PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906032

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906032
Grid Scale Battery - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Grid Scale Battery Market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 108.16 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 87.29 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 315.83 billion, growing at 23.9% CAGR over 2026-2031.
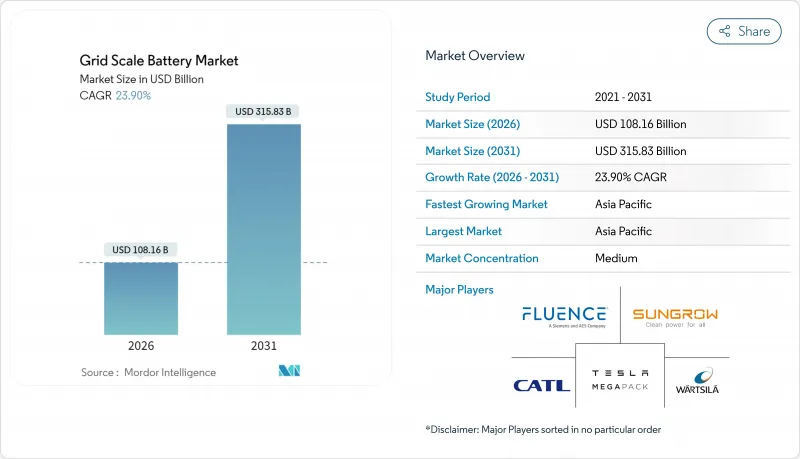
Rapid cost declines in lithium-ion technology, binding renewable-portfolio standards, and urgent grid-modernization programs are accelerating procurement decisions across utilities, developers, and large energy users. Utility-scale installations climbed to 173 GWh in 2024, with California and Texas accounting for the largest additions as both states pursue aggressive 2030 renewable targets. Asia-Pacific's manufacturing scale and policy support have entrenched cost leadership, while performance incidents such as the 2022 Moss Landing fire sharpen industry focus on safety innovation. Investors are responding with record capital flows into long-duration technologies that complement the dominant lithium-ion fleet, signaling an evolution in project economics and revenue stacking strategies.
Global Grid Scale Battery Market Trends and Insights
Declining Lithium-Ion Battery Costs
Average lithium-ion pack prices fell to USD 139/kWh in 2023, a 97% slide since 1991, and manufacturers expect sub-USD 100/kWh levels by 2026. Cost pressure stems from gigafactory scaling, manufacturing automation, and optimized supply chains in China, the United States, and Europe. CATL's Qilin 2.0 and BYD's Blade 2.0 platforms add 6C fast-charging and higher energy densities, reducing balance-of-plant costs for four-hour systems. These improvements unlock lower-priced power-purchase agreements and shorten payback periods, sustaining order pipelines even amid interest-rate volatility. As unit economics improve, developers increasingly favor larger system formats to capture economies of scale, accelerating the learning curve on installation and commissioning practices.
Renewable-Energy Integration Mandates
California seeks 11.5 GW of storage by 2026, Mexico now requires 5% storage in utility-scale renewables, and Europe's Fit-for-55 package drives a regional buildout exceeding 21.9 GWh in 2024. Policymakers view storage as essential for meeting net-zero milestones, integrating variable solar and wind, and postponing gas-peaking additions. National roadmaps are translating mandates into competitive auctions and technology-neutral capacity markets, enabling developers to secure revenue contracts that de-risk financing. Mandates also accelerate procurement of hybrid solar-plus-storage PPAs that guarantee project offtake and hedge merchant risk.
Critical-Mineral Supply-Chain Constraints
Forecast demand for lithium, cobalt, and nickel could outstrip committed mining capacity by 2030, exposing developers to price spikes and delivery delays. China refines 60% of global lithium and 75% of cobalt, while the DRC holds 70% of mined cobalt output, concentrating geopolitical risk. Sodium-ion and iron-air chemistries are emerging alternatives: China commissioned the world's first 100 MWh sodium-ion plant in 2024, and US firms pilot iron-air systems for 100-hour endurance. Industry consortia lobby for diversified offtake agreements and recycling mandates to ease raw-material dependency.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Grid Reliability & Resiliency Needs
- Favourable Policy Incentives (IRA, EU Net-Zero)
- Battery-Storage Safety & Fire-Risk Concerns
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The lithium-ion segment controlled 91.30% of the grid-scale battery market share in 2025 and generated the largest contribution to the grid-scale battery market size at USD 79.68 billion, expanding at a 24.1% CAGR through 2031. Cost parity with peaking gas, high round-trip efficiencies, and established supply chains sustain its position. Within lithium-ion, lithium iron phosphate eclipses nickel manganese cobalt for stationary use, offering 4,000-6,000 cycles and lower thermal-runaway risk. Meanwhile, CATL's second-generation sodium-ion modules promise viable substitution in cold climates, and manufacturers anticipate commercial shipments by 2026.
Flow batteries recorded <3% of the 2025 grid-scale battery market size but lead long-duration tenders in Australia, California, and Germany. Vanadium redox systems deliver 25-year lifespans with near-zero degradation, translating to lower levelized-cost per MWh over project life. Venture investments in iron-air and zinc hybrid-cathode technologies surged in 2025 as utilities seek 8+ hour discharge for renewable over-generation. Solid-state battery pilots in Japan use sulfide electrolytes to improve volumetric energy density, although commercial output remains several years away. The chemistry mix is therefore shifting toward application-specific optimization rather than a single winning platform.
The Grid Scale Battery Market Report is Segmented by Battery Chemistry (Lithium-Ion, Lead-Acid, Sodium-Based, Flow Batteries, and Other Emerging Chemistries), Application (Frequency Regulation, Energy Arbitrage/Bill Management, Load Shifting and Peak Shaving, Renewable-Energy Time-Shifting, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific held 46.20% of the grid-scale battery market share in 2025 and is on track for a 25.2% CAGR between 2026 and 2031, anchored by China's manufacturing dominance and export-oriented policy incentives. Chinese suppliers such as CATL and BYD negotiate multi-gigawatt contracts in Europe and North America while investing in regional assembly plants to mitigate trade barriers. Japan's decarbonization roadmap triggers partnerships to build 100 MW of storage by 2027, and India's Production Linked Incentive scheme channels subsidies toward local gigafactories. South Korea pursues high-end solid-state research and premium export niches, whereas Australia leverages abundant renewables to install storage for firmed capacity.
North America ranks second in total deployments, catalyzed by the Inflation Reduction Act's tax credits and state-level renewable procurement mandates. California's roadmap targets 11.5 GW by 2026, and Texas exceeds 8 GW in interconnection agreements, propelling the region's grid-scale battery market size to USD 29.3 billion in 2026. Queue reforms by FERC aim to clear 540 GW of pending storage-linked projects, yet interconnection timelines still average more than three years, representing a material headwind. Canada prioritizes grid reliability in remote provinces through battery-diesel hybrid systems, and Mexico enforces a 5% storage requirement for new renewable projects, creating an emerging demand pipeline.
Europe's urgency accelerated after 2024 energy-security disruptions, lifting installed capacity to 21.9 GWh that year. Germany's Bundesnetzagentur recognizes batteries in capacity reserves and black-start services, while the United Kingdom's capacity market secures 15-year contracts that stabilize cash flows. Southern European nations integrate storage with utility-scale solar to mitigate afternoon curtailment, and Nordic operators pair batteries with hydropower to enhance frequency control. Legislation under the EU Clean Energy Package harmonizes grid-service definitions, fostering cross-border trading of battery services. Regulatory tailwinds underpin a 23.2% CAGR for the region through 2031.
- Tesla
- Fluence
- Sungrow Power Supply
- Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL)
- Wartsila
- Panasonic
- LG Energy Solution
- Samsung SDI
- BYD
- East Penn
- GS Yuasa
- Clarios
- AES Corporation
- Powin Energy
- Hitachi Energy
- NEC ES (Koch)
- EnerSys
- ESS Tech
- Ambri
- Redflow
- EnerVenue
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Declining lithium-ion battery costs
- 4.2.2 Renewable-energy integration mandates
- 4.2.3 Grid-reliability & resiliency needs
- 4.2.4 Favourable policy incentives (IRA, EU Net-Zero, etc.)
- 4.2.5 Hybrid solar-plus-storage PPAs & revenue stacking
- 4.2.6 Data-centre micro-grids demand firm clean power
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Critical-mineral supply-chain constraints
- 4.3.2 Battery-storage safety & fire-risk concerns
- 4.3.3 Interconnection-queue bottlenecks
- 4.3.4 Ancillary-service revenue cannibalisation
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Battery Chemistry
- 5.1.1 Lithium-ion (LFP, NMC, NCA)
- 5.1.2 Lead-acid
- 5.1.3 Sodium-based (NAS, Sodium-ion)
- 5.1.4 Flow Batteries (Vanadium, Iron, Zinc-Br)
- 5.1.5 Other Emerging Chemistries (Metal-air, Solid-state)
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Frequency Regulation
- 5.2.2 Energy Arbitrage/Bill Management
- 5.2.3 Load Shifting and Peak Shaving
- 5.2.4 Renewable-Energy Time-Shifting
- 5.2.5 Transmission and Distribution Deferral
- 5.2.6 Black-Start and Grid-Forming Support
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.1.3 Mexico
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.2.1 Germany
- 5.3.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.2.3 France
- 5.3.2.4 Italy
- 5.3.2.5 Spain
- 5.3.2.6 Nordic Countries
- 5.3.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.3.1 China
- 5.3.3.2 India
- 5.3.3.3 Japan
- 5.3.3.4 South Korea
- 5.3.3.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.3.3.6 Australia and New Zealand
- 5.3.3.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.3.5.3 South Africa
- 5.3.5.4 Egypt
- 5.3.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Tesla
- 6.4.2 Fluence
- 6.4.3 Sungrow Power Supply
- 6.4.4 Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL)
- 6.4.5 Wartsila
- 6.4.6 Panasonic
- 6.4.7 LG Energy Solution
- 6.4.8 Samsung SDI
- 6.4.9 BYD
- 6.4.10 East Penn
- 6.4.11 GS Yuasa
- 6.4.12 Clarios
- 6.4.13 AES Corporation
- 6.4.14 Powin Energy
- 6.4.15 Hitachi Energy
- 6.4.16 NEC ES (Koch)
- 6.4.17 EnerSys
- 6.4.18 ESS Tech
- 6.4.19 Ambri
- 6.4.20 Redflow
- 6.4.21 EnerVenue
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




