PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1934648

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1934648
Smart Transformers - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
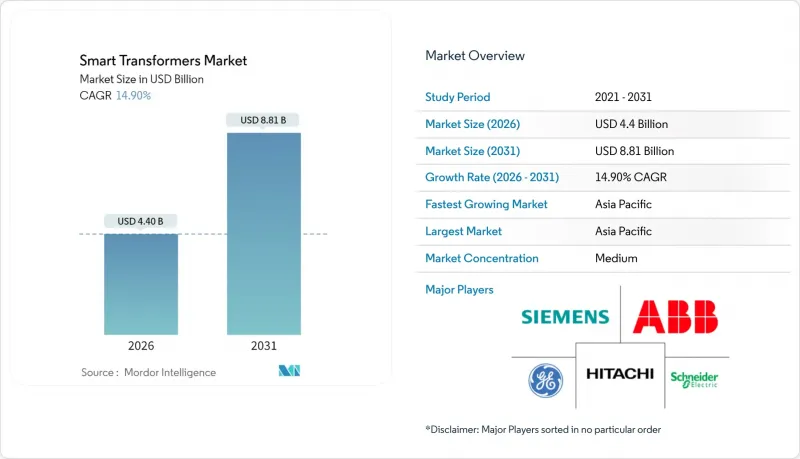
The Smart Transformers Market was valued at USD 3.83 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 4.4 billion in 2026 to reach USD 8.81 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 14.90% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
Demand escalates as utilities replace end-of-life grid assets, integrate volatile renewable generation, and digitize power flows to cut technical losses. Government funding programs, such as the USD 14.5 billion U.S. Grid Resilience and Innovation Partnerships initiative, shorten project timelines while artificial-intelligence-based predictive maintenance tools lift asset utilization and defer new capital outlays. Rising rail-freight electrification and fast-charging corridors widen the addressable base beyond traditional utility spending, and equipment makers gain differentiation through fire-safe natural ester fluids and cyber-secure control platforms.
Global Smart Transformers Market Trends and Insights
Aging Grid Infrastructure Upgrades
More than 70% of installed transformers in advanced economies exceed 25 years of service, prompting utilities to consider intelligent replacements that can handle bidirectional power flows and real-time load shifting. Lead times for large conventional units rose to 210 weeks in 2024, prompting many operators to opt for smart alternatives that increase thermal capacity by up to 40%, postpone substation expansions, and align with long-term resiliency targets.
Renewable-Integration Voltage Volatility
Wind and solar output introduces millisecond-level voltage swings that overwhelm legacy on-load tap changers. Smart transformers equipped with power electronics stabilize voltage more quickly than conventional devices, reduce flicker complaints, and lower the need for standalone STATCOM or capacitor banks, making them central to grids where renewables now account for more than 30% of the energy supply.
High Upfront CAPEX vs. Conventional Units
Price premiums of 40-60% deter procurement teams that evaluate equipment on initial cost rather than lifecycle value. The gap narrows once separate voltage-regulation hardware and monitoring cabinets are factored in, yet financing hurdles persist until transformer-as-a-service contracts become a standard across lenders.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Smart-Grid Funding Surges
- AI-Based Predictive-Maintenance Adoption
- Transformer-Level Cyber-Risk Exposure
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Distribution transformers held 62.40% of 2025 revenue. Their dense placement across feeders makes them primary nodes for voltage regulation, asset-health reporting, and bidirectional power flow. Replacement cycles average 15 years, so utilities integrate sensors and tap logic during scheduled swaps rather than wait for mass failures. The segment's 15.85% CAGR reflects mandated grid-edge digitalization programs in urban areas, where rooftop solar and EV chargers are proliferating. Power transformers serve bulk transmission; although volumes are lower, each unit's value is high, propelling steady capital infusions for fiber-optic temperature probes and digital twins that maximize conductor loading.
Distribution units are increasingly specifying natural ester fluids, which boost fire points above 350 °C and enable indoor placement that reduces real-estate costs. Predictive analytics smooths voltage across secondary networks, preventing nuisance inverter trips and improving customer satisfaction metrics. Utilities apply machine-learning outputs to forecast overload risk and plan reconfiguration, delaying substation expansions. High-voltage power transformers integrate online bushing monitors and dissolved-gas analysers, cutting emergency replacement budgets and aligning with asset-management key performance indicators.
Hardware represented 57.80% of 2025 revenue, yet the smart transformers market now rewards algorithmic differentiation. Vendor roadmaps prioritize edge-based analytics that compress latency and reduce cloud bandwidth. Software grows at a 17.10% CAGR as utilities license modules for topology optimization and cyber-threat hunting. Hardware innovation continues around amorphous metal cores and 3D-printed windings that shrink no-load losses, but margins gravitate toward subscription dashboards and firmware updates.
Services emerge as the third pillar. Operators lacking data-science capacity outsource condition-monitoring centers, converting capital expenditures (capex) into operational expenditures (opex) with multi-year performance guarantees. Manufacturers bundle firmware patches with vulnerability management to satisfy regulators and avoid revenue-threatening cybersecurity fines. Over time, the model shifts from one-off equipment sales toward recurring revenue that hinges on predictive accuracy and SLA adherence.
Transformers below 69 kV claimed 52.20% of 2025 spending and posted a 15.15% CAGR through 2031. Distributed energy resources inject variability at these voltages, requiring rapid tap changes and harmonic mitigation. Sub-transmission (69-138 kV) units link regional loops to feeders, and digital monitors detect geomagnetic-induced current events that would otherwise force manual intervention. High- and extra-high-voltage classes utilize fiber-optic winding probes and online PD sensors, safeguarding assets whose outage costs can run into millions per day.
Distribution-class smart transformers stabilize feeder voltage during clustered fast-charger sessions, easing customer-side inverter tripping and utility penalty exposure. Advanced algorithms coordinate multiple voltage regulators, minimizing step changes that shorten component life. In higher classes, utilities build digital twins to test relay settings virtually, approving load transfers in minutes instead of weeks.
The Smart Transformers Market Report is Segmented by Type (Distribution and Power), Component (Hardware, Software and Analytics, and More), Voltage Class (Distribution, High, and More), Insulation (Oil-Immersed, Solid-State, and More), Phase (Single-Phase and Three-Phase), Rating (Below 500 MVA, and More), Application (Smart Grid, and More), End-User (Utilities, and More), and Geography (North America, Asia-Pacific, and More).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific commanded 43.20% of global revenue in 2025 and posts a 16.45% CAGR to 2031. China's State Grid alone budgets USD 88.7 billion for next-year upgrades that embed ultra-high-voltage smart transformers across its 1,100 kV corridors. India scales feeder automation around 175 GW of new renewable capacity, while Japan fortifies substations against seismic risk with dry-type smart units wired to tsunami-proof battery rooms. South Korea pilots solid-state devices in high-density industrial parks, leveraging local semiconductor supply chains to shorten procurement cycles. ASEAN nations rely on concessional finance to upgrade medium-voltage links, often bundling software analytics training with equipment tenders.
North America ranks second. The U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act unlocks multi-year grants that prioritize cyber-secure smart gear, with California utilities fast-tracking replacements after major wildfire verdicts. Texas targets feeder voltage stability to manage its large wind and solar mix, awarding framework agreements that include transformer-as-a-service clauses. Canada budgets grid-modernization grants for Arctic communities experimenting with microgrids, and Mexico's industrial clusters adopt smart transformers to meet ISO 50001 energy-management certifications.
Europe advances under the Green Deal. Germany accelerates renewable interconnections, specifying natural-ester-filled units for urban substations. France retrofits distribution transformers with IoT sensors to smooth voltage along heat-pump-heavy residential streets. The United Kingdom deploys digital twins across National Grid substations, reducing planned outage durations. Southern and Eastern European members secure cohesion funds for rail electrification, thereby bolstering demand for solid-state transformers.
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- Hitachi Energy Ltd.
- Schneider Electric SE
- General Electric Company
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions
- CG Power & Industrial Solutions Ltd.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Hyundai Electric & Energy Systems Co., Ltd.
- Hyosung Heavy Industries
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL)
- SPX Transformer Solutions, Inc.
- KONCAR - Electrical Industry Inc.
- TBEA Co., Ltd.
- SGB-SMIT Group
- Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
- WEG Group (Transformers Unit)
- JiangSu Huapeng Transformer Co., Ltd.
- Maschinenfabrik Reinhausen GmbH
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Aging grid infrastructure upgrades
- 4.2.2 Renewable-integration voltage volatility
- 4.2.3 Government smart-grid funding surges
- 4.2.4 AI-based predictive-maintenance adoption
- 4.2.5 Cyber-secure substation mandates
- 4.2.6 Rail electrification of freight corridors
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront CAPEX vs. conventional units
- 4.3.2 Transformer-level cyber-risk exposure
- 4.3.3 SiC device supply shortages
- 4.3.4 Certification bottlenecks in utility specs
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products & Services
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Distribution Transformers
- 5.1.2 Power Transformers
- 5.2 By Component
- 5.2.1 Hardware
- 5.2.2 Software and Analytics
- 5.2.3 Services
- 5.3 By Voltage Class
- 5.3.1 Distribution (Below 69 kV)
- 5.3.2 Sub-Transmission (69 to 138 kV)
- 5.3.3 High (138 to 345 kV)
- 5.3.4 Extra-High/Ultra (Above 345 kV)
- 5.4 By Insulation
- 5.4.1 Oil-Immersed
- 5.4.2 Dry-Type
- 5.4.3 Solid-State/Power-Electronics-Based
- 5.5 By Phase
- 5.5.1 Single-Phase
- 5.5.2 Three-Phase
- 5.6 By Rating (MVA)
- 5.6.1 Below 500 MVA (Low)
- 5.6.2 501 to 800 MVA (Medium)
- 5.6.3 801 to 1200 MVA (High)
- 5.7 By Application
- 5.7.1 Smart Grid
- 5.7.2 Traction Locomotive
- 5.7.3 EV Fast-Charge Infrastructure
- 5.7.4 Industrial Power-Quality Systems
- 5.7.5 Others
- 5.8 By End-User
- 5.8.1 Utilities
- 5.8.2 Commercial and Industrial
- 5.8.3 Residential
- 5.9 By Geography
- 5.9.1 North America
- 5.9.1.1 United States
- 5.9.1.2 Canada
- 5.9.1.3 Mexico
- 5.9.2 Europe
- 5.9.2.1 Germany
- 5.9.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.9.2.3 France
- 5.9.2.4 Italy
- 5.9.2.5 Russia
- 5.9.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.9.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.9.3.1 China
- 5.9.3.2 India
- 5.9.3.3 Japan
- 5.9.3.4 South Korea
- 5.9.3.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.9.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.9.4 South America
- 5.9.4.1 Brazil
- 5.9.4.2 Argentina
- 5.9.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.9.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.9.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.9.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.9.5.3 South Africa
- 5.9.5.4 Egypt
- 5.9.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.9.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ABB Ltd.
- 6.4.2 Siemens AG
- 6.4.3 Hitachi Energy Ltd.
- 6.4.4 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.4.5 General Electric Company
- 6.4.6 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 6.4.7 Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions
- 6.4.8 CG Power & Industrial Solutions Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Eaton Corporation plc
- 6.4.10 Hyundai Electric & Energy Systems Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Hyosung Heavy Industries
- 6.4.12 Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL)
- 6.4.13 SPX Transformer Solutions, Inc.
- 6.4.14 KONCAR - Electrical Industry Inc.
- 6.4.15 TBEA Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.16 SGB-SMIT Group
- 6.4.17 Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.18 WEG Group (Transformers Unit)
- 6.4.19 JiangSu Huapeng Transformer Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.20 Maschinenfabrik Reinhausen GmbH
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




