PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906996

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906996
Intrinsically Safe Equipment (IS Equipment) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The intrinsically safe equipment market was valued at USD 3.88 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 4.16 billion in 2026 to reach USD 5.86 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 7.12% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
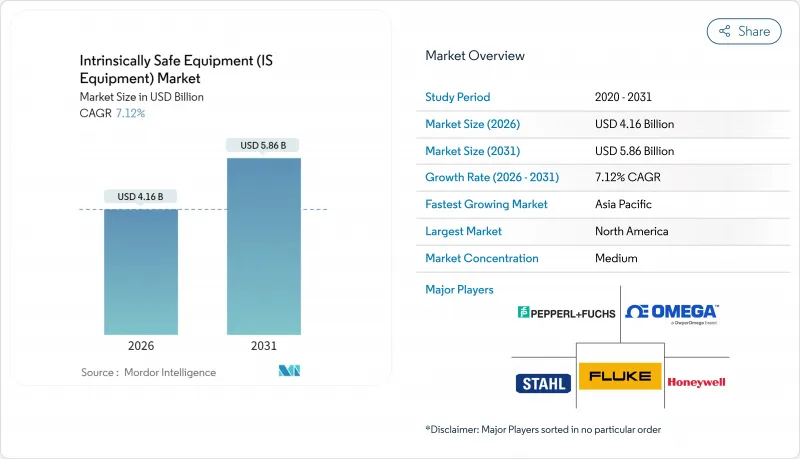
This expansion traces a shift from heavy flameproof housings toward digitally enabled, intrinsically safe architectures that blend regulatory compliance with Industry 4.0 connectivity. Demand accelerates as global standards tighten, mining and process industries expand, and wireless modules unlock retrofit projects once deemed uneconomic. Oil and gas operators remain the anchor customers, yet discrete manufacturers now adopt certified automation as volatile solvents enter production lines. Companies that master both certification and cybersecurity capture the most value as facility owners weigh lifecycle costs, supply-chain certainty, and predictive-maintenance capabilities when specifying new systems.
Global Intrinsically Safe Equipment (IS Equipment) Market Trends and Insights
Stringent Global Explosion-Safety Regulations
IEC 60079-11 Edition 7, released in January 2024, introduced 173 technical amendments, including tougher battery tests and a ban on catalytic sensors in Group IIC service, compelling retrofit spending across existing installations. EN IEC 60079-11:2024 entered the Official Journal in December 2024, and the prior 2012 edition will be de-harmonized by December 2027, which fixes a clear window for mandatory upgrades. Multinational plants juggle ATEX and IECEx paperwork that still lacks synchronized submission schedules despite technical alignment. The regulation also broadens scope beyond equipment to cover field wiring under IEC 60079-14:2024, stimulating demand for certified installation and recertification services. Together these actions boost the intrinsically safe equipment market as operators replace non-compliant assets and lock in long-term maintenance contracts tied to the new rules.
Industry 4.0-Driven Demand for IS Sensors and Instrumentation
Digital transformation raises the need for real-time data from hazardous zones, positioning intrinsically safe sensors as frontline enablers. Ethernet-APL now carries power and data on a single twisted pair up to 1 km, letting plant owners place smart instruments in Zone 1 and Zone 2 with no performance trade-off. Wireless nodes reduce cabling costs and simplify retrofits, as shown by SmartPower modules that support multi-year battery life in harsh areas. Underground mines adopt these devices to stream gas levels and equipment health to surface operations centers, shifting safety from periodic checks to continuous oversight. The same architecture underpins predictive maintenance, where edge analytics detect abnormal vibrations and flag service needs before breakdowns occur. Facility owners thus gain both compliance assurance and productivity improvements, accelerating purchases across Asia-Pacific and the Gulf Cooperation Council states.
High Certification Cost and Design Complexity
Gaining ATEX approval can cost EUR 15,000-50,000 per variant, and IECEx tests add USD 20,000-60,000, sums that push smaller firms out of contention. Edition 7 rule changes require additional battery stress, spark ignition, and component spacing tests, often driving multiple design revisions. Firms must also maintain ISO 9001 and QA audits to keep certificates active, embedding recurring overhead into each product line. The expense skews competition toward multinationals with in-house labs and dedicated compliance teams, concentrating intellectual property and deterring fresh entrants. Emerging-market suppliers struggle the most, as local labs lack throughput, forcing overseas testing that lengthens lead times and inflates budgets.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Expansion of Oil and Gas and Mining Activities
- Cost-Saving Shift from Ex d to Ex i Architectures
- Shortage of Certified IS-Grade Electronic Components
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Zone 1 applications commanded 38.15% of the intrinsically safe equipment market share in 2025, underscoring their ubiquity in refineries and chemical plants where explosive atmospheres arise during maintenance. Zone 1 spending remains steady as operators blend legacy wiring with new IoT-ready devices that streamline predictive maintenance. In contrast, Zone 0 displays a 8.31% CAGR as printed sensors and wireless hubs finally make real-time monitoring feasible where flammable gases persist continuously. This uptick signals a philosophical shift from isolation toward active risk mitigation, especially in subsea wells and pharmaceutical reactors where downtime costs outweigh device premiums. Zone 2 retains relevance for loading docks and warehouses needing inexpensive compliance solutions, while dust Zones 20-22 gain modest traction in food and pharma sites investing in automation. Suppliers now build modular boards that meet multiple zone requirements via firmware toggles and fuse changes, compressing development cycles and inventory.
Wireless gateways certified for Zone 1 now talk to safe-area historians over single-pair Ethernet. The broader intrinsically safe equipment market therefore enjoys expanded addressable endpoints without extra cable trays. Integrators value such gateways because they reduce engineer-hours on complex barrier calculations. As standards bodies refine guidance for multi-gas, multi-dust areas, zone-crossing architectures will cement themselves as design best practices, ensuring continued double-digit shipments into Zone 0 even after the current retrofit surge subsides.
Class 1 systems focused on gas and vapor hazards held 62.10% of 2025 revenue and are forecast to grow at a 8.76% CAGR through 2031 as methane detection, hydrogen leak monitoring, and LNG handling drive sensor upgrades. Operators retrofit pipelines with optical gas-imaging cameras linked to intrinsically safe edge boxes that perform AI-based leak quantification on site, slashing remediation time. Class 2 dust equipment finds new purchasers in biomass power plants and additive-manufacturing shops, where fine powders present ignition risks previously overlooked. The intrinsically safe equipment market size for Class 2 is projected to expand modestly as more countries adopt NFPA 652-style regulations.
Class 3 applications remain niche, serving textiles and woodworking, yet demand holds steady thanks to rising automation of cutting lines that create airborne fibers. Suppliers aim to reuse Class 1 designs by replacing gaskets and adding dust filters, saving test costs. Ethernet-APL especially benefits Class 1 because gas groups allow higher permissible power than dust, simplifying switch deployment. This compatibility further entrenches Class 1 as the proving ground for new intrinsically safe networking concepts that later trickle to dust and fiber sectors.
The Intrinsically Safe Equipment Report is Segmented by Zone (Zone 0, Zone 20, Zone 1, and More), Class (Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3), Product Type (Sensors, Detectors, Switches, and More), End User (Oil and Gas, Mining, Power and Utilities, Chemical and Petrochemical, Processing and Manufacturing, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America controlled 38.20% of 2025 revenue as OSHA and NFPA rules anchored continuous modernization across shale basins, Gulf Coast refineries, and underground mines. Honeywell's 2024 reorganization consolidated sensing and safety technologies into a single automation division, signaling that major suppliers aim to deliver unified hardware-software stacks that meet both safety and productivity needs. U.S. operators also lead in adopting intrinsically safe LTE/5G gateways, seeing the technology as a hedge against workforce shortages.
Asia-Pacific posts the fastest 8.55% CAGR through 2031, fueled by new refinery builds in China, petrochemical expansion in India, and large-scale copper and lithium mining in Australia. Governments link export licenses to IEC or ATEX compliance, steering local manufacturers toward certified components. Chinese automation vendors collaborate with European test houses to shorten certification schedules, enlarging the regional supplier ecosystem and boosting the intrinsically safe equipment market. Europe retains a sizable installed base under the ATEX directive, and EN IEC 60079-11:2024 will likely become mandatory by 2027, driving accelerated replacements. Germany leads in advanced chemical complexes, integrating Zone-crossing sensor networks to achieve emissions targets. The United Kingdom and Norway continue to invest in offshore intervention equipment that meets both intrinsic safety and cybersecurity rules dictated by the North Sea Transition Authority. Elsewhere, Middle East NOCs deploy intrinsically safe SCADA upgrades across large gas projects, while Brazilian sugar-ethanol distilleries switch from explosionproof motors to intrinsically safe variable-frequency drives that cut energy use. Collectively these regional narratives sustain robust global demand.
- Pepperl + Fuchs SE
- Honeywell International Inc.
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Schneider Electric SE
- R. Stahl AG
- BARTEC Top Holding GmbH
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- MSA Safety Inc.
- Dragerwerk AG and Co. KGaA
- OMEGA Engineering (Spectris plc)
- Fluke Corporation (Fortive)
- Banner Engineering Corp.
- Extronics Ltd.
- CorDEX Instruments Ltd.
- Bayco Products Inc.
- Kyland Technology Co. Ltd.
- Georgin SAS
- ABB Measurement and Analytics (added sub-brand)
- Teledyne FLIR LLC
- PATLITE Corp.
- G.M. International srl
- RAE Systems by Honeywell
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Stringent global explosion-safety regulations
- 4.2.2 Industry 4.0-driven demand for IS sensors and instrumentation
- 4.2.3 Expansion of oil and gas and mining activities
- 4.2.4 Cost-saving shift from Ex d to Ex i architectures
- 4.2.5 Growth of wireless IS modules for remote, predictive maintenance
- 4.2.6 Printed, ultra-low-power sensor arrays unlocking retrofit markets
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High certification cost and design complexity
- 4.3.2 Fragmented approval timelines across regions
- 4.3.3 Shortage of certified IS-grade electronic components
- 4.3.4 Rising cybersecurity-compliance cost for IS wireless devices
- 4.4 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Zone
- 5.1.1 Zone 0
- 5.1.2 Zone 20
- 5.1.3 Zone 1
- 5.1.4 Zone 21
- 5.1.5 Zone 2
- 5.1.6 Zone 22
- 5.2 By Class
- 5.2.1 Class 1
- 5.2.2 Class 2
- 5.2.3 Class 3
- 5.3 By Product Type
- 5.3.1 Sensors
- 5.3.2 Detectors
- 5.3.3 Switches
- 5.3.4 Transmitters
- 5.3.5 Isolators and Barriers
- 5.3.6 LED Indicators
- 5.3.7 Other Types
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Oil and Gas
- 5.4.2 Mining
- 5.4.3 Power and Utilities
- 5.4.4 Chemical and Petrochemical
- 5.4.5 Processing and Manufacturing
- 5.4.6 Other End Users
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Spain
- 5.5.3.5 Italy
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Pepperl + Fuchs SE
- 6.4.2 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.3 ABB Ltd.
- 6.4.4 Siemens AG
- 6.4.5 Eaton Corporation plc
- 6.4.6 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.4.7 R. Stahl AG
- 6.4.8 BARTEC Top Holding GmbH
- 6.4.9 Emerson Electric Co.
- 6.4.10 Rockwell Automation Inc.
- 6.4.11 MSA Safety Inc.
- 6.4.12 Dragerwerk AG and Co. KGaA
- 6.4.13 OMEGA Engineering (Spectris plc)
- 6.4.14 Fluke Corporation (Fortive)
- 6.4.15 Banner Engineering Corp.
- 6.4.16 Extronics Ltd.
- 6.4.17 CorDEX Instruments Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Bayco Products Inc.
- 6.4.19 Kyland Technology Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.20 Georgin SAS
- 6.4.21 ABB Measurement and Analytics (added sub-brand)
- 6.4.22 Teledyne FLIR LLC
- 6.4.23 PATLITE Corp.
- 6.4.24 G.M. International srl
- 6.4.25 RAE Systems by Honeywell
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




