PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939039

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939039
Asia-Pacific Gas Turbine MRO - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
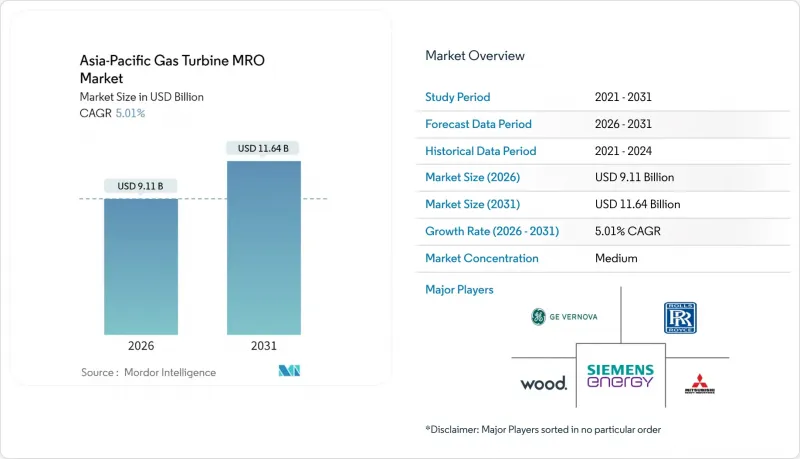
The Asia-Pacific Gas Turbine MRO Market was valued at USD 8.68 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 9.11 billion in 2026 to reach USD 11.64 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 5.01% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
Heightened overhaul activity as fleets age, rapid adoption of hydrogen-ready upgrade kits, and large-scale digital twin roll-outs anchor near-term demand. Independent service providers are expanding parts-manufacturer-approval (PMA) portfolios, lowering overhaul costs for operators that face capital constraints. Supply-chain bottlenecks in hot-section castings are prompting utilities to dual-source critical components, spurring regional investments in foundry capacity. Meanwhile, switch-overs from coal to gas in China and India underpin long-term service-agreement (LTSA) signings, locking in multi-year maintenance revenues. Finally, exponential data-center electricity demand pushes aeroderivative shop visits sharply higher, widening the addressable service pool for high-availability, quick-start units.
Asia-Pacific Gas Turbine MRO Market Trends and Insights
Aging APAC turbine fleet approaching 100 k EOH overhaul threshold
Thousands of units installed during the 2000s industrial boom are now hitting the 100,000 EOH mark, a milestone that compels full hot-gas-path refurbishment. Operators in China and India face overhaul bills ranging between 19% and 33% of new-build cost, an outlay many curb by deploying reverse-engineering and remaining-life-extension techniques that postpone capital replacement. Independent service firms specialising in rotor life rebuilds secure new work as asset owners pursue cost-effective alternatives to OEM programs.
Coal-to-gas shift in China & India drives new LTSA signings
Although gas produced just 3% of China's 2024 power, Beijing inked 27 million t per year LNG contracts to underpin its transition strategy. Generators respond by locking in 6- to 12-year LTSAs that stabilise maintenance cash flows and guarantee availability metrics that grids increasingly demand. A parallel pattern emerges in India as market liberalisation pushes state-run and private utilities toward bundled service deals featuring performance guarantees.
Renewable intermittency curtails baseload run-hours
As solar and wind capacity climbs, combined-cycle gas turbines increasingly swing from baseload to cycling duty. Frequent start-stops elevate thermal stresses, amplifying component fatigue and reshaping spares demand profiles toward more combustor and seal replacements relative to long-life rotors.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- OEM digital twins slash unplanned outages by >15%
- Data-center peaker demand spikes aeroderivative shop visits
- Global hot-section casting shortage inflates spare-part lead times
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Gas turbines rated above 120 MW now account for 51.78 % of Asia-Pacific's MRO spend and are expanding fastest at 5.52 % a year. Operators value these big machines for their scale economies and high thermal efficiency, which keeps unit-cost electricity low even as fuel prices fluctuate. Thailand's 5,300 MW complex, built around eight M701JAC units, illustrates the trend; those machines have already logged 100,000 operating hours while holding efficiency near 64 %. Below-120 MW turbines still matter, especially for cogeneration, distributed generation, and peaking duty in rapidly industrializing ASEAN nations, but their growth pace lags. Overhauls on large units fall every 24,000-30,000 hours and typically cost 19 %-33 % of a new machine, yet operators increasingly offset that expense by ordering hydrogen-ready upgrades that preserve efficiency while cutting emissions.
Combined-cycle plants generate 68.42 % of regional MRO revenue and should rise 5.88 % annually through 2031. The draw is simple: pairing a gas turbine with a steam bottoming cycle pushes thermal efficiency beyond 64 %, far better than a simple-cycle setup. Recent builds, China's Guangming project among them, show how these plants can co-fire hydrogen without major design changes, supporting decarbonization plans while preserving grid flexibility. Simple-cycle units still fill niche roles where fast starts and lower capital cost outweigh fuel burn, but they attract less long-term service revenue. Combined-cycle operators lean heavily on six- to twelve-year service agreements that bundle parts, labor, and performance guarantees-arrangements that simplify budgeting and sharpen availability targets.
The Asia-Pacific Gas Turbine MRO Market Report is Segmented by Capacity (Below 30 MW, 31 To 120 MW, and Above 120 MW), Turbine Cycle (Combined Cycle and Open/Simple Cycle), Service Type (Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul), End-User Industry (Power Generation, Oil and Gas, and Industrial and Other), and Geography (China, India, Japan, South Korea, ASEAN Countries, Australia and New Zealand, and Rest of Asia-Pacific).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- General Electric (GE Vernova)
- Siemens Energy
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Rolls-Royce
- MTU Aero Engines
- John Wood Group
- EthosEnergy
- Ansaldo Energia
- Sulzer
- Doosan Enerbility
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- Harbin Electric
- Shanghai Electric
- Toshiba Energy Systems
- Bharat Heavy Electricals (BHEL)
- Power Machines
- Fluor
- Bechtel
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Wartsila
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Aging APAC turbine fleet approaching 100k EOH overhaul threshold
- 4.2.2 Coal-to-gas shift in China & India drives new LTSA signings
- 4.2.3 OEM digital twins slash unplanned outages by >15 %
- 4.2.4 Data-center peaker demand spikes aeroderivative shop visits
- 4.2.5 Hydrogen-ready upgrade kits trigger mid-life inspections
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Renewable intermittency curtails baseload run-hours
- 4.3.2 Global hot-section casting shortage inflates spare-part lead times
- 4.3.3 Skilled?technician gap widens in ASEAN
- 4.3.4 PMA parts disrupt OEM warranty economics
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Capacity
- 5.1.1 Below 30 MW
- 5.1.2 31 to 120 MW
- 5.1.3 Above 120 MW
- 5.2 By Turbine Cycle
- 5.2.1 Combined Cycle
- 5.2.2 Open/Simple Cycle
- 5.3 By Service Type
- 5.3.1 Maintenance
- 5.3.2 Repair
- 5.3.3 Overhaul
- 5.4 By End-user Industry
- 5.4.1 Power Generation
- 5.4.2 Oil and Gas (Up-/Mid-/Down-stream)
- 5.4.3 Industrial and Other
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 China
- 5.5.2 Japan
- 5.5.3 India
- 5.5.4 South Korea
- 5.5.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.5.6 Australia and New Zealand
- 5.5.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 General Electric (GE Vernova)
- 6.4.2 Siemens Energy
- 6.4.3 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- 6.4.4 Rolls-Royce
- 6.4.5 MTU Aero Engines
- 6.4.6 John Wood Group
- 6.4.7 EthosEnergy
- 6.4.8 Ansaldo Energia
- 6.4.9 Sulzer
- 6.4.10 Doosan Enerbility
- 6.4.11 Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- 6.4.12 Harbin Electric
- 6.4.13 Shanghai Electric
- 6.4.14 Toshiba Energy Systems
- 6.4.15 Bharat Heavy Electricals (BHEL)
- 6.4.16 Power Machines
- 6.4.17 Fluor
- 6.4.18 Bechtel
- 6.4.19 MAN Energy Solutions
- 6.4.20 Wartsila
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




