PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940689

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940689
United States Transformer - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
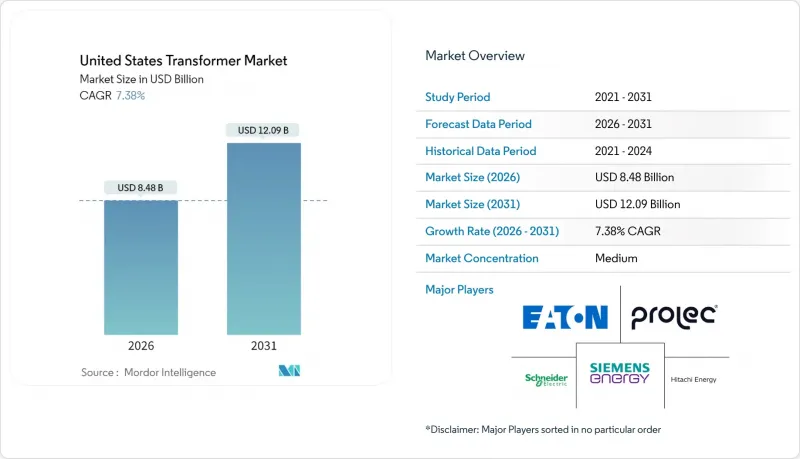
The United States Transformer market is expected to grow from USD 7.90 billion in 2025 to USD 8.48 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 12.09 billion by 2031 at 7.38% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Federal grid modernization appropriations, record EV-charging deployments, and an unprecedented wave of data center construction are widening the order pipeline and insulating revenue growth from economic softening. More than USD 14 billion of Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and Inflation Reduction Act funds have been ring-fenced for grid-resilience projects, anchoring multiyear procurement commitments for domestic suppliers. Medium-rating units benefit most from distributed-generation interconnections, which dominate distribution system upgrades, while utility capital expenditures (CAPEX) cycles continue to prioritize high-voltage autotransformers for new interstate corridors and substation refurbishments. Despite raw material shortages and a 60-week average lead time, the pricing environment remains favorable, as domestic quotations trade four to five times higher than in several overseas regions, thereby reinforcing manufacturers' margins.
United States Transformer Market Trends and Insights
IIJA & IRA grid-hardening grants
Federal programs have become the single largest source of funding for transformers in the country. The Department of Energy's GRIP initiative has allocated USD 7.6 billion across 104 projects, unlocking 55 GW of new transmission capacity and upgrading 1,650 miles of lines. Complementary state and tribal awards totaling USD 1.3 billion finance local substation hardening, undergrounding works, and adaptive protection systems that directly lift unit demand. The Transmission Facilitation Program's revolving USD 2.5 billion fund de-risks milestone ventures, such as the 525 kV Southern Spirit HVDC line, each of which requires clusters of 350 MVA single-phase transformers with enhanced short-circuit withstand capability. These allocations create a predictable order floor for the US transformer market, encouraging suppliers to expand domestic core-winding and test-bay capacities. Utilities also leverage federal cost-sharing to accelerate the replacement of assets that exceed nameplate loading or fail to meet modern resilience standards.
Commercial-fleet electrification
The pivot to battery-electric medium- and heavy-duty trucks is creating concentrated load pockets that exceed the capability of existing 25 kVA to 50 kVA pole-top units. National Renewable Energy Laboratory modeling indicates that a 30% EV penetration could necessitate upgrades to approximately 2.2 million residential-class transformers. Depot charging for Class 8 trucks relies on 1 MVA isolation units that step down from 11 kV feeders to 1.4 kV AC bus systems, driving demand for pad-mounted units with forced-air cooling and advanced temperature monitoring. Five pilot states in the DOE Multi-State Transportation Electrification Impact Study will invest USD 2.3 billion in distribution upgrades through 2032, replacing roughly 30,000 service transformers. Utilities are therefore bundling transformer replacements with smart-meter rollouts to streamline customer-side connections. Manufacturers capable of shortening lead times for 1 MVA dry-type assemblies gain a competitive edge in urban freight corridors where delivery windows are compressed.
Mineral-oil lead-time & price volatility
Average delivery times for liquid-immersed units have stretched from 14 weeks in 2019 to 60-70 weeks in 2025, with outliers above two years for 230 kV ratings and higher. Import tariffs on cores and wound magnetic assemblies limit supply flexibility, while domestic factories can only meet about 20% of national demand, amplifying exposure to international disruptions. Producers report premium surcharges of USD 18 per gallon for inhibited mineral oil compared with 2024 levels, eroding project contingencies. Industry associations are lobbying for USD 1.2 billion in supplemental appropriations to underwrite the construction of new steel-lamination mills and a strategic insulating-oil reserve that could stabilize production economics. Utilities cushion project schedules by over-ordering spare units, but this safety inventory further tightens the spot market. The resulting price gyrations reduce the pace of discretionary replacements and moderate the US transformer market CAGR in the medium term.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Utility substation digitization
- Secondary-metro data-center build-outs
- PCB-related insurance premiums
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Large units retained a 43.37% share of the US transformer market in 2025, anchored by bulk-power corridors and HVDC terminals. The medium-rating class, spanning roughly 10 MVA to 100 MVA, is registering a 8.88% CAGR and is on track to lift its US transformer market size to about USD 3.68 billion by 2031. Utilities reconfigure secondary substations to manage renewable interconnections, causing medium-rating orders to represent nearly half of new solar-plant step-up filings under FERC Order 1920 regional-planning dockets. Storage-plus-PV hybrids require multiple 60 MVA to 90 MVA step-up units that integrate wide-bandwidth online gas analysis and dissolved-hydrogen alarms for fast-frequency response.
The large-rating segment still benefits from flagship interstate initiatives, such as the 525 kV Southern Spirit and Lake Erie HVDC links, each of which demands single-phase autotransformers above 300 MVA. Lead-time visibility for such extra-high-voltage units exceeds 100 weeks, prompting owners to place orders well before construction begins. Small-rating units below 10 MVA face slower expansion because the DOE 2029 efficiency rules mandate higher-grade cores, which raise unit prices and encourage fleet consolidation rather than one-for-one replacements. OEMs that automate core stacking for medium ratings can pivot production between large and small sizes, thereby smoothing factory utilization.
Oil-cooled transformers maintained a 73.02% share in 2025 due to proven overload capacity and favorable loss-evaluation economics for high-voltage corridors. Dry-type, air-cooled designs are nevertheless advancing at an 8.27% CAGR as municipalities tighten fire-code provisions in densely populated zones, prompting underground vault specifications to shift away from mineral oil. The US transformer market size for air-cooled units is expected to exceed USD 2.27 billion by 2031, if city ordinances continue to ban combustible fluids near critical infrastructure.
Suppliers have commercialized epoxy-resin encapsulated windings rated up to 72.5 kV, narrowing the performance gap with oil-immersed designs. Rising dielectric-fluid and containment-basin costs erode the relative advantage of oil-cooled units for 138 kV substations, particularly in coastal flood zones. Yet oil-immersed equipment remains indispensable at 230 kV and higher, where thermal-cycling robustness and impulse-voltage margins outweigh environmental premiums. Purchase decisions are increasingly influenced by total-cost-of-ownership models that incorporate fire-safety retrofits and insurance deductibles.
The United States Transformer Market Report is Segmented by Power Rating (Large, Medium, and Small), Cooling Type (Air-Cooled and Oil-Cooled), Phase (Single-Phase and Three-Phase), Transformer Type (Power and Distribution), and End-User (Power Utilities, Industrial, Commercial, and Residential). The Market Sizes and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Hitachi Energy (ABB spin-off)
- Siemens Energy
- General Electric - Prolec GE
- Eaton Corporation
- Schneider Electric
- Toshiba Energy Systems
- Mitsubishi Electric
- SPX Transformer Solutions
- Virginia Transformer Corp
- Howard Industries
- Sunbelt Solomon Solutions
- CG Power & Industrial
- WEG Transformers USA
- SGB-SMIT Group
- Hyundai Electric America
- Powell Industries
- Siemens Trench
- ERMCO
- Myers Power Products
- Hammond Power Solutions
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
- 1.2 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 U.S. grid-hardening funds under IIJA & IRA
- 4.2.2 Electrification of commercial fleets (medium-/heavy-duty EV depots)
- 4.2.3 Utility cap-ex cycle for sub-station digitisation
- 4.2.4 Data-centre build-out in secondary U.S. metros
- 4.2.5 Edge-case: Crypto-mining load shifting to Midwest
- 4.2.6 Reshoring of medium-voltage component manufacturing
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Long mineral-oil lead times & price volatility
- 4.3.2 PCB legacy liabilities driving insurance premiums
- 4.3.3 Tier-2 steel core shortage (Oriented electrical steel)
- 4.3.4 Increasing utility RFP preference for "Amorphous-core only"
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Power Rating
- 5.1.1 Large (Above 100 MVA)
- 5.1.2 Medium (10 to 100 MVA)
- 5.1.3 Small (Up to 10 MVA)
- 5.2 By Cooling Type
- 5.2.1 Air-cooled
- 5.2.2 Oil-cooled
- 5.3 By Phase
- 5.3.1 Single-Phase
- 5.3.2 Three-Phase
- 5.4 By Transformer Type
- 5.4.1 Power
- 5.4.2 Distribution
- 5.5 By End-User
- 5.5.1 Power Utilities (includes, Renewables, Non-renewables, and T&D)
- 5.5.2 Industrial
- 5.5.3 Commercial
- 5.5.4 Residential
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Hitachi Energy (ABB spin-off)
- 6.4.2 Siemens Energy
- 6.4.3 General Electric - Prolec GE
- 6.4.4 Eaton Corporation
- 6.4.5 Schneider Electric
- 6.4.6 Toshiba Energy Systems
- 6.4.7 Mitsubishi Electric
- 6.4.8 SPX Transformer Solutions
- 6.4.9 Virginia Transformer Corp
- 6.4.10 Howard Industries
- 6.4.11 Sunbelt Solomon Solutions
- 6.4.12 CG Power & Industrial
- 6.4.13 WEG Transformers USA
- 6.4.14 SGB-SMIT Group
- 6.4.15 Hyundai Electric America
- 6.4.16 Powell Industries
- 6.4.17 Siemens Trench
- 6.4.18 ERMCO
- 6.4.19 Myers Power Products
- 6.4.20 Hammond Power Solutions
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




