PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910481

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910481
Military Aviation Maintenance, Repair, And Overhaul - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The military aviation MRO market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 45.75 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 44.63 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 51.75 billion, growing at 2.5% CAGR over 2026-2031.
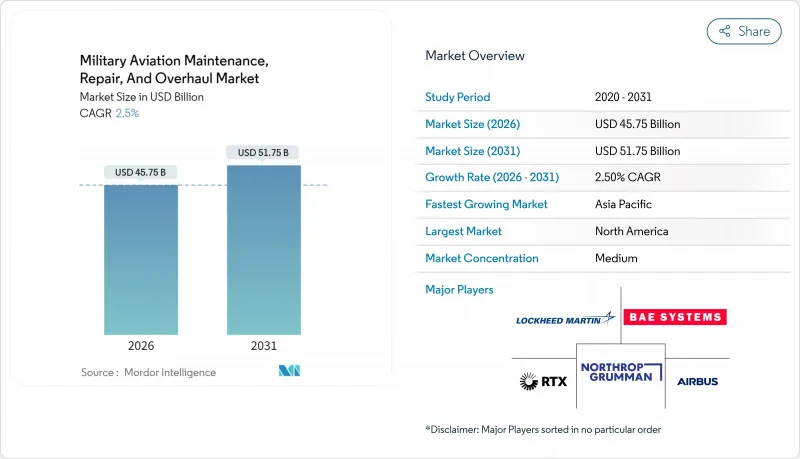
This measured expansion reflects a mature yet indispensable sector reshaped by aging fleets, fleet-life extension initiatives, and heightened geopolitical tensions. Accelerated modernization programs for legacy aircraft, sustained investment in digital twin technology, and the proliferation of unmanned platforms are altering maintenance requirements and opening new provider revenue opportunities. Meanwhile, persistent supply-chain fragility and a looming skilled-labor shortage threaten to constrain capacity, pushing operators to adopt predictive maintenance and performance-based logistics (PBL) to maintain readiness at lower cost. These structural shifts underpin a gradual move toward outsourced services, with independent providers gaining traction as defense ministries seek cost efficiency without compromising security. Together, these dynamics reinforce a steady outlook for the military aviation MRO market through the decade's end.
Global Military Aviation Maintenance, Repair, And Overhaul Market Trends and Insights
Rising Fleet-Life Extension Programs Drive Sustained MRO Demand
Fleet-life extension initiatives are now the backbone of sustainment planning for legacy bombers, tankers, and fighters worldwide, reflecting a pragmatic strategy that blends fiscal prudence with readiness assurance. Operators view modernization contracts for platforms such as the B-52 and KC-135 as a hedge against the budget and schedule risk inherent in clean-sheet aircraft development. Extending service to 2050 obliges depots to perform deep structural remediation, corrosion mitigation, and mission-system upgrades that often surpass original manufacturing tolerances. Work scopes routinely include complete rewiring, composite panel replacement, and radar-absorbent-material refreshes to preserve low-observable performance. Such labor-intensive projects absorb skilled technicians for months, keeping hangars full even during procurement downturns. As modernization cascades through global fleets, specialized providers capable of managing obsolescence, parts reclamation, and digital records integration secure predictable, multi-year revenue streams that anchor overall MRO growth.
Multinational Defense Agreements Expand Interoperability Requirements
Allied readiness frameworks now mandate standard maintenance protocols, technical documentation, shared inventories, and reframing sustainment from an isolated national task to a collective security prerequisite. The F-35 global support solution, with regional hubs in Australia and Europe, shows how pooling heavy-maintenance events lowers per-flight-hour cost while guaranteeing surge capacity during crises. Establishing common tooling and certification standards lets technicians traverse national lines without redundant training, accelerating turnaround times for coalition squadrons. Nonetheless, strict technology-transfer rules compel providers to balance openness with safeguarding sensitive data. Certification bodies must harmonize software-validation procedures so upgrades released by one country remain airworthy across partner fleets. For independent MROs, aligning cybersecurity, export-control compliance, and sovereign supply-chain preferences is becoming a competitive differentiator. The net result is a larger, more stable work package that depends on trust, transparency, and proven performance across multiple jurisdictions.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities Constrain MRO Capacity
Single-source suppliers and aging tooling create brittle supply networks where minor disruptions cascade into months-long aircraft on-ground incidents. Critical forgings for legacy engines may originate from only one qualified vendor, whose unexpected outage can immobilize entire fleets. Long lead times compel operators to stockpile rotables, yet warehouse expansions inflate overhead and capital locked in inventory. Export-license delays add unpredictability for multinational programs, especially when geopolitical tensions tighten licensing scrutiny. Depots explore additive manufacturing for non-flight-critical parts to counteract risk, though certification hurdles remain formidable. Digital traceability platforms are being introduced to monitor supplier health, flagging early signs of capacity shortfall. Until diversified sources, advanced forecasting, and additive solutions scale, supply-chain fragility will remain the most immediate brake on MRO throughput and revenue realization.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- APAC Defense Spending Surge Accelerates Regional MRO Growth
- Digital Twin Technology Revolutionizes Predictive Maintenance
- Workforce Shortages Threaten Maintenance Capacity
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Fixed-wing fleets dominated 59.72% of the 2025 military aviation MRO market size owing to large inventories of combat and transport aircraft that require routine heavy checks and periodic avionics refreshes. UAVs, however, represent the fastest-growing segment with a 6.58% CAGR, reflecting strategic investments in swarm-enabled autonomy under the Pentagon's Replicator initiative.
While fixed-wing platforms will maintain the largest maintenance workload, UAV growth forces providers to adapt to high-volume, rapid-turn processes distinct from depot-level overhauls. Rotary-wing demand remains stable, especially for special-operations-configured UH-60 and MH-47 variants that require classified hangar access and accelerated turnaround. The resulting platform mix calls for flexible capacity planning so providers can capture rising UAV volumes without jeopardizing legacy airframe support, sustaining a balanced expansion across the military aviation MRO market.
Engine overhaul captured 42.12% of 2025 revenue, underscoring how propulsion systems account for the single largest maintenance spend and carry stringent performance and certification standards. Component repair and overhaul is projected to pace the field at a 3.39% CAGR, driven by digital-twin-informed diagnostics that lower inspection costs and enable targeted part replacements.
Airframe maintenance demand is steady as service-life extensions require structural reinforcement, corrosion control, and composite repairs. The shift limits line maintenance growth and military aviation MRO market penetration to condition-based scheduling, yet remains critical for forward-deployed readiness. Performance-based contracts continue to bundle multiple service types, allowing providers to leverage efficiencies across shop specialties and deepen military aviation MRO market penetration.
The Military Aviation Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) Market Report is Segmented by Application (Fixed-Wing, Rotary-Wing, and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles), MRO Type (Engine Overhaul, Airframe Maintenance, and More), Service Provider (OEM-Affiliated Centers, Independent MROs, and More), End-User (Air Force, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America's 37.35% share is rooted in the US' inventory of more than 13,000 military aircraft, underpinned by large-scale contracts such as Boeing's USD 2.3 billion C-17 sustainment award. However, chronic parts shortages and a looming technician retirement wave threaten to erode productivity, compelling service branches to accelerate digital-twin adoption and invest in workforce development. Canada's partnership with L3Harris to establish an F-35 depot illustrates how allied cooperation reinforces continental readiness.
Asia-Pacific is the most dynamic arena, expanding at a 4.32% CAGR as regional powers respond to heightened geopolitical risk. Japan increased its 2024 defense budget by 21% to USD 55.3 billion, and India's USD 2.34 billion MiG-29 upgrade venture demonstrates a deliberate pivot toward indigenous sustainment capability. China's steady USD 314 billion allocation represents a substantial underlying driver even without direct market participation by Western contractors. These factors collectively elevate the region's importance to the military aviation MRO market over the forecast horizon.
Europe sustains a mature yet opportunity-rich environment. The ReArm Europe initiative earmarks EUR 800 billion (USD 938.57 billion) for defense, yet implementation hinges on political alignment and supplier capacity. Recent moves, such as F-16 MRO capability expansion in Slovakia, signal the gradual decentralization of sustainment within NATO. Environmental regulations also compel European operators to embark on engine retrofit campaigns, extending mid-life platforms while advancing emission-reduction goals. These developments keep Europe relevant in the evolving military aviation MRO market, though actual growth may trail headline funding commitments.
- Airbus SE
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- RTX Corporation
- BAE Systems plc
- Saab AB
- Elbit Systems Ltd.
- Rolls-Royce Holdings plc
- Safran SA
- MTU Aero Engines AG
- Leonardo S.p.A.
- Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd.
- Korean Aerospace Industries, Ltd.
- AAR CORP.
- StandardAero Aviation Holdings, Inc.
- General Atomics
- Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd.
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising fleet-life extension programs
- 4.2.2 Expansion of multinational readiness agreements
- 4.2.3 Growth in defense spending of emerging Asia-Pacific nations
- 4.2.4 OEM digital-twin enabled service packages
- 4.2.5 Increased rotorcraft usage for special operations
- 4.2.6 Sustainability mandates driving engine retrofits
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Supply-chain fragility for defense-grade spares
- 4.3.2 Skilled-labor shortages at depot-level facilities
- 4.3.3 Budget-cycle unpredictability in Western Europe
- 4.3.4 Export-control restrictions on critical avionics
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Application
- 5.1.1 Fixed-wing
- 5.1.1.1 Combat Aircraft
- 5.1.1.2 Transport and Tanker Aircraft
- 5.1.1.3 Special Mission Aircraft
- 5.1.1.4 Others
- 5.1.2 Rotary-wing
- 5.1.2.1 Utility/Transport Helicopters
- 5.1.2.2 Attack Helicopters
- 5.1.3 Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
- 5.1.1 Fixed-wing
- 5.2 By MRO Type
- 5.2.1 Engine Overhaul
- 5.2.2 Airframe Maintenance
- 5.2.3 Component Repair and Overhaul
- 5.2.4 Line Maintenance
- 5.3 By Service Provider
- 5.3.1 OEM-Affiliated Centers
- 5.3.2 Independent MROs
- 5.3.3 In-house Military Depots
- 5.4 By End-User
- 5.4.1 Air Force
- 5.4.2 Naval Aviation
- 5.4.3 Army Aviation
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.2 France
- 5.5.2.3 Germany
- 5.5.2.4 Russia
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 Israel
- 5.5.5.1.3 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Airbus SE
- 6.4.2 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.3 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.4 RTX Corporation
- 6.4.5 BAE Systems plc
- 6.4.6 Saab AB
- 6.4.7 Elbit Systems Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Rolls-Royce Holdings plc
- 6.4.9 Safran SA
- 6.4.10 MTU Aero Engines AG
- 6.4.11 Leonardo S.p.A.
- 6.4.12 Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Korean Aerospace Industries, Ltd.
- 6.4.14 AAR CORP.
- 6.4.15 StandardAero Aviation Holdings, Inc.
- 6.4.16 General Atomics
- 6.4.17 Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd.
- 6.4.18 L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




