PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939128

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939128
Data Center Cooling - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2032)
The data center cooling market was valued at USD 10.80 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 12.41 billion in 2026 to reach USD 28.54 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 14.90% during the forecast period (2026-2032).
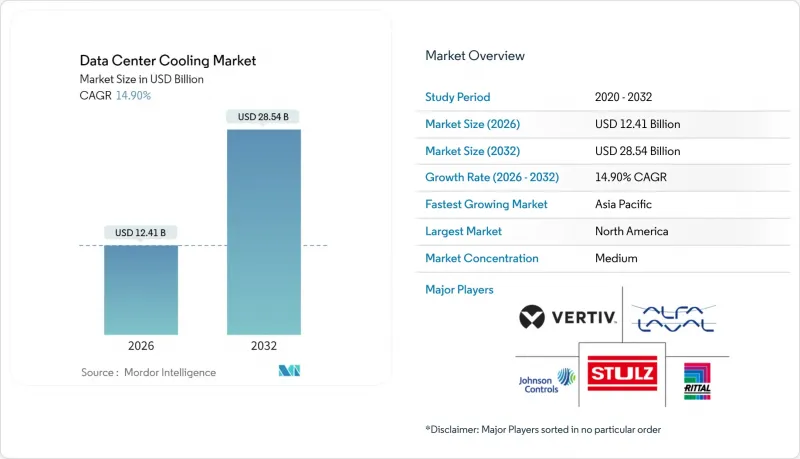
Ongoing migration from air-based to liquid-based thermal systems underpins this expansion, while hyperscale build-outs, AI chip heat loads and low-GWP refrigerant mandates reinforce near-term purchasing momentum. Liquid solutions already claim a 46% data center cooling market share, and their 17.50% CAGR through 2031 signals lasting preference for direct-to-chip and immersion architectures. Hyperscale operators represent the single largest demand node, yet edge and micro-site deployments now post the fastest growth at 18.00% as 5G densifies rural networks. Geographically, North America contributes 76% of spending, but Asia-Pacific's 18.20% CAGR highlights accelerating spend in Singapore, China and Japan, where high-density designs offset land constraints. Competitive dynamics intensified in 2024-2025: Johnson Controls divested USD 8.1 billion of HVAC assets to Bosch to double down on data center-specific chillers, and Schneider Electric added immersion specialist Motivair to its portfolio, signaling a strategic pivot toward liquid engineering.
Global Data Center Cooling Market Trends and Insights
AI and HPC workload heat-density surge
GPU-dense servers now dissipate beyond 200 kW per rack, dwarfing legacy 10 kW envelopes and rendering conventional CRAC units ineffective. Direct-to-chip cold plates and full-immersion baths have therefore moved from pilots to production floors, particularly inside Meta and Microsoft AI clusters. Chipmakers embed liquid interface channels in next-generation packages, eroding the barrier between compute silicon and facility infrastructure Regulatory bodies simultaneously push PUE below 1.3, creating a dual-pressure environment that favors liquid technologies.
Hyperscale footprint expansion in secondary metros
Operators chase lower land costs and cleaner power in Phoenix, Columbus and Osaka, but those locations often lack mature utility infrastructure. As a result, projects specify modular chillers and rear-door heat exchangers that shorten commissioning cycles and tolerate wide ambient swings. Secondary-city climates also grant more free-air hours, lowering lifecycle cost metrics that drive board-level cap-ex approvals.
Cap-ex premium of advanced liquid technologies
Immersion tanks cost 60% more than traditional hot-aisle containment, and specialized dielectric fluids range USD 5-7 per liter, challenging ROI in sites below 2 MW. Nevertheless, energy savings of 30-40% compress payback to under three years in high-electricity-tariff regions.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Mandatory PUE / GHG disclosure regulations
- Global heat-wave frequency raising cooling demand
- Retrofit complexity in legacy white-spaces
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The data center cooling market size for liquid methods reached USD 5.90 billion in 2026 and will eclipse USD 15.33 billion by 2032, advancing at 17.25% CAGR. Direct-to-chip pipelines dominate new AI racks, while dual-phase immersion tubs claim niche workloads such as crypto hashing clusters. Air-based chiller and CRAC arrays remain common in enterprise environments where rack densities linger below 15 kW, yet their share declines annually as regulations squeeze PUE targets. Vendors counter with hybrid coolers marrying glycol loops and adiabatic pads to extend free-cooling seasons.
Rear-door heat exchangers bridge the gap for operators unwilling to re-rack entire halls; a single exchanger lifts rack capacity from 12 kW to 30 kW without floor welding. Meanwhile, patents on microconvective cold plates promise 350 W/cm2 heat flux removal, foreshadowing liquid's march into mainstream x86 servers. Edge enclosures import factory-sealed coolant modules to slash on-site labor, aligning with unmanned operation mandates.
Computer-room air handlers still account for 30.60% of spend, but their 3.75% CAGR lags the overall data center cooling market. Conversely, chillers and heat-exchanger units will log 15.70% CAGR as liquid adoption expands pipework demand. Pumps, valves and redundancy manifolds form a USD 1.95 billion submarket in 2026, benefitting from direct-to-chip loop proliferation. AI-driven supervisory software posts the fastest growth, trimming fan RPM and compressor staging to save 15-25% energy at Google and Alibaba campuses. Integrated suites that blend hardware, telemetry and machine-learning controls command premium pricing yet deliver quantifiable OPEX reduction, convincing CFOs faster than standalone consoles.
Data Center Cooling Market is Segmented by Cooling Technology (Air-Based Cooling, Liquid-Based Cooling), Cooling Component (Computer-Room Air Handlers (CRAH/CRAC), Chillers and Heat-Exchanger Units, and More), Data Center Type (Hyperscale, Enterprise, Colocation), End-User Industry (IT and Telecom, Retail and Consumer Goods, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America recorded USD 9.35 billion of data center cooling market size in 2026, driven by hyperscale campuses in Phoenix, Atlanta and Columbus that favor liquid chillers able to exploit reclaimed wastewater for condenser loops. Extended summer heat waves shorten free-air windows, prompting operators to add adiabatic trim coolers for resilience.
Asia-Pacific contributed USD 1.73 billion in 2026 but will surpass USD 4.64 billion by 2032 on an 17.85% CAGR. Singapore reinstated new-build permits contingent on sub-1.3 PUE targets, steering bids toward seawater and liquid immersions. Tokyo's densification strategy stacks multi-story halls using direct-expansion coils for each floor, while Mumbai's coastal humidity inclines projects toward hybrid fluid coolers that mitigate water scarcity.
Europe generated USD 1.14 billion in 2026, with Nordic states extracting 250 MW of district-heating value from data center exhaust water. Frankfurt and Amsterdam now impose waste-heat-reuse quotas, nudging procurements toward high-grade water loops. Middle East and Africa adopt liquid cooling to battle 50 °C ambient peaks; Dubai's collocated solar farm plus thermal-storage tank trims chiller electricity by 17%. Latin America saw emergent builds in Queretaro and Santiago, where cooler night air favors indirect evaporative modules that achieve 1.2 PUE despite high daytime highs.
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Vertiv
- Schneider Electric
- Stulz
- Rittal
- Johnson Controls
- Alfa Laval
- Fujitsu General
- Hitachi
- CoolIT Systems
- LiquidStack
- Asetek
- Asperitas
- Chilldyne
- Mikros Technologies
- Kaori Heat Treatment
- Lenovo
- Nortek Air Solutions
- Delta Electronics
- Munters
- Airedale (Modine)
- Black Box (Chatsworth Prod.)
- Submer
- GRC (Green Revolution Cooling)
- Coolcentric
- Starline
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 AI and HPC workload heat-density surge
- 4.2.2 Hyperscale footprint expansion in secondary metros
- 4.2.3 Mandatory PUE / GHG disclosure regulations
- 4.2.4 Global heat-wave frequency raising cooling demand
- 4.2.5 Monetisation of waste heat via district-energy loops
- 4.2.6 Tax-incentivised edge build-outs in rural grids
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Cap-ex premium of advanced liquid technologies
- 4.3.2 Retrofit complexity in legacy white-spaces
- 4.3.3 Limited supply of low-GWP refrigerants
- 4.3.4 Warranty-risk from non-standard immersion fluids
- 4.4 Key Cost Considerations for Cooling
- 4.4.1 Analysis of Key Cost Overheads Related to DC Operations (Cooling Focus)
- 4.4.2 Comparative Study of Cooling Technologies (Design Complexity, PUE, Pros/Cons, Weather Utilization)
- 4.4.3 Key Innovations and Developments in Data Center Cooling
- 4.4.4 Key Energy-Efficiency Practices Adopted in Data Centers
- 4.5 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.7 Technological Outlook
5 ANALYSIS OF CURRENT DATA CENTER FOOTPRINT
- 5.1 Analysis of IT Load Capacity (MW) and Area footprint (Sq. Ft.) of Data Centers (for the period of 2019-2031)
- 5.2 Analysis of the major Data Center Hotspots
- 5.3 Analysis of Major Upcoming Hyperscale Facilities
6 MARKET SIZE and GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE, USD BN)
- 6.1 By Cooling Technology
- 6.1.1 Air-based Cooling
- 6.1.1.1 Chiller and Economizer
- 6.1.1.2 CRAH (Computer-Room Air Handler)
- 6.1.1.3 Cooling Tower (Direct, Indirect, Two-Stage)
- 6.1.1.4 Other Air-based Cooling Technologies
- 6.1.2 Liquid-based Cooling
- 6.1.2.1 Immersion Cooling
- 6.1.2.2 Direct-to-Chip Cooling
- 6.1.2.3 Rear-Door Heat Exchanger
- 6.1.1 Air-based Cooling
- 6.2 By Cooling Component
- 6.2.1 Computer-Room Air Handlers (CRAH/CRAC)
- 6.2.2 Chillers and Heat-Exchanger Units
- 6.2.3 Cooling Towers and Dry Coolers
- 6.2.4 Pumps and Valves
- 6.2.5 Control and Monitoring Software
- 6.3 By Data Center Type
- 6.3.1 Hyperscale (Owned and Leased)
- 6.3.2 Enterprise (On-Premise)
- 6.3.3 Colocation
- 6.4 By End-user Industry
- 6.4.1 IT and Telecom
- 6.4.2 Retail and Consumer Goods
- 6.4.3 Healthcare
- 6.4.4 Media and Entertainment
- 6.4.5 Federal and Institutional Agencies
- 6.4.6 Other End users
- 6.5 By Geography
- 6.5.1 North America
- 6.5.1.1 United States
- 6.5.1.2 Canada
- 6.5.1.3 Mexico
- 6.5.2 South America
- 6.5.2.1 Brazil
- 6.5.2.2 Argentina
- 6.5.2.3 Chile
- 6.5.2.4 Rest of South America
- 6.5.3 Europe
- 6.5.3.1 Germany
- 6.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 6.5.3.3 France
- 6.5.3.4 Rest of Europe
- 6.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 6.5.4.1 China
- 6.5.4.2 India
- 6.5.4.3 Japan
- 6.5.4.4 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 6.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 6.5.5.1 Middle East
- 6.5.5.2 Africa
- 6.5.1 North America
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Market Share Analysis
- 7.2 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 7.2.1 Vertiv
- 7.2.2 Schneider Electric
- 7.2.3 Stulz
- 7.2.4 Rittal
- 7.2.5 Johnson Controls
- 7.2.6 Alfa Laval
- 7.2.7 Fujitsu General
- 7.2.8 Hitachi
- 7.2.9 CoolIT Systems
- 7.2.10 LiquidStack
- 7.2.11 Asetek
- 7.2.12 Asperitas
- 7.2.13 Chilldyne
- 7.2.14 Mikros Technologies
- 7.2.15 Kaori Heat Treatment
- 7.2.16 Lenovo
- 7.2.17 Nortek Air Solutions
- 7.2.18 Delta Electronics
- 7.2.19 Munters
- 7.2.20 Airedale (Modine)
- 7.2.21 Black Box (Chatsworth Prod.)
- 7.2.22 Submer
- 7.2.23 GRC (Green Revolution Cooling)
- 7.2.24 Coolcentric
- 7.2.25 Starline
8 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES and FUTURE OUTLOOK
9 INVESTMENT ANALYSIS




