PUBLISHER: TrendForce | PRODUCT CODE: 1848182

PUBLISHER: TrendForce | PRODUCT CODE: 1848182
On-Chip Cooling Race: TSMC, Samsung, Intel Strategies Analysis
The surge in AI applications has fueled the development and growth of the semiconductor industry but has also brought new challenges. Apart from advanced process technology nearing physical limits and the increasing difficulty of process miniaturization, heat dissipation has emerged as a primary concern for major semiconductor foundries.
Chips used in AI servers, particularly GPUs, continue to improve in terms of performance. Consequently, the thermal design power (TDP) of individual chips has reached kilowatt levels. The traditional air cooling technology is approaching its physical limits, making way for the rise of liquid cooling technology. At the same time, the semiconductor industry and related academic research institutions are actively investing in the development of embedded liquid cooling solutions within chips.
Key Highlights:
- Thermal Management Challenges Brought by Advanced Processes.
- Emergence of On-Chip Cooling Technology.
- On-Chip Embedded Cooling.
- Embedded On-Chip Cooling to Become a Key Cooling Technology in the Future.
- Deployment in On-Chip Cooling Solutions among Major Foundries (TSMC / Samsung / Intel).
- Deployment in On-Chip Cooling Solutions among Major Foundries.
SAMPLE VIEW
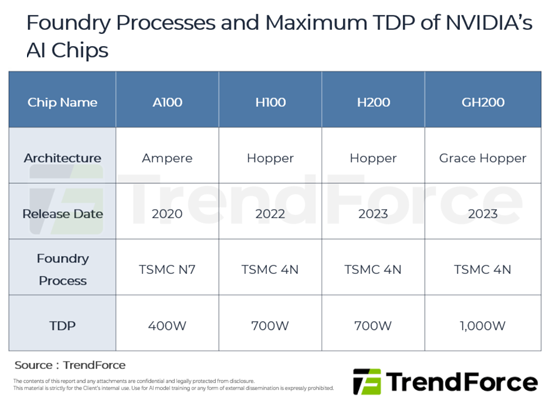
Table of Contents
1. AI Chips Are Getting Hotter and Hotter
- Table 1: Foundry Processes and Maximum TDP of NVIDIA's AI Chips
2. Thermal Management Challenges Brought by Advanced Processes
- Figure 1: Traditional Cooling Architecture for Semiconductor Chip and Temperature Variations
- Figure 2: Simulation Test Results from IMEC
3. Latest Developments in Cooling Technologies
- Table 2: Comparison of Current Cooling Technologies
4. Emergence of On-Chip Cooling Technology
- Figure 3: Srikanth Rangarajan and Research Team Segmented Cooling Technology of Chips from Inside Out into T1-T4
- Figure 4: Structural Schematics of TED Embedded Thermoelectric Component
- Figure 5: Structural Schematics of Embedded Micro-Jet Cooling
- Figure 6: Comparison of Cooling Effect between Traditional Liquid-Cooling and Embedded Micro-Jet Cooling under the Same 500micrometer Unit
- Figure 7: Microchannel Cooling Embedded in Power Electronic Chips
- Figure 8: Cross-Sectional Comparison of Traditional Cold Plates and Microchannel Cooling Components
- Figure 9: Technical Advancement of Next-Gen HBM Cooling
- Figure 10: KAIST's Projection on Various Technical Nodes and Corresponding Cooling Technology of HBM
5. Deployment in On-Chip Cooling Solutions among Major Foundries
- Figure 11: TSMC's IMC-Si Process
- Table 3: Comparison of Samsung's FOWLP Technology
- Figure 12: Intel's Package-Level Liquid-Cooling Technology
- Figure 13: Intel Showcasing TIM Solutions Corresponding to Various Application Scenarios and Cost
6. TRI's View




