PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911487

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911487
Indonesia Plant-Based Food And Beverages - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
Indonesia plant-based food and beverages market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 1.11 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 1.04 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 1.56 billion, growing at 6.94% CAGR over 2026-2031.
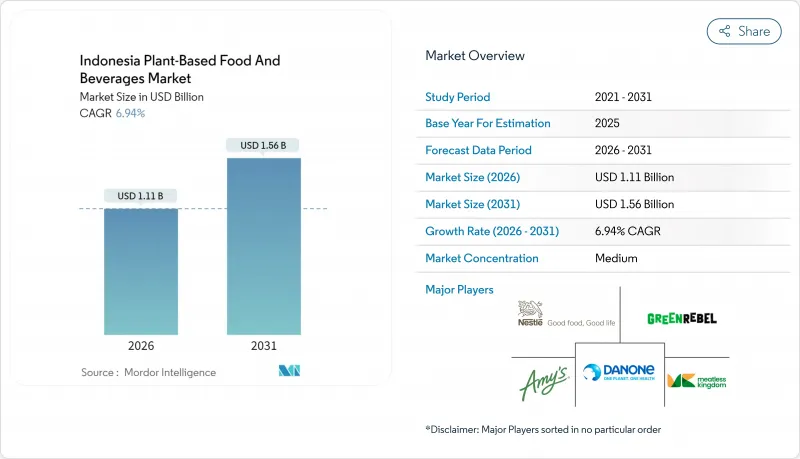
This growth trajectory reflects Indonesia's unique position as the world's largest Muslim-majority nation embracing plant-based alternatives while navigating complex halal certification requirements and deeply rooted culinary traditions. The market's expansion coincides with Indonesia's broader food security initiatives, as the government pursues agricultural self-sufficiency through its Swasembada Pangan program, targeting increased domestic production of key commodities, including soybeans and other plant proteins . Dairy-alternative beverages hold the largest revenue share, while meat substitutes post the fastest growth as local innovators scale through food-service partnerships. Ingredient diversification beyond soy, an improving cold-chain network, and the integration of halal compliance into product design further sustain growth momentum. Competition remains fragmented, creating room for regional specialists to flourish alongside global multinationals.
Indonesia Plant-Based Food And Beverages Market Trends and Insights
Growing Consumer Health and Wellness Awareness
Indonesia's health consciousness surge directly correlates with rising non-communicable disease prevalence, particularly diabetes and cardiovascular conditions affecting urban populations. The government's promotion of plant-based diets through official health ministry communications positions plant-forward nutrition as a preventive healthcare strategy, creating institutional legitimacy for alternative proteins. This health-driven demand particularly benefits dairy alternatives, as lactose intolerance affects 90% of Indonesians, making plant-based milk a functional necessity rather than lifestyle choice. Urban millennials and Gen Z consumers increasingly view plant-based foods as premium wellness products, willing to pay higher prices for perceived health benefits. The trend accelerates in Java's metropolitan areas where healthcare access and nutritional education create informed consumer bases. However, rural populations remain price-sensitive, requiring affordable plant-based options to achieve mass market penetration.
Rising Ethical Concerns for Animal Welfare
Animal welfare consciousness emerges gradually within Indonesia's predominantly Muslim population, where halal dietary requirements already emphasize humane treatment principles. Urban educated consumers increasingly question industrial livestock practices, creating demand for ethically produced alternatives that align with Islamic values of compassion toward animals. This ethical shift particularly influences younger demographics exposed to global sustainability narratives through social media and international education. The trend gains momentum in cosmopolitan cities like Jakarta and Surabaya, where exposure to international food cultures normalizes plant-based choices. Local Islamic scholars' endorsements of plant-based foods as inherently halal eliminate religious barriers, potentially accelerating adoption among devout consumers. The movement remains nascent compared to Western markets but shows potential for significant growth as environmental and ethical awareness expands.
Consumer Hesitation over Taste and Texture
Indonesian consumers maintain strong preferences for traditional food textures and flavors, creating significant barriers for plant-based alternatives that fail to replicate familiar sensory experiences. Academic research reveals that taste and texture rank as primary factors determining plant-based food acceptance among Indonesian consumers, with products requiring extensive formulation work to match local palate expectations. The challenge intensifies in regions with distinct culinary traditions, where consumers expect specific mouthfeel characteristics in meat and dairy products developed over generations. Plant-based manufacturers must invest heavily in R&D to achieve acceptable organoleptic properties, increasing product development costs and time-to-market. Regional taste preferences vary significantly across Indonesia's diverse archipelago, requiring localized product formulations that complicate manufacturing and distribution strategies. Success depends on achieving sensory parity with conventional products while maintaining cost competitiveness, a technical challenge that continues to limit market penetration rates.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Advances in Product Innovation and Quality
- Supportive Government Policies and Initiatives
- Challenges in Raw Material Supply Chains
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Dairy-alternative beverages command 37.20% market share in 2025, driven by Indonesia's high lactose intolerance prevalence and expanding coffee culture in urban centers. Oatside's successful market entry demonstrates how localized product development creates competitive advantages, with the company's chocolate malt variant specifically targeting Indonesian teenagers and achieving significant social media engagement through partnerships with local schools. Meat substitutes emerge as the fastest-growing segment at 7.02% CAGR through 2031, benefiting from Green Rebel's strategic partnerships with major food service chains and innovative products like rendang-flavored plant-based options that resonate with local tastes.
Non-dairy ice cream and frozen desserts gain traction in premium urban markets, while non-dairy cheese and yogurt segments remain nascent due to limited local consumption habits and higher price points. Plant-based spreads and butters show potential for growth, particularly in Bali's tourism-driven market where international dietary preferences influence local food trends. The packaged milk subcategory within dairy alternatives benefits from established distribution networks and consumer familiarity, while coffee and tea applications drive innovation in barista-grade formulations designed for Indonesia's thriving cafe culture.
Soy maintains 39.56% market share in 2025, leveraging Indonesia's traditional tempeh and tofu expertise, though import dependency creates supply chain vulnerabilities that manufacturers increasingly address through diversification strategies. Pea protein emerges as the fastest-growing ingredient source at 7.07% CAGR through 2031, offering superior functional properties and reduced allergenicity compared to soy-based alternatives. Oat-based products gain momentum through brands like Oatside, which sources Australian oats to ensure consistent quality while building local production capabilities in Java.
Coconut-based ingredients benefit from Indonesia's position as a major global coconut producer, providing cost advantages and supply security for manufacturers developing tropical-flavored products. Rice and wheat ingredients serve niche applications, particularly in gluten-free formulations targeting health-conscious urban consumers. Almond-based products face challenges due to import requirements and higher costs, limiting market penetration to premium segments. The diversification trend reflects manufacturers' strategic efforts to reduce single-ingredient dependency while creating unique value propositions tailored to local taste preferences and supply chain realities.
The Indonesia Plant-Based Food and Beverage Market is Segmented by Product Type (Meat Substitutes, Dairy Alternative Beverages, Non-Dairy Ice Cream, and More), Ingredient Source (Soy, Almond, and More), Form (Chilled/Shelf-Stable, and Frozen), Distribution Channel (On-Trade and Off-Trade), and Region (Western Indonesia and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Amy's Kitchen, Inc.
- Green Rebel Foods
- Meatless Kingdom
- Nestle S.A.
- Danone S.A.
- Beyond Meat Inc.
- Impossible Foods Inc.
- Vitasoy Int'l Holdings
- Upfield (Violife)
- Unilever plc
- The Kraft Heinz Company
- PepsiCo Inc.
- Quorn Foods
- KARANA Foods
- So Good Food (JAPFA)
- Nutrifood Indonesia
- ABC Kogen Dairy
- Oatly Group
- OmniFoods
- Mayora Indah Tbk
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing Consumer Health and Wellness Awareness
- 4.2.2 Rising Ethical Concerns for Animal Welfare
- 4.2.3 Advances in Product Innovation and Quality
- 4.2.4 Supportive Government Policies and Initiatives
- 4.2.5 Cultural Acceptance of Plant-Based Foods
- 4.2.6 Rise of Food Technology Startups
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Consumer Hesitation over Taste and Texture
- 4.3.2 Challenges in Raw Material Supply Chains
- 4.3.3 Regulatory and Certification Barriers
- 4.3.4 Limited Awareness among Certain Populations
- 4.4 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE and VOLUME)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Meat Substitutes
- 5.1.1.1 Tofu
- 5.1.1.2 Tempeh
- 5.1.1.3 Others
- 5.1.2 Dairy-Alternative Beverages
- 5.1.2.1 Packaged Milk
- 5.1.2.2 Packaged Smoothies
- 5.1.2.3 Coffee
- 5.1.2.4 Tea
- 5.1.2.5 Other Plant-based Beverages
- 5.1.3 Non-Dairy Ice-Cream and Frozen Desserts
- 5.1.4 Non-Dairy Cheese
- 5.1.5 Non-Dairy Yogurt
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.1.1 Meat Substitutes
- 5.2 By Ingredient Source
- 5.2.1 Soy
- 5.2.2 Almond
- 5.2.3 Pea
- 5.2.4 Oat
- 5.2.5 Wheat
- 5.2.6 Rice
- 5.2.7 Coconut
- 5.2.8 Other Sources
- 5.3 By Form
- 5.3.1 Chilled/Shelf-Stable
- 5.3.2 Frozen
- 5.4 By Distribution Channel
- 5.4.1 On-Trade
- 5.4.2 Off-Trade
- 5.4.2.1 Supermarkets / Hypermarkets
- 5.4.2.2 Convenience/Grocery Stores
- 5.4.2.3 Online Retail Stores
- 5.4.2.4 Other Distribution Channels
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 Western Indonesia
- 5.5.2 Eastern Indonesia
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Positioning
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Amy's Kitchen, Inc.
- 6.4.2 Green Rebel Foods
- 6.4.3 Meatless Kingdom
- 6.4.4 Nestle S.A.
- 6.4.5 Danone S.A.
- 6.4.6 Beyond Meat Inc.
- 6.4.7 Impossible Foods Inc.
- 6.4.8 Vitasoy Int'l Holdings
- 6.4.9 Upfield (Violife)
- 6.4.10 Unilever plc
- 6.4.11 The Kraft Heinz Company
- 6.4.12 PepsiCo Inc.
- 6.4.13 Quorn Foods
- 6.4.14 KARANA Foods
- 6.4.15 So Good Food (JAPFA)
- 6.4.16 Nutrifood Indonesia
- 6.4.17 ABC Kogen Dairy
- 6.4.18 Oatly Group
- 6.4.19 OmniFoods
- 6.4.20 Mayora Indah Tbk
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




