PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1907207

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1907207
Food Processing Machinery - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
Food processing machinery market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 88.21 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 83.48 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 116.18 billion, growing at 5.67% CAGR over 2026-2031.
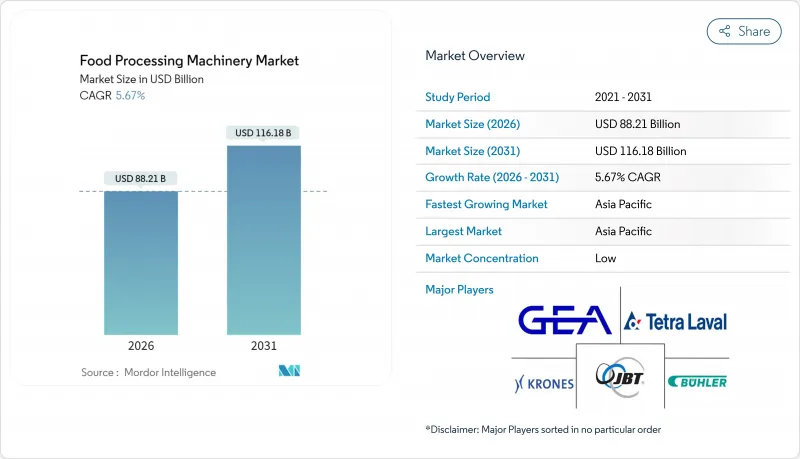
Steady modernization of plant floors, stricter hygiene regulations, and rising consumption of packaged foods underpin this growth trajectory. Processing machinery continues to command the largest revenue share because manufacturers view primary transformation equipment as the surest route to throughput gains and consistent product quality. Asia-Pacific's industrial build-out, coupled with expanding middle-class purchasing power, accelerates regional demand for advanced systems that comply with evolving food-safety mandates. Automation remains pivotal; semi-automatic lines dominate current installations, yet smart and AI-enabled equipment records the fastest uptake as firms pursue predictive maintenance, resource efficiency, and real-time quality monitoring. Competitive intensity stays moderate in a fragmented supplier base, enabling technology disruptors to win share with specialized, connected solutions.
Global Food Processing Machinery Market Trends and Insights
Rising Demand for Processed and Convenience Foods
Consumer lifestyle shifts toward convenience-oriented consumption patterns drive sustained equipment investment across processing and packaging segments. The U.S. ready meals market reached USD 63.3 billion with a 9.1% CAGR growth, creating upstream demand for flexible processing lines capable of handling diverse product formulations and packaging formats. This trend particularly benefits manufacturers offering modular systems that accommodate rapid product changeovers without extensive reconfiguration. Ghost kitchen operators increasingly specify compact, ventless equipment solutions that maximize space utilization while enabling multi-concept food preparation, as demonstrated by Alto-Shaam's Vector H Series Multi-Cook Oven powering Virtual Chef Hall's seven-concept operations. The convergence of delivery-focused business models with advanced processing technology creates new market segments for equipment suppliers targeting urban commissary operations.
Rapid Automation and IoT Integration in Plant Floors
Manufacturing intelligence platforms transform food processing from reactive maintenance toward predictive operational models that optimize equipment utilization and product quality. Rockwell Automation's FactoryTalk Analytics platform enables real-time monitoring of processing parameters, reducing unplanned downtime by up to 30% while improving overall equipment effectiveness. This technological shift particularly impacts high-volume processing environments where marginal efficiency gains translate to significant cost savings. Smart processing equipment increasingly incorporates edge computing capabilities that enable local decision-making without relying on cloud connectivity, addressing latency concerns in time-sensitive operations. The integration of artificial intelligence in food processing machinery, exemplified by Chef Robotics' AI-enabled depositing systems achieving greater than 30% improvement in consistency and yield, demonstrates how machine learning algorithms optimize portion control and reduce food waste.
High Capex and Opex of Advanced Hygienic Machinery
Investment barriers for sophisticated processing equipment create market segmentation between large-scale manufacturers and smaller operators seeking cost-effective automation solutions. Advanced hygienic design requirements, including 316L stainless steel construction and specialized surface finishes, significantly increase equipment costs compared to standard industrial machinery. GEA's introduction of entry-level thermoforming machines specifically targets small and medium-sized companies seeking advanced packaging capabilities without the capital commitment of high-end systems. Operating expenses compound initial investment challenges, as specialized cleaning chemicals, validation procedures, and maintenance protocols require ongoing financial commitments. This cost structure particularly impacts emerging market manufacturers who must balance automation benefits against capital constraints, creating opportunities for equipment suppliers offering flexible financing and leasing models.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Stricter Global Food-Safety and Hygiene Regulations
- Expanding Food Manufacturing Capacity Across APAC
- Escalating Energy and Skilled-Labor Costs
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Processing equipment captured 53.92% of 2025 revenue within the food processing machinery market, reflecting manufacturers' focus on core value generation. Thermal, non-thermal, and extrusion technologies form the backbone of capacity expansions and recorded a 5.04% CAGR outlook. Buhler's SmartLine release, including the DirectBake Smart oven produced in India, tailors high-end combustion and recipe controls to local price points. Packaging machinery ranks second in revenue yet increasingly integrates with upstream processes through unified controls that synchronize fill rates, sealing temperatures, and label feeds. Utilities such as CIP skids, waste-handling units, and HVAC systems tie into overarching plant-wide dashboards that analyze water, energy, and chemical consumption. This linkage illustrates how the food processing machinery market is moving from machine-level performance to holistic line optimization.
Demand for flexible, small-batch thermal systems rises alongside D2C brands and ghost kitchens that prioritize rapid changeovers. At the other end of the scale, mega-plants order high-throughput evaporators, UHT units, and aseptic fillers to serve export channels. Suppliers that modularize heat exchangers, pumps, and valve manifolds allow processors to phase investments over multiple budget cycles, keeping adoption on track even when cash flows fluctuate. As cyber-secure PLCs and industrial Ethernet become standard, equipment interoperability becomes a competitive requirement rather than a luxury.
The Food Processing Machinery Market is Segmented by Machinery Type (Processing Machinery and More), Automation Level (Manual, Semi-Automatic, Fully Automatic, Smart and AI-Enabled), Application (Bakery and Confectionery, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East, and Africa). Forecasts are Provided in Value Terms (USD).
Geography Analysis
In 2025, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to contribute 38.21% to global revenue and is set to grow at a CAGR of 5.33%. This underscores the region's pivotal role in global capacity expansion. Factors such as surging food exports, urban consumption, and government incentives for modernizing domestic processing bolster the region's growth. Multinational giants, including Cargill in Indonesia and Lonza in India, are broadening their localized manufacturing to cater to both domestic markets and nearby export corridors. Procurement teams in the region are increasingly favoring machinery suppliers who offer shorter lead times, local spare parts, and swift after-sales service. This trend fuels demand for modular systems, automated inspection technologies, and continuous processing lines, all tailored to the region's unique crop and livestock profiles.
North America is focusing on optimizing its existing infrastructure instead of pursuing greenfield expansions. Processors are channeling investments into digital retrofits, predictive maintenance systems, and energy-efficient upgrades. Rising tariffs on steel and aluminium, leading to a 25% spike in equipment fabrication costs-are nudging buyers to turn to regional OEMs or global firms with U.S.-based assembly units. The market is witnessing a robust adoption of robotics for tasks like portioning, packaging, and sanitation. This shift is largely driven by labor shortages, stringent hygiene standards, and the challenge of managing production variability across diverse product SKUs.
In South America, the Middle East, and Africa, there's a concerted push to establish foundational food processing infrastructure. This initiative aims to bolster food security, curtail post-harvest losses, and invigorate rural agro-industrial value chains. Innovations like mobile fruit processing units, containerized dairy lines, solar-powered dehydrators, and low-pressure poultry scalders are being deployed. These technologies are especially beneficial in areas with limited cold-chain access and inconsistent grid connectivity. While government-backed modernization grants and public-private partnerships are aiding small and mid-sized processors in upgrading their equipment, challenges like foreign exchange volatility and a reliance on imports are causing delays in machinery orders. Nevertheless, the overarching goal in these regions remains clear: to bridge critical capacity gaps, enhance local value addition, and align supply with the growing domestic demand.
- Buhler AG
- GEA Group AG
- Tetra Laval (Tetra Pak)
- John Bean Technologies (JBT)
- Krones AG
- Marel hf.
- Alfa Laval AB
- SPX FLOW Inc.
- Tomra Systems ASA
- Satake Corp.
- Anko Food Machine Co.
- Hosokawa Micron Corp.
- Atlas Pacific Engineering
- Provisur Technologies
- Syntegon Technology
- Marelec Food Tech
- Key Technology
- Heat and Control
- Middleby Corp.
- Urschel Laboratories
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising demand for processed and convenience foods
- 4.2.2 Rapid automation and IoT integration in plant floors
- 4.2.3 Stricter global food-safety and hygiene regulations
- 4.2.4 Expanding food manufacturing capacity across APAC
- 4.2.5 Shift toward flexible small-batch lines for D2C and ghost kitchens
- 4.2.6 Near-shoring incentives & tariff regimes in U.S./EU
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High capex and opex of advanced hygienic machinery
- 4.3.2 Escalating energy and skilled-labor costs
- 4.3.3 Semiconductor & sensor shortages delaying deliveries
- 4.3.4 Cyber-security risks in connected processing equipment
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Machinery Type
- 5.1.1 Processing Machinery
- 5.1.1.1 Primary Processing
- 5.1.1.2 Thermal Processing
- 5.1.1.3 Non-Thermal Processing
- 5.1.1.4 Extrusion and Forming Systems
- 5.1.2 Packaging Machinery
- 5.1.2.1 Primary Packaging
- 5.1.2.2 Secondary Packaging
- 5.1.2.3 End-of-Line packaging
- 5.1.2.4 Vacuum / MAP / Aseptic Systems
- 5.1.3 Utilities and Ancillary Systems
- 5.1.1 Processing Machinery
- 5.2 By Automation Level
- 5.2.1 Manual
- 5.2.2 Semi-Automatic
- 5.2.3 Fully Automatic
- 5.2.4 Smart and AI-Enabled
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Bakery and Confectionery
- 5.3.2 Meat/Seafood and Meat-Alternative
- 5.3.3 Dairy and Dairy-Alternative
- 5.3.4 Beverages
- 5.3.5 Fruits, Vegetables & Nuts
- 5.3.6 Ready Meals and Meal Kits
- 5.3.7 Others
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 Italy
- 5.4.2.4 France
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Netherlands
- 5.4.2.7 Poland
- 5.4.2.8 Belgium
- 5.4.2.9 Sweden
- 5.4.2.10 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 Indonesia
- 5.4.3.6 South Korea
- 5.4.3.7 Thailand
- 5.4.3.8 Singapore
- 5.4.3.9 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Colombia
- 5.4.4.4 Chile
- 5.4.4.5 Peru
- 5.4.4.6 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 South Africa
- 5.4.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.3 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.4.5.5 Egypt
- 5.4.5.6 Morocco
- 5.4.5.7 Turkey
- 5.4.5.8 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Buhler AG
- 6.4.2 GEA Group AG
- 6.4.3 Tetra Laval (Tetra Pak)
- 6.4.4 John Bean Technologies (JBT)
- 6.4.5 Krones AG
- 6.4.6 Marel hf.
- 6.4.7 Alfa Laval AB
- 6.4.8 SPX FLOW Inc.
- 6.4.9 Tomra Systems ASA
- 6.4.10 Satake Corp.
- 6.4.11 Anko Food Machine Co.
- 6.4.12 Hosokawa Micron Corp.
- 6.4.13 Atlas Pacific Engineering
- 6.4.14 Provisur Technologies
- 6.4.15 Syntegon Technology
- 6.4.16 Marelec Food Tech
- 6.4.17 Key Technology
- 6.4.18 Heat and Control
- 6.4.19 Middleby Corp.
- 6.4.20 Urschel Laboratories
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook




