PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940615

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940615
Ultra-Thin Glass - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Ultra-Thin Glass Market was valued at USD 14.18 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 15.73 billion in 2026 to reach USD 26.39 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 10.92% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
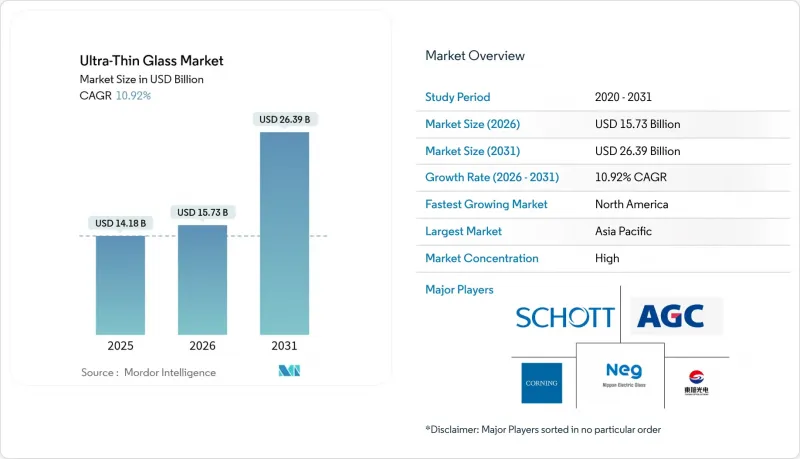
Multiple technology transitions propel this expansion: foldable consumer devices need bendable cover lenses, electric vehicles specify lightweight glazing that trims battery load, and chiplet-based processors require glass interposers that preserve signal fidelity at ever-higher I/O densities. Thinness below 1 millimeter also unlocks new optical stacks for micro-LED and flexible OLED displays, while chemical-strengthened panels extend drop and scratch resistance in premium handsets. Rising capital outlays by semiconductor leaders for glass substrates, combined with automakers' shift toward panoramic head-up displays, broaden addressable demand across three high-value supply chains. Raw-material purity requirements and precision forming still elevate cost structures, yet continuous float and fusion draw line upgrades are narrowing the delta with conventional sheet glass.
Global Ultra-Thin Glass Market Trends and Insights
Growing Demand from Consumer Electronics
Surging smartphone, tablet, and wearable volumes keep the ultra-thin glass market firmly anchored to consumer electronics. Samsung's Galaxy Z Fold6 employs sub-100 µm chemically strengthened glass that bends hundreds of thousands of times while retaining optical clarity. Corning's Gorilla Glass Ceramic 2 integrates nanocrystals for higher hardness without compromising transparency. Device makers also embed thin-glass antenna windows to maximise 5G throughput, reinforcing cross-component pull. Supply-chain localisation within Vietnam and India further raises shipment velocity, tightening collaboration between panel makers and glass suppliers. These factors collectively push average glass area per handset upward even as unit growth moderates, cementing a stable multi-year revenue foundation for the ultra-thin glass market.
Rapid Adoption in Foldable Smartphones & Notebooks
Flexible form factors drive incremental square metres because each foldable display uses two to three times the glass area of a bar-type phone. SCHOTT's ultra-thin glass reached 30 µm thickness while withstanding over 300,000 bends at 1 mm radius, an industry record. Notebook makers now prototype 17-inch fold-outs that collapse into 13-inch footprints, multiplying substrate demand per device. Co-developed anti-shatter coatings distribute surface stress, letting assemblers trade polyimide films for harder glass facings. With price premiums narrowing, foldable penetration is expected to hit double-digit share of flagship shipments by 2027, embedding strong volume tailwinds within the ultra-thin glass market.
High Cost of High-Purity Raw Materials & Precision Processing
Semiconductor-grade sand must achieve 99.999% purity; deposits in Spruce Pine, North Carolina are one of the few sources and regularly command USD 10,000 per ton according to supplier price lists. Fusion draw furnaces require platinum-rhodium channels and ultra-clean atmospheres, inflating capital intensity to USD 350 million per line for Gen-10 display sizes. Smaller entrants struggle to amortise such outlays, slowing capacity diffusion and tempering the ultra-thin glass market growth rate in near-term planning cycles.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Advancements in Flexible OLED & Micro-LED Display Lines
- Weight-Reduction Needs in Automotive Glazing & HUDs
- Brittleness & Yield Loss During Large-Area Handling
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Soda-lime compositions delivered scale and growth, posting a 45.52% share in 2025 while maintaining a 11.55% CAGR outlook. Their lower melting temperatures cut furnace energy by up to 15% versus aluminosilicate, aligning with decarbonisation pledges. NSG's UFF float glass now integrates 35% cullet yet meets optical flatness for AMOLED cover lenses. Aluminosilicate entrants like Corning's Gorilla Glass reach 800 Vickers hardness, serving premium phones and automotive interiors. Borosilicate and alkali-free variants underpin semiconductor dielectrics owing to superior thermal shock resistance.
Premium segments lift average selling prices, but soda-lime's entrenched production base provides cost leverage for mass handset models, ensuring it remains the anchor of the ultra-thin glass market. Manufacturers layer ion-exchange treatments on soda-lime sheets to bridge durability gaps, while specialized lithium-aluminosilicate grades address wafer-level optics and AR waveguide applications.
Float and microfloat lines generated 50.12% of 2025 revenue and enjoy the highest 12.24% CAGR because modern tin baths now output ribbons as thin as 0.4 mm with surface waviness under 0.1 µm. Pilkington's latest plant leverages counter-current nitrogen curtains to suppress tin pick-up, delivering near-optical-grade surfaces. Pioneered by Corning, fusion draw methods yield defect-free surfaces without grinding or polishing, crucial for high-resolution displays. Down-draw techniques allow 30 µm thickness control, servicing foldable cover glass lines, while roll-to-roll slit draw opens continuous flexible glass webs for wearable sensors.
Break-even throughput for float remains the lowest, cementing its status as the entry route for new participants in the ultra-thin glass market. Yet fusion's pristine surfaces increasingly command premium price tiers, pushing suppliers to run hybrid operations and diversify risk across application buckets.
The Ultra-Thin Glass Market Report Segments the Industry by Glass Type (Aluminosilicate, Soda-Lime Ultra-Thin, and More), Manufacturing Process (Fusion Draw, Down-Draw / Overflow, and More), Application (Semiconductor Substrate, Touch Panel Displays, and More), End-User Industry (Automotive, Biotechnology, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific accounted for 49.08% of 2025 revenue thanks to densely integrated display and semiconductor ecosystems in China, South Korea, and Japan. Expansion programs such as Samsung Display's Gen-8.6 OLED fab and TSMC's advanced packaging lines provide stable pull for float and fusion substrates. Japanese firms add specialised glass for augmented-reality optics, while Taiwanese assemblers ramp through-glass via pilot runs. Regional diversification, though, gains urgency as geopolitical trade rules tighten, prompting Korean and Japanese suppliers to co-invest in lines within Southeast Asia to derisk logistics.
North America is projected to register the fastest 11.32% CAGR through 2031 due to semiconductor reshoring and electric-vehicle glass adoption. Intel's Arizona glass substrate campus targets risk production in 2026 and has already procured specialised fusion equipment. Corning's 2025 first-quarter results showed 13% core sales growth to USD 3.7 billion, buoyed by specialty materials for generative-AI data-centre optics. Midwest state incentives also fund a Glass Centre of Excellence in Ohio that supports circular recycling trials, an early step toward easing waste bottlenecks for the ultra-thin glass market.
Europe remains a technology-rich yet moderately paced terrain. AGC Glass Europe invests in vacuum-insulated glass lines that leverage 0.3 mm panes to hit <0.5 W/m2K window U-factors. Guardian and VELUX co-develop tempered VIG panes for net-zero buildings, underscoring policy-driven demand. Automotive glazing specialists in Germany and Finland supply panoramic roofs for premium EV platforms, sustaining a balanced growth path and embedding sustainability credentials that resonate with regulators and buyers alike.
- AGC Inc.
- Central Glass Co., Ltd.
- Changzhou Almaden Co., Ltd.
- Corning Incorporated
- CSG Holding Co., Ltd.
- Emerge Glass
- Fraunhofer
- Irico Group New Energy Company Limited
- Nippon Electric Glass Co., Ltd.
- Nippon Sheet Glass Co., Ltd.
- Nitto Denko Corporation.
- OFILM
- Samsung
- SCHOTT AG
- Taiwan Glass Ind. Corp.
- Tunghsu Optoelectronic Technology
- Xinyi Glass Holdings Limited.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing demand from consumer electronics
- 4.2.2 Rapid adoption in foldable smartphones & notebooks
- 4.2.3 Advancements in flexible OLED & micro-LED display lines
- 4.2.4 Weight-reduction needs in automotive glazing & HUDs
- 4.2.5 Glass interposers for chiplet packaging
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High cost of high-purity raw materials & precision processing
- 4.3.2 Brittleness & yield loss during large-area handling
- 4.3.3 Limited recycling streams for greater than 0.3 mm glass waste
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Glass Type
- 5.1.1 Aluminosilicate (e.g., Gorilla, Dragontrail)
- 5.1.2 Borosilicate / Alkali-Free
- 5.1.3 Soda-Lime Ultra-Thin
- 5.1.4 Others (Lithium-Aluminosilicate, etc.)
- 5.2 By Manufacturing Process
- 5.2.1 Fusion Draw
- 5.2.2 Down-Draw / Overflow
- 5.2.3 Float & Microfloat
- 5.2.4 Slit Draw / Roll-to-Roll
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Semiconductor Substrate
- 5.3.2 Touch Panel Displays
- 5.3.3 Fingerprint Sensors
- 5.3.4 Automotive Glazing
- 5.3.5 Other Applications (Automotive Displays and Glazing, etc.)
- 5.4 By End-User Industry
- 5.4.1 Consumer Electronics
- 5.4.2 Automotive
- 5.4.3 Biotechnology
- 5.4.4 Other End-User Industries (Energy and Power, etc.)
- 5.5 By Region
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 China
- 5.5.1.2 India
- 5.5.1.3 Japan
- 5.5.1.4 South Korea
- 5.5.1.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 North America
- 5.5.2.1 United States
- 5.5.2.2 Canada
- 5.5.2.3 Mexico
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share(%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Info, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 AGC Inc.
- 6.4.2 Central Glass Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.3 Changzhou Almaden Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.4 Corning Incorporated
- 6.4.5 CSG Holding Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Emerge Glass
- 6.4.7 Fraunhofer
- 6.4.8 Irico Group New Energy Company Limited
- 6.4.9 Nippon Electric Glass Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Nippon Sheet Glass Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Nitto Denko Corporation.
- 6.4.12 OFILM
- 6.4.13 Samsung
- 6.4.14 SCHOTT AG
- 6.4.15 Taiwan Glass Ind. Corp.
- 6.4.16 Tunghsu Optoelectronic Technology
- 6.4.17 Xinyi Glass Holdings Limited.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment
- 7.2 Development of Advanced Glass for Solar Energy Projects




