PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1937417

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1937417
United Kingdom Car Loan - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The United Kingdom car loan market is expected to grow from USD 77.73 billion in 2025 to USD 81.08 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 100.21 billion by 2031 at 4.32% CAGR over 2026-2031.
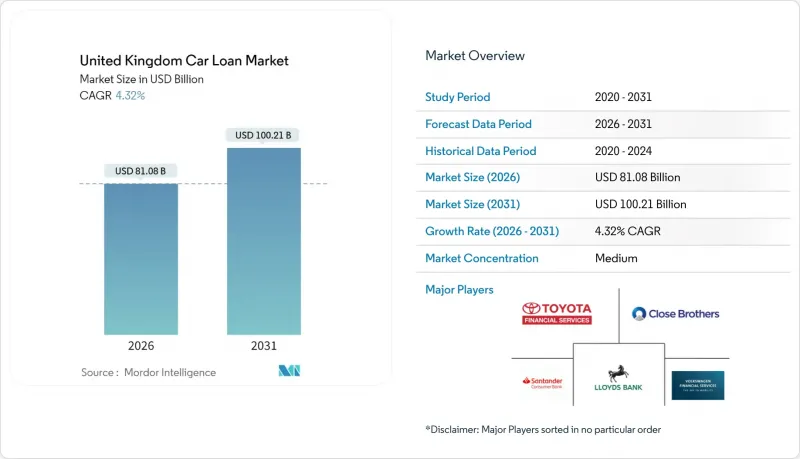
Demand remains resilient as court clarity on dealer commissions calms regulatory risk and the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) advances a sector-wide redress framework. Digitization accelerates underwriting speeds, while agency-model rollouts let original-equipment-manufacturer (OEM) captives recapture finance margins. Electric-vehicle (EV) financing expands in response to the Zero Emission Vehicle (ZEV) mandate, yet volatile used-EV values compel tighter loan-to-value ratios. Fintech entrants armed with alternative credit engines widen access for near-prime applicants, intensifying competition against incumbent banks and dealer-led point-of-sale (POS) channels.
United Kingdom Car Loan Market Trends and Insights
Digitised Point-of-Sale Platforms Accelerate Dealer-Originated Approval Times
Automated decisioning now delivers 80% of approvals inside 60 seconds, shrinking proposal-to-payout intervals for more than 4,000 dealer forecourts. Technology investments by Evolution Funding, Close Brothers, and MotoNovo raise average dealer conversion rates to 40% from prior 28% levels. API links with classifieds portals give lenders real-time vehicle-demand insights, sharpening risk-based pricing. The FCA's Consumer Duty framework incentivizes further digitization because automated systems evidence fair treatment. Independent dealers gain access to sophisticated underwriting once reserved for franchised groups, narrowing competitive gaps. Electronic signatures and remote onboarding remove geographic barriers, letting rural retailers match urban finance performance.
Growing Adoption of Green-EV Finance Products Tied to the ZEV Mandate
The ZEV mandate compels 22% EV sales in 2024, rising to 80% by 2030, spurring lenders to launch battery-specific products. Close Brothers pledged GBP 1 billion for battery-electric-vehicle lending over five years. Residual-value swings used EVs retain only 46% of cost versus 85% two years earlier, forcing lenders to recalibrate risk capital. BNP Paribas's partnership with Jaguar Land Rover bundles charging, energy, and lifecycle services, illustrating integrated mobility finance. Government tariff waivers and full-expensing allowances add policy certainty, lengthening loan tenors acceptable to risk committees. Fleet salary-sacrifice schemes multiply because tax advantages offset depreciation anxiety for corporate buyers.
Potential GBP 9-18 Billion Redress Over Legacy Discretionary-Commission Cases
FCA review findings expose lenders to as much as GBP 18 billion in compensation liabilities, prompting Lloyds to provision GBP 1.25 billion already. Close Brothers forecasts GBP 10-15 million yearly compliance costs, constraining lending appetite. This coming October 2025 consultation could mandate repayments on contracts dating to 2007, freezing expansion plans until capital buffers strengthen. Smaller brokers have existed, reducing product choice and denting competition. Securitization and asset sales shore up capital but elevate funding costs, widening price gaps against fintech rivals. Dividends remain suspended at several banks, signaling defensive priorities.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- OEM Deposit-Subsidy Campaigns Amid Agency-Model Rollouts
- Fleet Electrification Boosting Salary-Sacrifice and Contract-Hire Demand
- Rising Used-EV Residual-Value Volatility Inflates Lender Risk Capital
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Non-captive banks controlled 40.12% of the United Kingdom car loan market in 2025, leveraging long-standing dealer ties and diversified funding. Yet non-banking financial services post the fastest 4.83% CAGR as platforms like Carmoola secure GBP 300 million securitizations to scale originations. Challenger lenders deploy open-banking data and behavioral analytics to price near-prime risk, compressing approval times to minutes. Traditional institutions counter with API upgrades and co-origination agreements, but legacy systems slow feature deployment. The FCA's uniform disclosure rules narrow differentiation that once favored high-street banks, nudging customers toward digital specialists.
The United Kingdom car loan industry nonetheless remains relationship-driven; POS dealers still originate most bank submissions. Regulatory capital resilience gives banks room to absorb redress costs, sustaining underwriting capacity during turbulence. Captive arms of OEMs integrate finance into online configurators, improving customer stickiness even as overall share lags volume lenders. Peer-to-peer platforms serve thin-file borrowers but face scaling limits from retail-investor funding. Consolidation may see capital-strong banks acquiring high-growth fintechs to blend cost efficiency with brand trust.
The United Kingdom Car Loan Market Report is Segmented by Loan Provider Type (Non-Captive Banks, Non-Banking Financial Services, Original Equipment Manufacturers Captives, Other Providers), Vehicle Type (New Car, Used Car), Distribution Channel (Dealership Point-Of-Sale, Online Direct Lending, Brokers & Marketplaces), and Geography (United Kingdom Regional Analysis). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Lloyds Banking Group (Black Horse)
- Volkswagen Financial Services UK
- Santander Consumer (UK)
- Close Brothers Motor Finance
- Toyota Financial Services UK
- Ford Credit Europe (UK)
- Stellantis Financial Services UK
- BMW Financial Services GB
- Mercedes-Benz Financial Services UK
- Barclays Partner Finance
- MotoNovo Finance
- Oodle Car Finance
- First Response Finance
- Startline Motor Finance
- CA Auto Finance UK
- Hitachi Capital Motor Finance
- RateSetter (Car Loan)
- Zuto
- CarFinance 247
- Funding Circle Vehicle Finance
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Table of Contents - United Kingdom Car Loan Market
2 Introduction
- 2.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 2.2 Scope of the Study
3 Research Methodology
4 Executive Summary
5 Market Landscape
- 5.1 Market Overview
- 5.2 Market Drivers
- 5.2.1 Digitised point-of-sale (POS) platforms accelerate dealer-originated approval times
- 5.2.2 Growing adoption of "green-EV" finance products tied to UK ZEV mandate incentives
- 5.2.3 OEM deposit-subsidy campaigns amid agency-model roll-outs
- 5.2.4 Fleet electrification boosting salary-sacrifice & contract-hire demand
- 5.2.5 FCA-driven commission disclosure rules increasing migration to fixed-rate loans
- 5.2.6 Alternative credit-risk engines (open-banking & bureau-API) widen near-prime access
- 5.3 Market Restraints
- 5.3.1 Potential £9-18 bn redress over legacy discretionary-commission cases
- 5.3.2 Rising used-EV residual-value volatility inflates lender RV risk capital
- 5.3.3 Stricter affordability rules under Consumer Duty curb sub-prime approval rates
- 5.3.4 Bank funding-cost spikes widen pricing gap vs. captives & fintech lenders
- 5.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 5.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 5.6 Technological Outlook
- 5.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 5.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 5.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 5.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
6 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 6.1 By Loan Provider Type (Value)
- 6.1.1 Non-Captive Banks
- 6.1.2 Non-banking Financial Services
- 6.1.3 Original Equipment Manufacturers (Captives)
- 6.1.4 Other Providers
- 6.2 By Vehicle Type (Value)
- 6.2.1 New Car
- 6.2.2 Used Car
- 6.3 By Distribution Channel (Value)
- 6.3.1 Dealership Point-of-Sale
- 6.3.2 Online Direct Lending
- 6.3.3 Brokers & Marketplaces
7 Competitive Landscape
- 7.1 Market Concentration
- 7.2 Strategic Moves
- 7.3 Market Share Analysis
- 7.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 7.4.1 Lloyds Banking Group (Black Horse)
- 7.4.2 Volkswagen Financial Services UK
- 7.4.3 Santander Consumer (UK)
- 7.4.4 Close Brothers Motor Finance
- 7.4.5 Toyota Financial Services UK
- 7.4.6 Ford Credit Europe (UK)
- 7.4.7 Stellantis Financial Services UK
- 7.4.8 BMW Financial Services GB
- 7.4.9 Mercedes-Benz Financial Services UK
- 7.4.10 Barclays Partner Finance
- 7.4.11 MotoNovo Finance
- 7.4.12 Oodle Car Finance
- 7.4.13 First Response Finance
- 7.4.14 Startline Motor Finance
- 7.4.15 CA Auto Finance UK
- 7.4.16 Hitachi Capital Motor Finance
- 7.4.17 RateSetter (Car Loan)
- 7.4.18 Zuto
- 7.4.19 CarFinance 247
- 7.4.20 Funding Circle Vehicle Finance
8 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 8.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




