PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906134

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906134
Electrodeionization (EDI) Technology - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
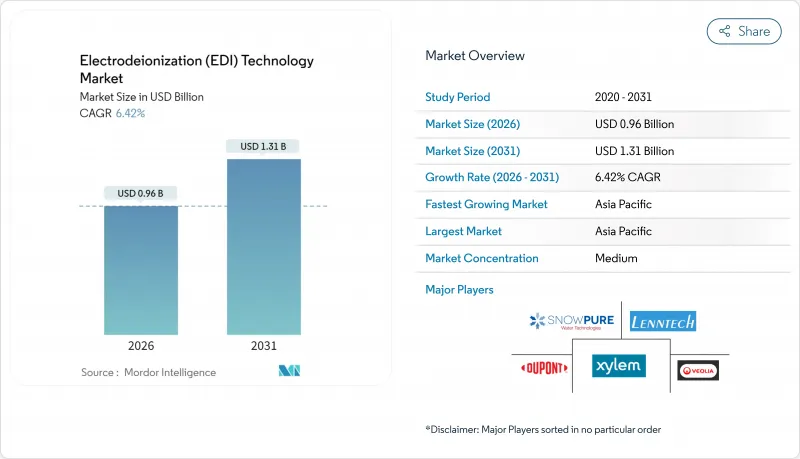
The Electrodeionization (EDI) Technology Market was valued at USD 0.9 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 0.96 billion in 2026 to reach USD 1.31 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 6.42% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
Demand acceleration is rooted in the shift toward chemical-free ultrapure water production for high-pressure boilers, semiconductor fabrication, and biopharmaceutical processes. Continuous regeneration capability eliminates hazardous regenerants and downtime, improving the total cost of ownership in comparison with mixed-bed ion exchange. Rapid green-hydrogen build-outs, heightened PFAS discharge limits, and the rising value placed on 24/7 bioprocess uptime add further momentum. Meanwhile, competitive differentiation centers on spiral-wound module design, hybrid membrane-resin innovations, and turnkey skid packages that reduce skilled-labor needs during commissioning.
Global Electrodeionization (EDI) Technology Market Trends and Insights
Green-Hydrogen Electrolyzer Demand for Ultrapure Water
Producing 1 kg of green hydrogen requires 9-10 liters of ultrapure water, and electrolyzer OEMs now specify electrodeionization polishing to meet sub-0.1 µS/cm resistivity targets essential for membrane electrode longevity. Large projects such as the Helios complex integrate desalination with EDI to protect billion-dollar electrolyzer assets. Adoption favors compact spiral-wound stacks that fit modular hydrogen skids and achieve more than or equal to 90% recovery while cutting footprint.
Continuous Bioprocessing Adoption in Cell- and Gene-Therapy Plants
Moving from batch to continuous manufacturing requires uninterrupted high-purity utility streams. EDI's electrical self-regeneration eliminates resin changeouts that would otherwise halt 24/7 bioreactors, ensuring compliance with USP and EP water specifications. The technology's low weak-base leakage preserves delicate cell-culture media and supports single-use facility rollouts.
Rise of Membrane Capacitive Deionization for Less than 1 µs/Cm Specs
MCDI delivers 40-70% lower energy demand and up to 95% recovery compared with RO-EDI hybrids, positioning it as a low-cost alternative for mildly saline feeds. Emerging carbon-nanotube electrodes further shrink LCC, enticing sustainability-focused industries.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Modular EDI Skids for Edge-Cloud Micro-Data Centers
- PFAS Discharge Limits Favoring Chemical-Free Polishing
- Skilled-Labor Shortage for High-Pressure EDI Commissioning
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Plate-and-frame designs retained 61.26% of the electrodeionization technology market share in 2025 owing to heritage installations and straightforward gasket maintenance. Utilities value their linear flow paths and ease of module replacement. However, spiral-wound stacks are climbing at a brisk 6.63% CAGR as space-constrained facilities, notably semiconductor fabs and mobile hydrogen skids, prioritize a smaller footprint.
Energy consumption per cubic meter narrows between the formats as vendors optimize channel hydraulics and current density. Hybrid innovations, such as membrane-free electrodeionization that merges features of both geometries, are poised to reset cost curves and broaden the electrodeionization (EDI) technology market size across mid-tier industrial users.
The Electrodeionization(EDI) Technology Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Plate-And-Frame Module, and Spiral Wound Module), Application (Power Generation, Electronics and Semiconductors, Food and Beverage, Pharmaceuticals, and Other Applications), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle-East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific led the electrodeionization (EDI) technology market with 41.24% revenue in 2025 and is projected to grow at 7.71% CAGR through 2031. Semiconductor manufacturing clusters in China, Taiwan, and South Korea install new fab lines that require ultrapure water resistivity at 18.2 MΩ-cm, standards readily met by multistage RO-EDI trains. Parallel coal-to-chemicals and biomass power developments also reinforce regional uptake. Government targets for gigawatt-scale green-hydrogen electrolyzers in Australia, Japan, and India magnify long-term visibility for EDI modules in process-water polishing skids.
North America presents a mature yet opportunity-rich landscape. The U.S. EPA's PFAS maximum contaminant levels catalyze the replacement of mixed-bed polishers with EDI, which avoids secondary brine waste. Biopharma hubs in Massachusetts and California invest in continuous twin-train EDI arrangements to secure validation redundancy. Municipalities exploring advanced treatment for reuse also evaluate electrically regenerated technologies to limit chemical exposure, especially in drought-prone states.
Europe's regulatory thrust toward circular economy and carbon-neutral industry sustains steady adoption. Renewable-energy incentives nurture green-hydrogen pilot plants in Germany, the Netherlands, and Spain, each specifying EDI polishing for electrolyzer feed streams. Scandinavian combined heat-and-power sites report strong field performance of Dow EDI modules in bioenergy condensate recovery loops, underscoring reliability in harsh Nordic climates. Latin America and the Middle-East and Africa trail in revenue but post rising growth as pulp-and-paper mills, desalination projects, and petrochemical complexes elevate water-quality standards.
- Applied Membranes Inc.
- Aqua Filsep water Treatment Pvt. Ltd
- Aquatech International LLC
- BWT Holding GmbH
- Deionx
- DuPont
- DuPont
- EUROWATER
- General Electric Company
- Lenntech B.V.
- MEGA AS
- Newterra
- Pure Water Group
- SnowPure LLC
- Veolia
- Xylem
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Green-Hydrogen Electrolyzer Demand for Ultrapure Water
- 4.2.2 Continuous Bioprocessing Adoption in Cell- And Gene-Therapy Plants
- 4.2.3 Modular EDI Skids for Edge-Cloud Micro-Data-Centers
- 4.2.4 Hybrid Membrane-Resin Cost-Down Innovations
- 4.2.5 PFAS Discharge Limits Favoring Chemical-Free Polishing
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Rise of Membrane Capacitive Deionization for Less than 1 µs/Cm Specs
- 4.3.2 Supply-Chain Risk for Fluoropolymer IEM Precursors
- 4.3.3 Skilled-Labor Shortage for High-Pressure EDI Commissioning
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Plate-and-frame Module
- 5.1.2 Spiral Wound Module
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Power Generation (Power Plants)
- 5.2.2 Electronics and Semiconductors
- 5.2.3 Food and Beverage
- 5.2.4 Pharmaceuticals
- 5.2.5 Other Applications
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.1.1 China
- 5.3.1.2 India
- 5.3.1.3 Japan
- 5.3.1.4 South Korea
- 5.3.1.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2 North America
- 5.3.2.1 United States
- 5.3.2.2 Canada
- 5.3.2.3 Mexico
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.3 France
- 5.3.3.4 Italy
- 5.3.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 South Africa
- 5.3.5.3 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Applied Membranes Inc.
- 6.4.2 Aqua Filsep water Treatment Pvt. Ltd
- 6.4.3 Aquatech International LLC
- 6.4.4 BWT Holding GmbH
- 6.4.5 Deionx
- 6.4.6 DuPont
- 6.4.7 DuPont
- 6.4.8 EUROWATER
- 6.4.9 General Electric Company
- 6.4.10 Lenntech B.V.
- 6.4.11 MEGA AS
- 6.4.12 Newterra
- 6.4.13 Pure Water Group
- 6.4.14 SnowPure LLC
- 6.4.15 Veolia
- 6.4.16 Xylem
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




