PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910550

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910550
Singapore 3PL - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Singapore 3PL Market was valued at USD 4.85 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 5.03 billion in 2026 to reach USD 6.04 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 3.71% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
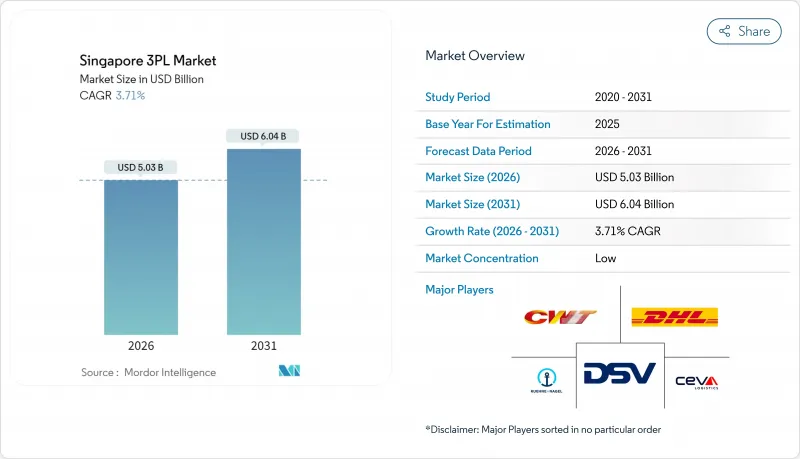
The steady expansion stems from Singapore's unrivaled multimodal connectivity, its network of 65 free-trade agreements, and a pipeline of infrastructure megaprojects that collectively deepen the city-state's role as Southeast Asia's principal transshipment and distribution hub. Rapid e-commerce penetration accelerated cold-chain demand from life-sciences production, and rising adoption of warehouse automation increases the addressable base for outsourced logistics, while hybrid asset models lower entry barriers for service innovation. At the same time, escalating land and labor costs, acute port congestion, and new carbon-reporting mandates add structural cost pressure that rewards operators with scale, automation, and strong regulatory compliance capabilities. Strategic acquisitions by global logistics majors highlight how ownership of premium Singapore footprints is becoming essential for end-to-end Asia-Pacific supply-chain orchestration.
Singapore 3PL Market Trends and Insights
Explosive Growth of Domestic & Cross-Border E-commerce
Southeast Asia's online retail boom is transforming demand profiles for fulfillment speed, reverse-logistics services, and last-mile routing efficiency. Singapore captures outsized volumes because merchants consolidate inventory in the republic to reach 680 million regional consumers in two-to-three-day delivery windows. Logistics providers are scaling parcel-sortation lines and integrating customs-clearance APIs to handle higher SKU complexity and return flows. Singapore Post quadrupled processing capacity to 400,000 parcels daily at its Regional eCommerce Logistics Hub after a USD 22.2 million upgrade, illustrating the capital intensity of this response. Social-commerce sellers and bulky-item categories further broaden the revenue pool for third-party specialists, while regulatory harmonization across ASEAN lowers cross-border friction and boosts volumes handled through Singapore gateways.
Government Megaprojects (Tuas Mega-Port, Changi Cargo Hub)
The USD 20 billion Tuas Mega-Port, slated for full completion by 2040 with 65 million TEU annual capacity, introduces fully automated quay cranes, driverless vehicles, and AI-driven berth scheduling that together compress vessel turnaround times and trim operating costs for logistics users. Parallel expansion of Changi Airport's cargo infrastructure, including a second air-freight logistics park, will lift capacity from 3 million to 5.4 million tons yearly and embed a free-trade zone model that accelerates transshipment cycle times. These long-horizon projects dovetail with supply-chain rerouting caused by geopolitical disruptions, giving Singapore a first-mover advantage in capturing diverted traffic as neighboring gateways confront land and depth constraints.
Escalating Real Estate & Labor Costs
Industrial rents climbed to USD 11.8-31.1 per m2 monthly in 2025 amid land scarcity, while nominal wages advanced 5.2% even as GDP growth lagged. Security officers now earn at least USD 1,961 per month under the Progressive Wage Model, and compulsory pension contributions for gig couriers add a 17-20% payroll burden. These structural cost inflators compress margins for providers relying on labor-intensive warehousing and last-mile fleets, prompting accelerated automation rollouts and selective offshoring of non-core activities.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cold-chain Demand from Life-sciences & Precision Medicine
- ASEAN Trade Integration & Singapore's Free-trade Network
- Port & Airport Congestion from Demand Surges
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Domestic Transportation Management accounted for 32.65% of the Singapore third-party logistics market in 2025, reflecting the complexity of orchestrating final-mile routes across a densely populated island supported by multimodal links. The segment continues to grow steadily as retailers push tighter cut-off times and real-time visibility expectations. Value-Added Warehousing & Distribution, while representing a smaller revenue base, is forecast to deliver a 7.02% CAGR through 2031 as merchants outsource kitting, labeling, and returns management to trim working capital. Higher margin profiles and sticky contracts attract new entrants, but the capital spend required for mezzanine-floor automation preserves an edge for incumbents.
Edge-computing sensors and AI-powered slot-assignment software have cut pick-to-ship cycles by 20%, heightening customer expectations and boosting demand for orchestration platforms that bundle transport, warehousing, and customs clearance into a single SLA. Cross-border trucking lanes linking Singapore to Malaysia and Thailand add route density that benefits international transportation management providers. As hybrid electric trucks gain mileage, firms integrating battery-swap nodes within their depot networks stand to capture incremental wallet share, reinforcing the structural shift from pure haulage toward integrated logistics solutions within the Singapore third-party logistics market.
The Singapore Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Market Report is Segmented by Service (Domestic Transportation Management, International Transportation Management, and More), by End User (Automotive, Energy & Utilities, Manufacturing, Life Sciences & Healthcare, Technology & Electronics, E-Commerce, and More), and by Logistics Model (Asset-Light, Asset-Heavy, Hybrid). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- DHL Group
- DSV
- CEVA Logistics
- CWT Ltd
- Kuehne + Nagel
- Toll Group
- Nippon Express
- UPS Inc.
- FedEx
- Singapore Post Ltd (SingPost)
- CJ Logistics Asia
- Rhenus Logistics Pte Ltd
- Yang Kee Logistics Pte Ltd
- Ninja Van
- Uparcel
- Kintetsu World Express
- Yusen Logistics
- Nippon Express
- Geodis
- Kerry Logistics
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Explosive growth of domestic & cross-border e-commerce
- 4.2.2 Government megaprojects (Tuas Mega-Port, Changi Cargo Hub)
- 4.2.3 Cold-chain demand from life-sciences & precision medicine
- 4.2.4 ASEAN trade integration & Singapore's free-trade network
- 4.2.5 Warehouse-automation & robotics adoption race
- 4.2.6 Battery-swap infrastructure enabling heavy-EV fleets
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Escalating real-estate & labour costs
- 4.3.2 Port & airport congestion from demand surges
- 4.3.3 Cyber-security compliance costs for 3PL IT stacks
- 4.3.4 Mandatory carbon-reporting burdens on SMEs
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Singapore as ASEAN Trans-shipment Hub
- 4.9 E-commerce Sector Snapshot (Domestic & Cross-border)
- 4.10 Covid-19 Impact Review and Geo-Political Events
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Domestic Transportation Management (DTM)
- 5.1.1.1 Roadways
- 5.1.1.2 Railways
- 5.1.1.3 Airways
- 5.1.1.4 Waterways
- 5.1.2 International Transportation Management (ITM)
- 5.1.2.1 Roadways
- 5.1.2.2 Railways
- 5.1.2.3 Airways
- 5.1.2.4 Waterways
- 5.1.3 Value-Added Warehousing & Distribution (VAWD)
- 5.1.1 Domestic Transportation Management (DTM)
- 5.2 By End User
- 5.2.1 Automotive
- 5.2.2 Energy & Utilities
- 5.2.3 Manufacturing
- 5.2.4 Life Sciences & Healthcare
- 5.2.5 Technology & Electronics
- 5.2.6 E-commerce
- 5.2.7 Consumer Goods & FMCG
- 5.2.8 Food & Beverages
- 5.2.9 Others
- 5.3 By Logistics Model
- 5.3.1 Asset-Light (Management-Based)
- 5.3.2 Asset-Heavy (Own Fleet & Warehouses)
- 5.3.3 Hybrid
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration Analysis
- 6.2 Strategic Moves & Investments
- 6.3 Market-Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 DHL Group
- 6.4.2 DSV
- 6.4.3 CEVA Logistics
- 6.4.4 CWT Ltd
- 6.4.5 Kuehne + Nagel
- 6.4.6 Toll Group
- 6.4.7 Nippon Express
- 6.4.8 UPS Inc.
- 6.4.9 FedEx
- 6.4.10 Singapore Post Ltd (SingPost)
- 6.4.11 CJ Logistics Asia
- 6.4.12 Rhenus Logistics Pte Ltd
- 6.4.13 Yang Kee Logistics Pte Ltd
- 6.4.14 Ninja Van
- 6.4.15 Uparcel
- 6.4.16 Kintetsu World Express
- 6.4.17 Yusen Logistics
- 6.4.18 Nippon Express
- 6.4.19 Geodis
- 6.4.20 Kerry Logistics
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook




