PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851983

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851983
Water And Wastewater Treatment Technologies - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Water And Wastewater Treatment Technologies Market size is estimated at USD 65.15 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 87.60 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.10% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
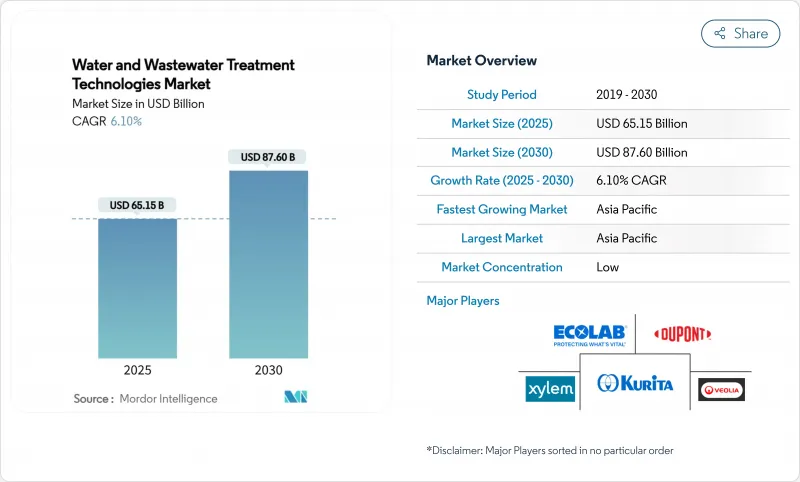
Robust growth flows from tightening environmental rules, rising zero-liquid-discharge expectations, and aggressive infrastructure upgrades that are unfolding in tandem across mature and emerging economies. Municipal utilities are front-loading investments to replace aging networks, while industrial users in water-stressed regions deploy advanced systems to secure permits and reclaim resources. Concurrently, artificial-intelligence tools are optimizing chemical dosing and asset uptime, turning operational savings into organic demand drivers. Consolidation is also reshaping competitive dynamics as integrated platforms emerge through mega-mergers, intensifying the innovation race in specialized niches such as PFAS destruction and microplastics removal.
Global Water And Wastewater Treatment Technologies Market Trends and Insights
Stricter Zero-Liquid-Discharge Mandates
Heightened enforcement in power, petrochemical, and mining sectors is converting compliance budgets into strategic capital as facilities install integrated thermal evaporation, crystallization, and membrane lines that recover salts and minerals while driving near-zero discharge. Early adopters are leveraging recovered by-products to offset part of their capex, widening the cost gap for laggards that still rely on basic physicochemical treatment. The mandate's force is greatest in Asia and the Gulf, where new permits increasingly require ZLD readiness as a pre-condition for operation. Investors therefore view ZLD capability as a proxy for long-term license security, pushing equipment backlogs higher across the value chain. Over the medium term these rules are expected to lift the water and wastewater treatment technologies market by roughly 1.8 percentage points of CAGR.
Growth in Decentralized Modular Treatment Plants
Rapid urban sprawl is outstripping the pace at which centralized facilities can be sited and financed, heightening interest in containerized systems that can be delivered in months rather than years. Modular lines allow phased capacity additions that synchronize with real estate development cycles, ensuring utilities avoid stranded investment in oversize assets. The approach lowers entry barriers for small and midsize municipalities that lack access to bond funding for mega-plants, opening new addressable pockets for equipment suppliers. Europe and North America pioneered pilots, but replicability in densely populated Asian corridors is scaling volumes. Over a long-term horizon the trend contributes 1.2 percentage points to growth in the water and wastewater treatment technologies market.
High Total Cost of Ownership for Advanced Membranes
Operational economics, not upfront purchase price, limit uptake of nanofiltration and reverse-osmosis modules. Progressive fouling raises cleaning frequency, shortening useful life and driving recurrent capital outlays that surpass initial equipment cost over a typical 12-year horizon. Compounded by the elevated power draw of 60-bar feed pumps, the hurdle is steepest for small utilities in developing markets that cannot leverage bulk chemical procurement or reliable grid power. As a result, many facilities postpone upgrades or adopt hybrid flowsheets that dilute membrane duty cycles. This structural cost drag is expected to shave 1.1 percentage points from the water and wastewater treatment technologies market's CAGR.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Industrial Reuse Quotas in Water-Stressed Regions
- AI-Enabled Smart Metering and Predictive Maintenance
- PFAS Regulation Uncertainty Delaying Technology Adoption
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Dissolved-solids removal systems captured 31.39% of water and wastewater treatment technologies market share in 2024 as reverse-osmosis and nanofiltration cemented their place in seawater desalination, brackish water reclamation, and high-recovery industrial lines. The segment's installed base continues to swell on the back of large municipal desalination projects such as Taiwan's 100,000 m3/day plant that broke ground in mid-2024.
Yet growth momentum tilts toward biological treatment and nutrient recovery technologies, which are forecast to log a 7.28% CAGR by 2030, a full percentage point above the total market average, helped by regulatory incentives that turn recovered phosphorus into a tradable fertilizer credit. At process level, breakthroughs like Fe(III)-triggered partial dissimilatory nitrate reduction coupled with anammox have boosted nitrogen removal beyond 95% while slashing energy demand, decreasing the payback hurdle for municipal biosolids upgrades.
The Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies Report is Segmented by Treatment Type (Oil/Water Separation, Suspended Solids Removal, Dissolved Solids Removal, and More), End-User Industry (Municipal Water and Wastewater Treatment, Food and Beverage, Pulp and Paper, Oil and Gas, Healthcare, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle-East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific holds a commanding 34.87% share of 2024 revenue and simultaneously records the highest 8.76% CAGR, underscoring a dual leadership seldom observed in mature infrastructure arenas. China continues to commission mega-desalination lines along coastal industrial parks, while Taiwan's mammoth seawater RO plant highlights how semiconductor clusters dictate municipal water policy.
North America sustains robust replacement outlays tied to aging 1970s-era assets and advanced regulatory frameworks. The region's early embrace of direct potable reuse and pending PFAS limits guide technology adoption patterns toward high-grade membranes, granular activated carbon, and novel electro-chemical destruction cells. Municipal water boards in Texas, Colorado, and California now require detailed life-cycle cost analyses that favor high-recovery architectures and AI-enabled monitoring, elevating software vendors within the water and wastewater treatment technologies market.
Europe remains a crucible for intellectual property, producing 40% of global water-related patents between 1992 and 2021, with PFAS remediation, resource-positive biosolids, and energy-neutral filtrations at the forefront.
- AECOM
- Aquatech
- Black & Veatch Corporation
- Doosan Enerbility
- DuPont
- Ecolab
- HDO
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- Kurita Water Industries Ltd.
- Mott MacDonald
- Pentair
- REMONDIS SE & Co. KG
- Siemens
- SLB
- Thermax Limited
- Veolia
- WABAG
- Xylem
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Stricter zero-liquid-discharge (ZLD) mandates
- 4.2.2 Growth in decentralized modular treatment plants
- 4.2.3 Rising industrial reuse quotas in water-stressed regions
- 4.2.4 Surge in capex for shale-based produced-water reuse
- 4.2.5 AI-enabled smart metering and predictive maintenance
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High total cost of ownership for advanced membranes
- 4.3.2 Limited Operation and Maintenance skill base in emerging economies
- 4.3.3 PFAS regulation uncertainty delaying tech adoption
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Treatment Type
- 5.1.1 Oil/Water Separation
- 5.1.2 Suspended Solids Removal
- 5.1.3 Dissolved Solids Removal
- 5.1.4 Biological Treatment/Nutrient and Metals Recovery
- 5.1.5 Disinfection/Oxidation
- 5.1.6 Other Types
- 5.2 By End-user Industry
- 5.2.1 Municipal Water and Wastewater Treatment
- 5.2.2 Food and Beverage
- 5.2.3 Pulp and Paper
- 5.2.4 Oil and Gas
- 5.2.5 Healthcare
- 5.2.6 Poultry and Aquaculture
- 5.2.7 Chemical and Petrochemical
- 5.2.8 Other End-user Industries
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.1.1 China
- 5.3.1.2 India
- 5.3.1.3 Japan
- 5.3.1.4 South Korea
- 5.3.1.5 ASEAN
- 5.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2 North America
- 5.3.2.1 United States
- 5.3.2.2 Canada
- 5.3.2.3 Mexico
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.3 France
- 5.3.3.4 Italy
- 5.3.3.5 Spain
- 5.3.3.6 Russia
- 5.3.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 South Africa
- 5.3.5.3 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 AECOM
- 6.4.2 Aquatech
- 6.4.3 Black & Veatch Corporation
- 6.4.4 Doosan Enerbility
- 6.4.5 DuPont
- 6.4.6 Ecolab
- 6.4.7 HDO
- 6.4.8 Hitachi, Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Kurita Water Industries Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Mott MacDonald
- 6.4.11 Pentair
- 6.4.12 REMONDIS SE & Co. KG
- 6.4.13 Siemens
- 6.4.14 SLB
- 6.4.15 Thermax Limited
- 6.4.16 Veolia
- 6.4.17 WABAG
- 6.4.18 Xylem
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment




