PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1937362

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1937362
Frozen Vegetables - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Frozen Vegetables market is expected to grow from USD 20.37 billion in 2025 to USD 21.51 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 28.29 billion by 2031 at 5.62% CAGR over 2026-2031.
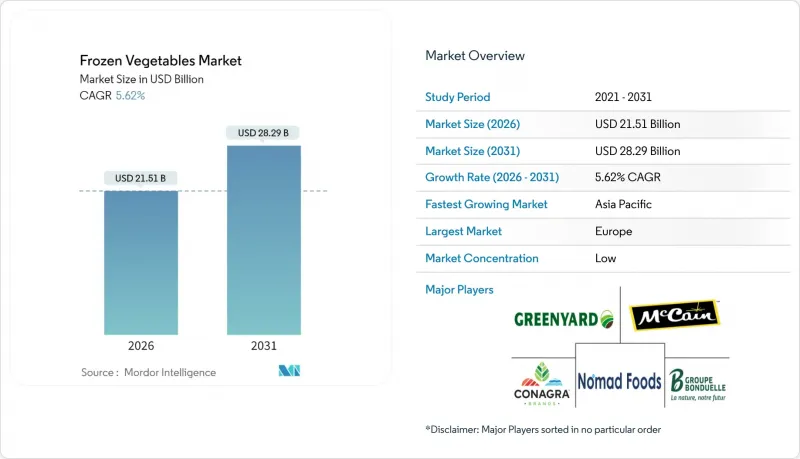
The market's expansion is fueled by increasing demand for convenient meal options, the growth of cold-chain infrastructure, and the rising popularity of plant-based diets. Innovations such as Individual Quick Freezing (IQF) and improved packaging technologies are critical in preserving the quality, flavor, and nutritional content of frozen vegetables. In addition to convenience, frozen vegetables ensure a reliable supply, offer extended shelf life, and contribute significantly to reducing food waste, aligning with global goals for food security and sustainability. Established manufacturers capitalize on vertical integration to achieve scale advantages, while emerging brands focus on direct-to-consumer approaches and sustainability-driven messaging to establish niche positions. Moreover, advancements in energy-efficient refrigeration, isochoric freezing, and AI-powered inventory systems enhance product quality and reduce operational costs, supporting profitability despite volatile energy prices. Regionally, Europe demonstrates mature consumption trends, while the Asia-Pacific region, driven by rapid urbanization, is poised to become the primary growth driver for the frozen vegetable market over the next decade.
Global Frozen Vegetables Market Trends and Insights
Convenience-driven meal preparation
Busy households are increasingly focusing on time-saving solutions without compromising nutritional quality, driving changes in frozen vegetable consumption patterns. This shift is driven by urbanization and the demands of dual-income families, resulting in a growing preference for ready-to-cook vegetable options. Conagra Brands' 2025 frozen food report highlights that frozen meals account for 32% of total frozen sales, with younger generations advocating for a broader range of options, including global cuisines and healthier alternatives. The rising adoption of air fryers has further accelerated this trend, demonstrating how frozen vegetables can deliver restaurant-quality results with minimal effort. Deep freezing extends the shelf life of vegetables well beyond that of fresh produce, reducing shopping frequency and minimizing spoilage. The German Frozen Food Institute reported that Germany's sales volume of deep-frozen vegetables reached 522,180 tons in 2024 . Additionally, advanced freezing technologies, such as Individual Quick Freezing (IQF), maintain the texture and nutritional content of vegetables, addressing previous consumer concerns about quality degradation that once limited the adoption of frozen vegetables.
Expansion of modern cold-chain infrastructure
Infrastructure modernization in emerging markets is establishing a strong foundation for the growth of the frozen vegetable market. Governments are increasingly focusing on cold chain development, recognizing its importance in ensuring food security and adding value to agriculture. In China, efforts to diversify the food supply include integrating cold chain logistics to minimize post-harvest losses and improve food distribution efficiency. In the United States, the cold storage market is expanding, driven by the growth of e-commerce and the implementation of automated storage solutions. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the volume of frozen vegetables in U.S. cold storage facilities reached 2,234.26 million pounds in 2024 . Technological advancements, such as AI-driven predictive analytics and IoT monitoring systems, are enhancing cold chain management by improving operational efficiency and reducing energy consumption. This infrastructure development is enabling market access in previously underserved regions, particularly in the Asia-Pacific, where cold chain investments are supporting agricultural modernization initiatives.
Volatile energy and refrigerant costs
Frozen vegetable operations grapple with energy cost volatility, which affects cold storage, transportation, and processing expenses, ultimately squeezing profit margins and influencing pricing strategies. Starting January 2029, the U.S. Department of Energy's new energy conservation standards for commercial refrigeration equipment will mandate significant capital investments for compliance, though they may lead to reduced operational costs in the long run. Under the EPA's Significant New Alternatives Policy program, refrigerant regulations impose compliance costs as firms shift to eco-friendly alternatives in retail food refrigeration and cold storage. Companies with vast cold chain networks face planning hurdles due to energy price fluctuations, necessitating advanced hedging strategies and operational agility to stay competitively priced.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing popularity of plant-based, vegetarian, and vegan diets
- Long shelf life and reduced food wastage
- Stringent regulatory restrictions on food safety
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Peas generated 34.72% of frozen vegetable market revenue in 2025, driven by their strong household familiarity and the cost efficiency of mechanical harvesting. Western Europe favors pea-based side dishes, while North Americans incorporate peas into mixed-vegetable options for children's menus, supporting baseline volumes. Broccoli, benefiting from its 'superfood' reputation and versatility in stir-fries and microwave steam bags, achieved the highest CAGR at 8.2%. The frozen vegetable market is increasingly targeting health-conscious consumers seeking antioxidant-rich products. Secondary categories, including corn, cauliflower, spinach, mushrooms, and asparagus, are experiencing steady growth due to greater recipe variety and the popularity of premium frozen meal kits. To cater to low-carb diet preferences, product developers are emphasizing riced cauliflower and spiralized zucchini, creating additional revenue opportunities without undermining core product segments.
Demand variations influence sourcing strategies: peas are primarily sourced through contract farming in the temperate regions of Belgium and the U.K. Conversely, broccoli and asparagus sourcing is shifting towards China and Peru to synchronize harvest schedules with processing operations. Risk management teams are expanding grower networks to mitigate regional climate risks. Premium innovations such as value-added glazing, light seasoning, and microwavable pouches are commanding higher price points, helping to counterbalance rising raw material costs. Consequently, the frozen vegetable market demonstrates strong margin resilience despite fluctuations in commodity prices.
The Global Frozen Vegetable Market Report is Segmented by Vegetable Type (Beans, Corn, Peas, Broccoli, Cauliflower, and More), Nature (Organic, Conventional), Distribution Channel (Supermarkets/Hypermarkets, Convenience Store, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Tons).
Geography Analysis
Europe maintains 34.06% of the frozen vegetable market revenue in 2025, driven by established consumption patterns, strict safety standards, and a robust refrigerated logistics network. European consumers increasingly prefer convenient, healthy, and sustainable food options. Frozen vegetables meet this demand with their year-round availability and preserved nutritional content. The growing adoption of plant-based diets, vegetarianism, and clean-label products further boosts demand for these nutrient-rich frozen offerings. Belgium leads in exports, primarily shipping IQF peas and mixed vegetables across the European bloc. While Germany, France, and the U.K. exhibit high household penetration rates, future growth hinges on organic, low-salt, and value-added product formats. Rising sustainability expectations are prompting the industry to adopt lighter packaging, driving research and development into recyclable mono-material pouches.
Asia-Pacific is projected to achieve a strong 5.85% CAGR through 2031, leading global market growth. In China, cold-chain modernization is a priority, supported by public-private joint ventures. These efforts enhance rural-to-urban distribution efficiency and strengthen national food security objectives. Domestic processors in China are increasingly competing with European exporters by promoting locally sourced products like broccoli, corn, and spinach, appealing to patriotic consumption trends. In India, states such as Gujarat and Maharashtra are expanding IQF capacity to meet the growing demand from quick-service restaurants in tier-1 and tier-2 cities. Meanwhile, Japan is attracting affluent consumers with premium frozen sushi and bento innovations, offering convenience without compromising traditional flavors.
North America is experiencing steady growth in the frozen vegetable market. Investments in automated cold warehouses, particularly in the Midwest and Gulf Coast, aim to address labor shortages and reduce energy consumption. Canada's compliance with U.S. traceability regulations simplifies cross-border supply chains. At the same time, Mexico is increasing vegetable production through protected agriculture, enhancing input availability. Processors are also diversifying sourcing strategies in response to climate challenges, such as droughts impacting yields in California. This includes a shift toward controlled-environment farms and greenhouse complexes. South America, along with the Middle East and Africa, presents emerging opportunities. In Brazil, the rise of economic supermarket formats is driving domestic frozen vegetable consumption, catering to busy urban professionals. In the United Arab Emirates, the Jebel Ali re-export hub facilitates the distribution of frozen vegetables from Europe and Asia across the Gulf, with food-service channels dominating demand. However, challenges such as cold-chain inefficiencies and power-grid instability persist. Government subsidies and solar-powered warehouses are gradually addressing these issues, unlocking the region's potential.
- Conagra Brands Inc
- Bonduelle S.A.
- Greenyard NV
- General Mills Inc.
- Nomad Foods (Birds Eye)
- McCain Foods Limited
- Pictsweet Farms
- Ardo NV
- Dole plc
- Earthbound Farm
- Mother Dairy Fruit and Vegetable
- ITC Ltd.
- Vivartia Holdings
- Al-Kabeer Group
- Hortex Holding
- Agrarfrost GmbH
- Simplot Company
- Hanamaru Foods
- Frosta AG
- SunOpta Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Convenience-driven meal preparation
- 4.2.2 Expansion of modern cold-chain infrastructure
- 4.2.3 Growing popularity of plant-based, vegetarian, and vegan diets
- 4.2.4 Long shelf life and reduced food wastage
- 4.2.5 Expansion of organized retail and e-commerce channels
- 4.2.6 Growing awareness of nutrition retention and safety standards
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Volatile energy and refrigerant costs
- 4.3.2 Stringent regulatory restrictions on food safety
- 4.3.3 Limited consumer awareness
- 4.3.4 Risk of product spoilage and quality degradation
- 4.4 Consumer Behaviour Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE AND VOLUME)
- 5.1 By Vegetable Type
- 5.1.1 Beans
- 5.1.2 Corn
- 5.1.3 Peas
- 5.1.4 Broccoli
- 5.1.5 Cauliflower
- 5.1.6 Mushroom
- 5.1.7 Asparagus
- 5.1.8 Spinach
- 5.1.9 Other Vegetable Types
- 5.2 By Nature
- 5.2.1 Organic
- 5.2.2 Conventional
- 5.3 By Distribution Channel
- 5.3.1 Supermarkets / Hypermarkets
- 5.3.2 Convenience Store
- 5.3.3 Specialty Store
- 5.3.4 Online Retail Store
- 5.3.5 Other Distribution Channels
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Colombia
- 5.4.2.4 Chile
- 5.4.2.5 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.2 Germany
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.4.3.6 Russia
- 5.4.3.7 Sweden
- 5.4.3.8 Belgium
- 5.4.3.9 Poland
- 5.4.3.10 Netherlands
- 5.4.3.11 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4.1 China
- 5.4.4.2 Japan
- 5.4.4.3 India
- 5.4.4.4 Thailand
- 5.4.4.5 Singapore
- 5.4.4.6 Indonesia
- 5.4.4.7 South Korea
- 5.4.4.8 Australia
- 5.4.4.9 New Zealand
- 5.4.4.10 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.4.5.5 Egypt
- 5.4.5.6 Morocco
- 5.4.5.7 Turkey
- 5.4.5.8 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Conagra Brands Inc
- 6.4.2 Bonduelle S.A.
- 6.4.3 Greenyard NV
- 6.4.4 General Mills Inc.
- 6.4.5 Nomad Foods (Birds Eye)
- 6.4.6 McCain Foods Limited
- 6.4.7 Pictsweet Farms
- 6.4.8 Ardo NV
- 6.4.9 Dole plc
- 6.4.10 Earthbound Farm
- 6.4.11 Mother Dairy Fruit and Vegetable
- 6.4.12 ITC Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Vivartia Holdings
- 6.4.14 Al-Kabeer Group
- 6.4.15 Hortex Holding
- 6.4.16 Agrarfrost GmbH
- 6.4.17 Simplot Company
- 6.4.18 Hanamaru Foods
- 6.4.19 Frosta AG
- 6.4.20 SunOpta Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




