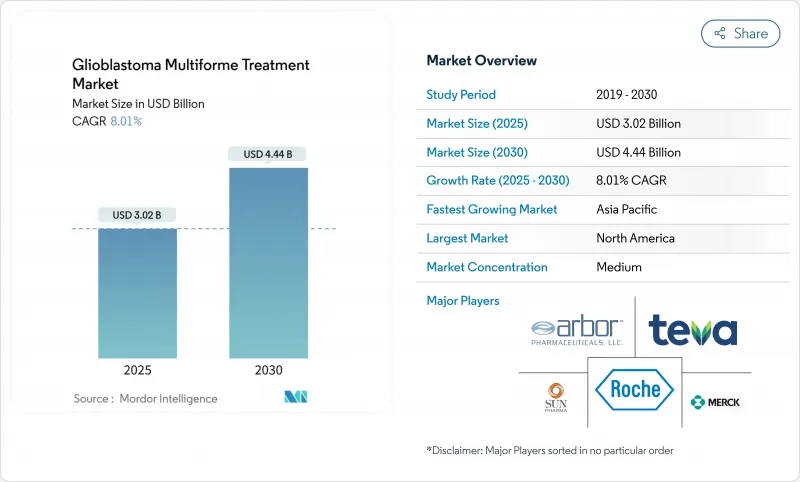
Growing demand for therapies that prolong survival, rapid adoption of Tumor-Treating Fields (TTFields) devices, orphan-drug incentives that accelerate approvals, and steady venture funding for blood-brain-barrier (BBB)-penetrating platforms underpin this trajectory. Investment is also spurred by the first major U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) breakthrough in decades -vorasidenib for Grade 2 IDH-mutant glioma-which has renewed confidence in multimodal development strategies. Meanwhile, physicians are shifting toward combination regimens because monotherapies deliver only incremental benefit, reinforcing the need for integrated device-drug approaches. Ongoing clinical trials that combine TTFields with immune checkpoint inhibition illustrate how developers intend to capture durable survival gains while mitigating toxicity.
Global Glioblastoma Multiforme Treatment Market Trends and Insights
Escalating Incidence of High-Grade Gliomas
Incidence trends keep the glioblastoma multiforme treatment market on a firm growth footing. Glioblastoma already represents nearly half of all malignant primary brain tumors worldwide, and rising diagnostic awareness is bringing more patients into care pathways earlier in their disease course. Neuro-oncology units at major academic centers are scaling to meet these volumes, creating predictable demand for approved drugs, TTFields devices, and related diagnostics. Higher case numbers also accelerate clinical-trial enrollment, shortening development cycles for next-generation therapies. Manufacturers leverage the larger addressable population to justify premium pricing strategies that fund further innovation.
Expanding R&D Pipelines and Orphan-Drug Incentives
Fast-track and orphan designations under U.S. and EU regulations reduce both cost and time-to-market, transforming glioblastoma from a historically unattractive niche into a commercial priority. The FDA's orphan approval of ERAS-801 for malignant glioma and the swift clearance pathway for vorasidenib demonstrate regulators' willingness to accept surrogate endpoints when unmet need is high. Exclusivity periods that follow such designations provide companies with revenue protection that offsets the risks associated with small patient populations. The environment is catalyzing cross-border licensing deals and big-pharma acquisitions, such as Merck's purchase of Modifi Biosciences, targeted at overcoming temozolomide resistance .
Stringent Reimbursement Hurdles for Novel Devices
Health-technology assessment bodies increasingly demand real-world cost-benefit evidence before granting coverage. For TTFields, payers often require post-market studies showing reductions in hospitalizations and adverse-event management costs. Delays of 12-24 months between regulatory clearance and final reimbursement decisions prolong the path to revenue, testing the liquidity of device firms. Outcome-based contracts that shift financial risk to manufacturers are becoming standard in Europe, raising hurdles for smaller entrants.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing Adoption of Tumor-Treating Fields (TTFields) Devices
- Venture Funding Surge for BBB-Penetrating Nanocarriers
- Temozolomide Resistance and MGMT Heterogeneity
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Chemotherapy generated 47.21% of total revenue in 2024 as generic temozolomide continues to anchor frontline protocols. TTFields therapy's 8.89% CAGR to 2030 signals accelerating clinician confidence in a device-centric approach that avoids systemic side effects. Radiation, including proton techniques, remains critical for local control, while a growing "others" basket contains vaccine, radiopharmaceutical, and immunotherapy combinations that are moving through mid-phase trials. Market participants increasingly bundle modalities: Novocure and MSD are evaluating TTFields plus pembrolizumab in registrational studies, reflecting consensus that multimodal attack is necessary for durable survival.
The treatment-mix shift influences supply chains and reimbursement models. TTFields systems create subscription-style consumables demand, distinct from one-time drug infusions. As new combinations reach approval, clinical pathways will feature sequential or concurrent regimens, adding complexity but enlarging the addressable spend. Developers that prove cost-effective integration of devices with drugs will capture outsized share.
Newly diagnosed cases dominated with 68.44% revenue in 2024, driven by the larger incident population and accepted Stupp protocol adoption. Yet the recurrent segment's 8.78% CAGR to 2030 illustrates where the innovation frontier lies. Alpha DaRT's FDA-supported pilot trial of radium-224 therapy and RRx-001 combination protocols are early examples of aggressive experimentation in salvage settings.
The recurrent focus encourages smaller, adaptive study designs, shortening timelines and reducing capital requirements. These features attract biotech venture funding and big-pharma option deals, as demonstrated by Merck's acquisition of Modifi Biosciences to tackle temozolomide resistance. Success here will likely ripple into frontline standards through combination expansion, closing the loop between recurrent and newly diagnosed care algorithms.
The Glioblastoma Multiforme Treatment Market Report is Segmented by Treatment Modality (Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy, and More), Patient Type (Newly Diagnosed GBM, Recurrent GBM), End User (Hospitals and Clinics, and More), Age Group (Adults, Pediatric, Geriatric), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America holds 40.14% of revenue because Medicare and private insurers reimburse TTFields and the latest chemotherapeutic agents, while more than 600 clinical centers provide trial infrastructure. Regulatory clarity and orphan-drug benefits encourage rapid launch of pipeline assets, and the region's dense venture-capital ecosystem funds early-stage innovation. Comprehensive neuro-oncology programs combine surgery, radiation, devices, and drug trials, positioning the United States as the reference market for new therapy rollouts.
Europe represents the second-largest regional opportunity but employs cost-effectiveness thresholds that mandate rigorous health-technology assessments. Germany has pioneered dendritic-cell therapy reimbursement for difficult-to-treat cancers, signaling selective openness to premium interventions. The European Medicines Agency's centralized procedure expedites marketing authorization, yet reimbursement remains country specific, lengthening time to broad uptake. Developers must navigate outcome-based agreements that align payment with survival or quality-of-life metrics.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing territory at 9.04% CAGR. Governments are investing in precision-medicine infrastructures, and major oncology hospitals are equipping operating suites for advanced neurosurgery. Japan's universal coverage system increasingly funds high-cost therapies when domestic clinical data demonstrate benefit, and China's centralized volume-based procurement initiatives are beginning to include neuro-oncology devices. Local manufacturers are entering the TTFields and nanoparticle spaces, thereby driving competitive pricing and broader access. Multinational firms partner with regional contract research organizations to run adaptive trials that expedite approval in key Asian markets.
- Arbor Pharmaceuticals
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Roche
- Merck
- Sun Pharmaceuticals Industries
- Lantern Pharma Inc.
- Pfizer
- Amgen
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
- Novocure Ltd
- Celldex Therapeutic
- AstraZeneca
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Novartis
- Kazia Therapeutics Ltd
- Northwest Biotherapeutics Inc.
- Kintara Therapeutics Inc.
- Bluebird bio Inc.
- DelMar Pharmaceuticals (Chimerix)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Escalating Incidence of High-Grade Gliomas
- 4.2.2 Age-Associated Rise in GBM Cases
- 4.2.3 Expanding R&D Pipelines & Orphan-Drug Incentives
- 4.2.4 Growing Adoption of Tumor-Treating Fields (Ttfields) Devices
- 4.2.5 AI-Enabled Radiogenomics Improving Early Detection
- 4.2.6 Venture Funding Surge For BBB-Penetrating Nanocarriers
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Stringent Reimbursement Hurdles for Novel Devices
- 4.3.2 High Therapy Cost Burden & Limited Cost-Effectiveness in Lmics
- 4.3.3 Temozolomide Resistance & MGMT Heterogeneity
- 4.3.4 Low Real-World Compliance with Ttfields Therapy
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Porters Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Treatment Modality
- 5.1.1 Chemotherapy
- 5.1.2 Radiation Therapy
- 5.1.3 Tumor-Treating Fields
- 5.1.4 Others
- 5.2 By Patient Type
- 5.2.1 Newly Diagnosed GBM
- 5.2.2 Recurrent GBM
- 5.3 By End User
- 5.3.1 Hospitals and Clinics
- 5.3.2 Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- 5.3.3 Others
- 5.4 By Age Group
- 5.4.1 Adults
- 5.4.2 Pediatric
- 5.4.3 Geriatric
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.3.1 Arbor Pharmaceuticals LLC
- 6.3.2 Bristol-Myers Squibb Co.
- 6.3.3 Eli Lilly and Co.
- 6.3.4 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- 6.3.5 Merck & Co. Inc.
- 6.3.6 Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
- 6.3.7 Lantern Pharma Inc.
- 6.3.8 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.9 Amgen Inc.
- 6.3.10 Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
- 6.3.11 Novocure Ltd
- 6.3.12 Celldex Therapeutics Inc.
- 6.3.13 AstraZeneca plc
- 6.3.14 GlaxoSmithKline plc
- 6.3.15 Novartis AG
- 6.3.16 Kazia Therapeutics Ltd
- 6.3.17 Northwest Biotherapeutics Inc.
- 6.3.18 Kintara Therapeutics Inc.
- 6.3.19 Bluebird bio Inc.
- 6.3.20 DelMar Pharmaceuticals (Chimerix)
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessmen




