PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1907344

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1907344
Japan Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Japan EV charging equipment market was valued at USD 0.29 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 0.46 billion in 2026 to reach USD 4.64 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 58.70% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
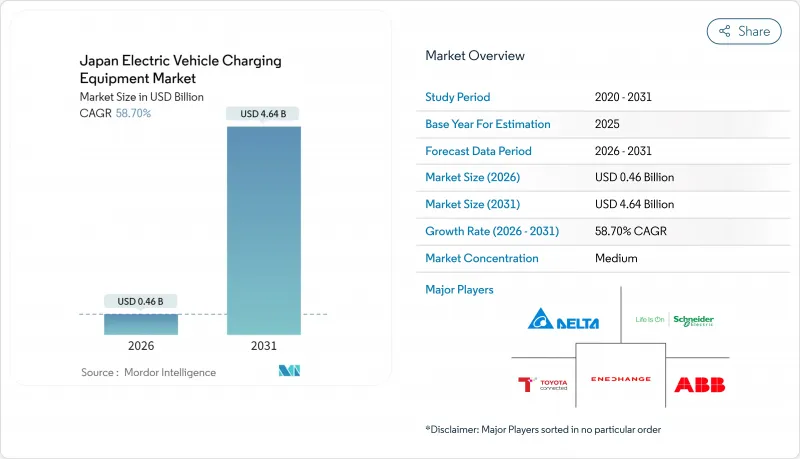
The Japan EV charging equipment market is propelled by the 2035 gasoline-vehicle sales ban, heavy green-growth spending, and nationwide integration of bidirectional chargers into the power system. Corporate electrification mandates issued by major keiretsu groups give the Japan EV charging equipment market an unusually predictable demand base, allowing faster network build-outs and earlier scale economies than consumer-led models. Technology advances-especially liquid-cooled cords, composite cables, and next-generation CHAdeMO/ChaoJi protocols-position equipment as grid assets rather than simple refueling hardware. Policy coherence between ministries and prefectures sustains subsidy pipelines that narrow payback periods, while component innovation drives total cost of ownership down. Although the Japan EV charging equipment market remains moderately fragmented, utilities have emerged as pivotal ecosystem orchestrators that unlock new revenue through demand-response programs
Japan Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market Trends and Insights
EV-Shift Stimulus From Japan's 2035 Gasoline-Car Sales Ban
The ban removes policy ambiguity and accelerates equipment investment because Japanese EV charging equipment market suppliers can confidently model ten-year cash flows. The Japanese government has earmarked trillions for charging build-outs and set a 300,000-public-port target by 2030, an almost eight-fold expansion. Commercial fleets must also comply, triggering immediate depot-charging demand that underpins the Japan EV charging equipment market's significant CAGR. Tokyo and adjacent prefectures attract the bulk of early funding, reflecting population density and corporate head-office concentration.
Corporate ESG-Fleet Electrification Mandates By Keiretsu Groups
In Japan, the distinctive keiretsu system shifts electric vehicle (EV) adoption from mere consumer choices to unified corporate strategies, leading to unique infrastructure demand patterns not seen in Western markets. Some Japanese companies have pledged to have fully electrified commercial fleets by 2030, locking in long-term charger contracts at factories and logistics hubs. Scale advantages lower per-port installation costs and accelerate return on investment, especially in the Kanto and Kansai economic belts.
Slow Condominium Retrofit Approvals Under the Building Management Act
Japan's Building Management Act mandates unanimous consent from all condominium owners for major electrical modifications. This requirement poses significant hurdles for installing residential charging stations, especially in urban areas dominated by condominium living. While the Act was crafted for traditional building modifications, it fails to address the nuances of EV infrastructure deployment. Here, decisions made by individual owners can have far-reaching implications on the building's overall electrical capacity and safety systems. As EV adoption surges, these constraints intensify, leading to infrastructure bottlenecks. Consequently, many new EV owners are pushed towards public charging solutions, which inflate operational costs and dampen the appeal of EV adoption.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Subsidized High-Power Charger Grants Under METI's Green Growth Fund
- V2H Tariff Premiums from Power Utilities
- High Land-Lease Costs for Public Fast-Charging Sites Near Expressways
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Passenger cars held a 93.48% Japan EV charging equipment market share in 2025, furnishing the baseline load for most public networks. Commercial vehicles, however, post a 64.30% CAGR that pulls equipment makers toward depot-grade DC blocks and advanced load-scheduling software. Fleet electrification contracts are typically multi-year, letting suppliers lock in recurring maintenance revenue and forecast parts demand more accurately. Logistics firms like Yamato and Sagawa deploy megawatt hubs that double as micro-grids, using stationary batteries to shave peak demand and sell ancillary services to utilities. These large installations create spillover benefits for retail drivers when operators open excess nighttime capacity to the public.
The corporate pivot also drives connector durability and payment integration innovation because fleet use cases require thousands of mating cycles and centralized billing. Higher throughput accelerates hardware replacement cycles, expanding the aftermarket for cables, seals, and switchgear. Suppliers that bundle hardware with SaaS fleet dashboards gain margin insulation because software churn remains low once integrated into logistics workflows. As corporate adoption scales, the commercial share of the Japan EV charging equipment market size is expected to rise, even if passenger cars remain numerically dominant.
The Others (terminal blocks, energy meters, safety mechanisms, etc.) category held 33.62% of the Japan EV charging equipment market share in 2025, but cords and cables are forecast to grow at a 63.90% CAGR. Lightweight composite sheathing cuts cable mass by 40%, mitigating ergonomic strain and reducing maintenance calls linked to dropped connectors. Domestic firms co-develop these designs with resin suppliers, securing exclusive supply contracts that shore up margins. Component scale economies lower per-unit cost significantly, widening adoption among small independent operators.
Traditional pedestal pillars face urban footprint constraints, prompting vendors to roll out slimline wall-mounts that bolt onto existing parking-lot lighting poles. Power supplies and control boards track the overall growth of Japan's EV charging equipment market size but gain an incremental bump from silicon-carbide MOSFET adoption, significantly improving conversion efficiency. Interoperability upgrades follow CHAdeMO's ChaoJi roadmap, ensuring new hardware remains backward-compatible with earlier vehicles. Suppliers that offer end-to-end hardware suites win municipal tenders because bundling simplifies procurement audits. The component race thus underscores how incremental engineering tweaks can swing large revenue pools in a fast-scaling market.
The Japan Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market Report is Segmented by Vehicle Type (Passenger Cars and Commercial Vehicles), Charging Equipment (Pillar, Cord and Cable, Control Boards, Charging Controllers, and Others), Charging Type (AC Charging Station, DC Charging Station, and NACS), and Application Type (Home Charging and Public Charging). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Panasonic Corporation
- Denso Corporation
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- Delta Electronics
- Nichicon Corporation
- Fujikura Ltd.
- Toshiba Corporation
- NEC Corporation
- Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd.
- Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings (TEPCO)
- ENECHANGE Ltd.
- Terra Motors Corporation
- Envision AESC Group
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 EV-Shift Stimulus from Japan's 2035 Gasoline-Car Sales Ban
- 4.2.2 Corporate ESG-Fleet Electrification Mandates by Keiretsu Groups
- 4.2.3 Subsidized High-Power Charger Grants Under METI's Green Growth Fund
- 4.2.4 V2H (Vehicle-To-Home) Tariff Premiums From Power Utilities
- 4.2.5 Grid-Balancing Demand for Bidirectional Chargers at Solar-Rich Prefectures
- 4.2.6 On-Street Charger Pilots Tied to 2025 World Expo Osaka
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Slow Condominium Retrofit Approvals Under Japan's Building Management Act
- 4.3.2 High Land-Lease Costs for Public Fast-Charging Sites Near Expressways
- 4.3.3 Persistent CHAdeMO / CCS / NACS Standards Fragmentation
- 4.3.4 Low Utilisation Rates (Below 8%) at Rural Charging Stations
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value (USD) and Volume (Units))
- 5.1 By Vehicle Type
- 5.1.1 Passenger Cars
- 5.1.2 Commercial Vehicles
- 5.2 By Charging Equipment
- 5.2.1 Pillar
- 5.2.2 Cord and Cable
- 5.2.3 Control Boards
- 5.2.4 Charging Controllers
- 5.2.5 Power Supplies
- 5.2.6 Others
- 5.3 By Charging Type
- 5.3.1 AC Charging Station
- 5.3.2 DC Charging Station
- 5.3.3 NACS (North American Charging System)
- 5.4 By Application Type
- 5.4.1 Home Charging
- 5.4.2 Public Charging
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, SWOT Analysis, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Panasonic Corporation
- 6.4.2 Denso Corporation
- 6.4.3 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 6.4.4 Hitachi, Ltd.
- 6.4.5 Delta Electronics
- 6.4.6 Nichicon Corporation
- 6.4.7 Fujikura Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Toshiba Corporation
- 6.4.9 NEC Corporation
- 6.4.10 Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings (TEPCO)
- 6.4.12 ENECHANGE Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Terra Motors Corporation
- 6.4.14 Envision AESC Group
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




