PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910523

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910523
Logistics Automation - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
Logistics automation market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 90.78 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 82.69 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 144.78 billion, growing at 9.78% CAGR over 2026-2031.
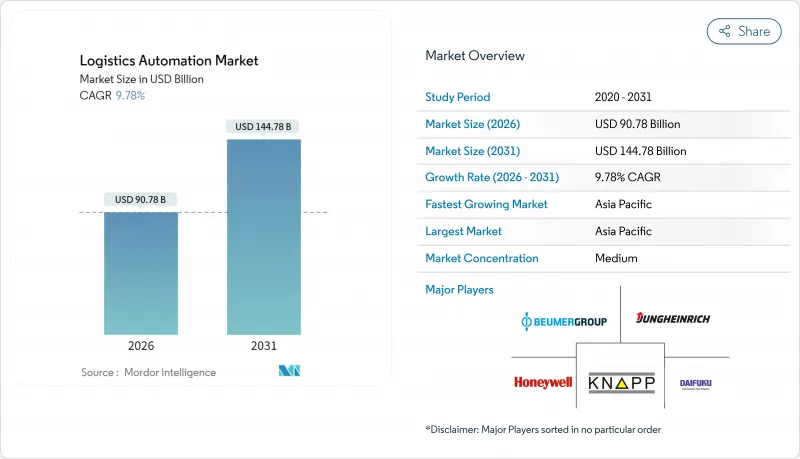
Rising e-commerce parcel volumes, acute labor shortages, and expanding corporate net-zero commitments are transforming automation from a tactical option into an essential pillar of modern supply chain design. Retailers now treat automated order-fulfillment capacity as a hedge against wage inflation, while the convergence of 5G and private LTE networks inside warehouses enables real-time orchestration between robots and yard vehicles that was previously impossible. Environmental targets are also influencing capital-spending priorities, with green-bond financing increasingly tied to energy-efficient systems for picking, storage, and transport. Against this backdrop, semi-automated deployments currently dominate, but fully automated projects are scaling quickly as AI vision and functional-safety chips clear certification hurdles, thereby lowering perceived execution risk. Geographically, Asia-Pacific is rewriting the playbook: government subsidies, greenfield facility growth, and a surge in private 5G pilots are combining to make the region both the largest and fastest-growing market node.
Global Logistics Automation Market Trends and Insights
Rapid E-Commerce Parcel Volumes Drive Infrastructure Modernization
Fulfillment operators now face holiday-level order velocity all year, forcing a shift from batch-picking to continuous, goods-to-person flows that shrink cycle times without expanding headcount. Retailers such as Kroger deepened automation partnerships with Ocado to guarantee same-day grocery delivery service levels that manual processes cannot sustain.Parallel advances in right-sizing technology enable UPS to cut packaging waste by 30% while maintaining steady throughput targets. Dense urban micro-fulfillment hubs are proliferating, and India alone is projected to reach more than 35 million ft2 of such space by 2027, intensifying demand for high-cube automation capable of monetizing every cubic foot in cost-constrained city warehouses. The velocity mandate now extends to automated carton closing, labeling, and last-mile hand-off, embedding robotics across the full e-commerce workflow. Together, these forces anchor the near-term growth engine for the logistics automation market.
Rising Labor Shortages Accelerate Automation Investment Cycles
Demographic headwinds have turned labor availability into a strategic bottleneck, especially in North America and Europe. The Indian PMI reached a 16-year high in March 2024, yet integrators such as NIDO Group are rolling out unmanned goods-movement platforms for Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, where skilled labor is scarce. Collaborative AMRs are easing the pinch: Fleet Feet reported productivity gains of 2-3X when mobile robots assumed repetitive transport chores, freeing human associates for exception handling tasks. Robotics-as-a-service contracts are rising because businesses want seasonal capacity without long-term payroll commitments. In the Asia-Pacific region, where manufacturing expansion outpaces workforce growth, these models are redefining adoption economics. The combination of constrained labor supply and flexible financing options is propelling the logistics automation market forward.
High Upfront Capital Requirements Constrain SME Adoption
Comprehensive warehouse projects can exceed USD 5 million when structural retrofits are combined with new equipment, keeping many small enterprises on the sidelines. Pay-per-pick subscription programs, championed by AutoStore, lower grid installation costs by up to 40% but do not eliminate construction and systems integration expenses. Access to affordable financing is toughest in emerging markets that also face currency volatility, elevating perceived risk. As a result, vendors with rental or service-based models are gaining share, and larger integrators are acquiring niche robotics firms to assemble turnkey packages that are easier for lenders to underwrite. Despite progress, CAPEX remains the most stubborn near-term brake on the logistics automation market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Corporate Net-Zero Commitments Reshape Facility Design Priorities
- Customs-Free Micro-Fulfillment Zones Enable Distributed Inventory Models
- Integration Complexity with Legacy IT Systems Delays Implementation
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Warehouse operations captured 59.55% of the 2025 revenue within the logistics automation market share, underscoring the immediate ROI companies achieve from goods-to-person pick stations, automated storage, and robotic sortation. These proven technologies thrive in controlled environments, letting retailers compress order-to-ship cycles without adding workers. Transportation automation is currently smaller but is slated for an 11.05% CAGR to 2031 as autonomous trucks and yard tractors transition from pilots to revenue service, especially along reliable freight corridors.
Continued innovation sustains warehouse leadership: AutoStore's 2025 launch of CarouselAI delivers retrofit-friendly robotic piece-picking, enabling existing sites to scale without concrete mezzanine work. Yet the functional boundary is blurring. Private 5G deployments at sites like CJ Logistics integrate indoor robots and autonomous yard vehicles, creating a unified data fabric that reduces dock-door congestion. Over the forecast horizon, integrated orchestration platforms could shift spending toward cross-functional solutions, but warehouses will remain the volume anchor of the logistics automation market.
The Logistic Automation Market Report is Segmented by Function (Warehouse Automation and Transportation Automation), Automation Level (Fully Automated Systems and Semi-Automated Systems), End-User Industry (E-Commerce and Parcel, Grocery Retail, Manufacturing, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
The Asia-Pacific region accounted for 31.30% of 2025 revenue and is projected to grow at a 11.56% CAGR to 2031, earning the region a dual distinction as both the largest and fastest-growing node of the logistics automation market. China has been the world's top industrial-robot buyer for 11 consecutive years, producing 430,000 units in 2023 while subsidizing roughly 17.5% of equipment costs to accelerate domestic uptake. India brings complementary momentum; Grade A warehouse inventory is on track to increase from 290 million to 400 million ft2 by 2027, driven by the National Logistics Policy's push to reduce logistics costs to 10% of GDP and by surging urban micro-fulfillment demand.
North America remains a cornerstone market, thanks to high labor costs that strengthen the payback math for automation, even as complex legacy IT systems and strict cybersecurity rules lengthen project cycles. The expansion of U.S. Foreign Trade Zones supports distributed inventory strategies, freeing automated hubs from duty liabilities until final sale and sharpening cross-border e-commerce competitiveness. Europe mirrors many of these patterns, with an added regulatory premium on carbon reduction, which is funneling capital toward energy-efficient AS/RS and AI route-planning tools.
Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are in earlier stages of adoption. Capital scarcity and limited integrator ecosystems slow headline growth, yet demographic trends and rapid e-commerce penetration outline substantial latent demand. As financing mechanisms evolve and local vendor footprints expand, these regions are positioned to become the next wave of contributors to the global logistics automation market.
- Dematic Corp. (KION Group AG)
- Daifuku Co., Ltd.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Jungheinrich AG
- Murata Machinery, Ltd.
- KNAPP AG
- TGW Logistics Group GmbH
- Kardex Holding AG
- Mecalux, S.A.
- BEUMER Group GmbH & Co. KG
- SSI SCHAFER AG
- Vanderlande Industries B.V.
- WITRON Logistik + Informatik GmbH
- Interroll Holding AG
- GreyOrange Pte Ltd.
- Locus Robotics Corp.
- Geek+ Technology Co., Ltd.
- Ocado Group plc (Ocado Intelligent Automation)
- AutoStore Holdings Ltd.
- Exotec SAS
- Fetch Robotics Inc. (Zebra Technologies)
- Korber Supply Chain GmbH
- Cimcorp Oy
- Manhattan Associates Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid e-commerce parcel volumes
- 4.2.2 Rising labor shortages and wage inflation
- 4.2.3 Corporate net-zero logistics commitments
- 4.2.4 Customs-free micro-fulfilment zoning laws
- 4.2.5 Convergence of 5G and private-LTE inside warehouses
- 4.2.6 Open-source robotics operating systems (ROS-2) maturation
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront CAPEX
- 4.3.2 Integration complexity with brown-field IT
- 4.3.3 Scarcity of functional-safety certified AI chips
- 4.3.4 Rising cyber-insurance premiums for OT networks
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors on the Market
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Function
- 5.1.1 Warehouse Automation
- 5.1.1.1 By Component
- 5.1.1.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.1.1.1.1 Mobile Robots (AGV, AMR)
- 5.1.1.1.1.2 Automated Storage And Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
- 5.1.1.1.1.3 Automated Sorting Systems
- 5.1.1.1.1.4 De-Palletizing/Palletizing Systems
- 5.1.1.1.1.5 Conveyor Systems
- 5.1.1.1.1.6 Automatic Identification and Data Collection (AIDC)
- 5.1.1.1.1.7 Order Picking
- 5.1.1.1.2 Software
- 5.1.1.1.3 Services
- 5.1.1.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.1.1 By Component
- 5.1.2 Transportation Automation
- 5.1.2.1 By Component
- 5.1.2.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.2.1.2 Software
- 5.1.2.1.3 Services
- 5.1.2.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Warehouse Automation
- 5.2 By Automation Level
- 5.2.1 Fully-automated Systems
- 5.2.2 Semi-automated Systems
- 5.3 By End-user Industry
- 5.3.1 E-commerce and Parcel
- 5.3.2 Food and Beverage
- 5.3.3 Grocery Retail
- 5.3.4 Apparel and Fashion
- 5.3.5 Manufacturing
- 5.3.6 Other End-user Industries
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.4.3.6 Russia
- 5.4.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4.1 China
- 5.4.4.2 Japan
- 5.4.4.3 India
- 5.4.4.4 South Korea
- 5.4.4.5 South-East Asia
- 5.4.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Middle East
- 5.4.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.4.5.2 Africa
- 5.4.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.4.5.2.2 Egypt
- 5.4.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Middle East
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Dematic Corp. (KION Group AG)
- 6.4.2 Daifuku Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.3 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.4 Jungheinrich AG
- 6.4.5 Murata Machinery, Ltd.
- 6.4.6 KNAPP AG
- 6.4.7 TGW Logistics Group GmbH
- 6.4.8 Kardex Holding AG
- 6.4.9 Mecalux, S.A.
- 6.4.10 BEUMER Group GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.11 SSI SCHAFER AG
- 6.4.12 Vanderlande Industries B.V.
- 6.4.13 WITRON Logistik + Informatik GmbH
- 6.4.14 Interroll Holding AG
- 6.4.15 GreyOrange Pte Ltd.
- 6.4.16 Locus Robotics Corp.
- 6.4.17 Geek+ Technology Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Ocado Group plc (Ocado Intelligent Automation)
- 6.4.19 AutoStore Holdings Ltd.
- 6.4.20 Exotec SAS
- 6.4.21 Fetch Robotics Inc. (Zebra Technologies)
- 6.4.22 Korber Supply Chain GmbH
- 6.4.23 Cimcorp Oy
- 6.4.24 Manhattan Associates Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment




