PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939600

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939600
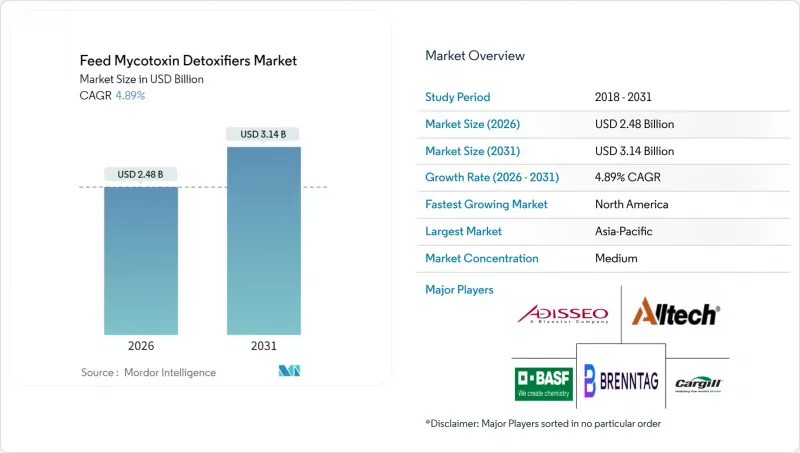
Feed Mycotoxin Detoxifiers - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
Feed mycotoxin detoxifier market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 2.48 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 2.36 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 3.14 billion, growing at 4.89% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Tightening maximum-limit regulations in the European Union and China, mounting evidence of climate-driven shifts in fungal contamination zones, and rapid expansion of industrial feed capacity in Asia-Pacific together underpin this strong growth momentum. Feed manufacturers are prioritizing broad-spectrum detoxification programs because co-occurrence of up to eight regulated toxins in single grain lots has become common in Serbia, Ethiopia, and other high-risk regions. Commercial mills are embedding automated mycotoxin testing and dosing infrastructure at the design stage, which reduces treatment costs and secures compliance with export-market standards. Competitive intensity is rising as enzyme-based biotransformers gain share by permanently degrading toxins rather than merely binding them, while premium pricing and regulatory gray areas in the Americas continue to temper adoption.
Global Feed Mycotoxin Detoxifiers Market Trends and Insights
Rising Incidence of Mycotoxin Contamination in Corn and Oil-Seed Meal Streams
Global surveys show fumonisin detection in 89-100% of Serbian maize samples and aflatoxin B1 concentrations as high as 527 µg/kg in drought years, breaching the European Union food limit by more than 100-fold. Ethiopian dairy concentrates posted 80.6% Aspergillus contamination, and 81.42% of isolates produced aflatoxins, highlighting the magnitude of the challenge. China loses 6 million tons of grain annually to mycotoxin degradation, amplifying the economic case for treatment. As climate volatility raises toxin peaks, mills are shifting from single-toxin binders to broad-spectrum solutions. The trend cements routine detoxifier use in high-risk supply chains now viewed as an operational necessity rather than an optional insurance policy.
Stricter Maximum-Limit Regulations in the EU, China and Southeast Asia
Regulatory bodies updated DON thresholds in 2022, forcing rapid reformulation across European and Chinese feed channels. Vietnam's Circular 61 and Thailand's new feed code mirrored these measures, widening the compliance net. Export-oriented mills must follow the strictest destination rule, effectively globalizing EU-level constraints. Faster enforcement cycles, often within 18 months, push buyers toward tested detoxifiers instead of incremental solutions. The same rulebooks set specific data requirements for enzyme-based products, favoring suppliers with complete dossiers and deterring late entrants.
Premium Pricing versus Traditional Binders for Cost-Sensitive Farmers
Multi-component products add USD 15-30 per ton to feed costs, while basic clay binders cost only USD 2-5 per ton. The differential strains budgets of smallholders in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, where feed already absorbs more than 70% of production costs. Returns manifest chiefly as avoided losses, a concept that is difficult to quantify for low-margin enterprises. Suppliers are experimenting with seasonal pricing and pay-as-you-benefit models to lower entry hurdles. Packaging detoxifiers into concentrate premixes also spreads incremental cost across multiple nutrients, enhancing acceptance.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Expansion of Commercial Compound-Feed Production Capacity
- Climate-Change-Driven Shift in Fusarium and Aspergillus Geographic Range
- Low Awareness Among Small and Backyard Livestock Producers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Binders accounted for 66.20% of feed mycotoxin detoxifier market share in 2025, while the biotransformers are projected to deliver a 4.93% CAGR through 2031. Binders are led by low-cost bentonite and montmorillonite clays validated over decades of commercial use. The segment benefits from simple registration pathways and abundant raw material supply. Binders are particularly favored for their ability to trap toxins in the animal's gastrointestinal tract, forming a binder-mycotoxin complex that is safely excreted. Their lower cost compared to other detoxifier types and easier usage patterns have also contributed significantly to their market dominance, especially in monogastric animals, where they are predominantly used.
Nevertheless, biotransformers witness the steepest trajectory among sub-additives. These are gaining particular traction in regions with advanced agricultural practices, where farmers are increasingly recognizing their role in improving animal health outcomes and feed efficiency. The segment's growth is also bolstered by rising concerns about feed safety and the increasing demand for innovative solutions in mycotoxin management. The feed mycotoxin binders and modifiers market is anticipated to see significant advancements in this area.
The Global Feed Mycotoxin Detoxifiers Market Report is Segmented by Sub-Additive (Binders, Biotransformers), Animal (Aquaculture, Poultry, Ruminants, Swine, and Other Animals), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East, and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (metric Tons).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific held the largest share of 31.05% of the feed mycotoxin detoxifier market in 2025, fueled by rapid industrial feed expansion and hot-humid climates conducive to fungal growth. New Vietnamese mills with 10 million-ton annual capacity embed automated toxin screening that triggers real-time dosing. China's farmer-held stockpile of 250 million tons incurs 8% storage losses, equivalent to 6 million tons of contaminated grain that require remediation annually.
The North American region is the fastest-growing region with a CAGR of 4.59% as the feed mycotoxin detoxifiers market demonstrates high technological adoption and a sophisticated understanding of feed safety across the United States, Canada, and Mexico. In Africa, surveys in Ethiopian dairy rations exposing 80.6% Aspergillus incidence confirm a chronic risk that undermines livestock gains from genetic and nutritional improvements. Climate modeling shows dual Fusarium and Aspergillus pressure expanding westward, reinforcing the need for continuous toxin management programs.
Europe shows stable growth, driven by tougher DON limits enacted in 2022. Northern growers now combat Fusarium levels once restricted to warmer latitudes. Brazil's heavy mill investments and lessons from past shipment rejections linked to aflatoxin contamination. Government extension programs in Brazil and Argentina now include mycotoxin management modules, elevating baseline awareness and supporting detoxifier uptake.
- Adisseo
- Alltech, Inc.
- BASF SE
- Brenntag SE
- Cargill Inc.
- EW Nutrition
- Impextraco NV
- Kemin Industries
- SHV (Nutreco NV)
- Special Nutrients
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
- 1.3 Research Methodology
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Animal Headcount
- 4.1.1 Poultry
- 4.1.2 Ruminants
- 4.1.3 Swine
- 4.2 Feed Production
- 4.2.1 Aquaculture
- 4.2.2 Poultry
- 4.2.3 Ruminants
- 4.2.4 Swine
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1 Argentina
- 4.3.2 Australia
- 4.3.3 Brazil
- 4.3.4 Canada
- 4.3.5 Chile
- 4.3.6 China
- 4.3.7 Egypt
- 4.3.8 France
- 4.3.9 Germany
- 4.3.10 India
- 4.3.11 Indonesia
- 4.3.12 Iran
- 4.3.13 Italy
- 4.3.14 Japan
- 4.3.15 Kenya
- 4.3.16 Mexico
- 4.3.17 Netherlands
- 4.3.18 Philippines
- 4.3.19 Russia
- 4.3.20 Saudi Arabia
- 4.3.21 South Africa
- 4.3.22 South Korea
- 4.3.23 Spain
- 4.3.24 Thailand
- 4.3.25 Turkey
- 4.3.26 United Kingdom
- 4.3.27 United States
- 4.3.28 Vietnam
- 4.4 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.5 Market Drivers
- 4.5.1 Rising incidence of mycotoxin contamination in corn and oil-seed meal streams
- 4.5.2 Stricter maximum-limit regulations in the EU, China, and Southeast Asia
- 4.5.3 Expansion of commercial compound-feed production capacity
- 4.5.4 Intensifying protein demand from poultry and aquaculture sectors
- 4.5.5 Biotransformer adoption boosted by antibiotic growth-promoter phase-outs
- 4.5.6 Climate-change-driven shift in Fusarium and Aspergillus geographic range
- 4.6 Market Restraints
- 4.6.1 Premium pricing versus traditional binders for cost-sensitive farmers
- 4.6.2 Low awareness among small and backyard livestock producers
- 4.6.3 Efficacy variability across multi-toxin challenges
- 4.6.4 Regulatory gray area for enzyme-based biotransformers in the Americas
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE AND VOLUME)
- 5.1 Sub Additive
- 5.1.1 Binders
- 5.1.2 Biotransformers
- 5.2 Animal
- 5.2.1 Aquaculture
- 5.2.1.1 By Sub Animal
- 5.2.1.1.1 Fish
- 5.2.1.1.2 Shrimp
- 5.2.1.1.3 Other Aquaculture Species
- 5.2.1.1 By Sub Animal
- 5.2.2 Poultry
- 5.2.2.1 By Sub Animal
- 5.2.2.1.1 Broiler
- 5.2.2.1.2 Layer
- 5.2.2.1.3 Other Poultry Birds
- 5.2.2.1 By Sub Animal
- 5.2.3 Ruminants
- 5.2.3.1 By Sub Animal
- 5.2.3.1.1 Beef Cattle
- 5.2.3.1.2 Dairy Cattle
- 5.2.3.1.3 Other Ruminants
- 5.2.3.1 By Sub Animal
- 5.2.4 Swine
- 5.2.5 Other Animals
- 5.2.1 Aquaculture
- 5.3 Region
- 5.3.1 Africa
- 5.3.1.1 By Country
- 5.3.1.1.1 Egypt
- 5.3.1.1.2 Kenya
- 5.3.1.1.3 South Africa
- 5.3.1.1.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.3.1.1 By Country
- 5.3.2 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2.1 By Country
- 5.3.2.1.1 Australia
- 5.3.2.1.2 China
- 5.3.2.1.3 India
- 5.3.2.1.4 Indonesia
- 5.3.2.1.5 Japan
- 5.3.2.1.6 Philippines
- 5.3.2.1.7 South Korea
- 5.3.2.1.8 Thailand
- 5.3.2.1.9 Vietnam
- 5.3.2.1.10 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2.1 By Country
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 By Country
- 5.3.3.1.1 France
- 5.3.3.1.2 Germany
- 5.3.3.1.3 Italy
- 5.3.3.1.4 Netherlands
- 5.3.3.1.5 Russia
- 5.3.3.1.6 Spain
- 5.3.3.1.7 Turkey
- 5.3.3.1.8 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.1.9 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.3.1 By Country
- 5.3.4 Middle East
- 5.3.4.1 By Country
- 5.3.4.1.1 Iran
- 5.3.4.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.4.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.3.4.1 By Country
- 5.3.5 North America
- 5.3.5.1 By Country
- 5.3.5.1.1 Canada
- 5.3.5.1.2 Mexico
- 5.3.5.1.3 United States
- 5.3.5.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.3.5.1 By Country
- 5.3.6 South America
- 5.3.6.1 By Country
- 5.3.6.1.1 Argentina
- 5.3.6.1.2 Brazil
- 5.3.6.1.3 Chile
- 5.3.6.1.4 Rest of South America
- 5.3.6.1 By Country
- 5.3.1 Africa
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Adisseo
- 6.4.2 Alltech, Inc.
- 6.4.3 BASF SE
- 6.4.4 Brenntag SE
- 6.4.5 Cargill Inc.
- 6.4.6 EW Nutrition
- 6.4.7 Impextraco NV
- 6.4.8 Kemin Industries
- 6.4.9 SHV (Nutreco NV)
- 6.4.10 Special Nutrients
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR FEED ADDITIVE CEOS




