PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850189

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850189
Cancer Diagnostics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
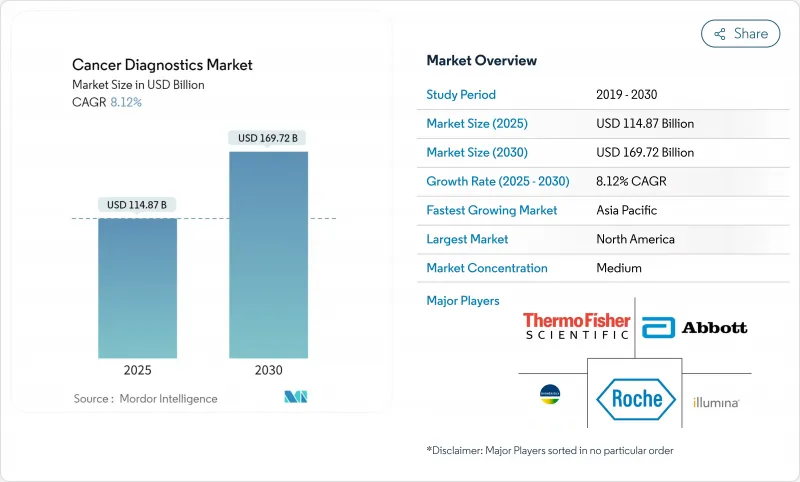
The cancer diagnostics market is valued at USD 114.87 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 169.72 billion by 2030, expanding to an 8.12% CAGR.
Accelerated approvals of artificial-intelligence tools, broader Medicare coverage for blood-based screening, and rapid adoption of liquid biopsy platforms are reshaping early detection pathways. FDA breakthrough designations for multi-cancer blood tests and point-of-care imaging devices illustrate a regulatory climate that favors innovation while raising competitive intensity. Governments are scaling population screening most visibly through the Biden Cancer Moonshot and Australia's new lung screening program, creating demand for decentralized solutions that fit within constrained public-health budgets. Strategic partnerships between imaging giants and AI specialists are driving productivity gains and shortening diagnostic turnaround times, while demographic shifts toward older populations sustain long-term test volume growth.
Global Cancer Diagnostics Market Trends and Insights
Increasing Government-Funded Screening Programs
Global health agencies are scaling population screening beyond breast and colorectal cancers. The ARPA-H POSEIDON initiative finances at-home multi-cancer tests, while Australia's lung screening roll-out moves diagnostics closer to underserved groups. Europe now recommends lung, prostate, and gastric screening, prompting vendors to build high-throughput, cost-efficient platforms suitable for national programs. Political alignment is evident in the USD 650 million U.S. allocation to community cancer projects, which prioritizes accessible diagnostics that can run outside tertiary hospitals.
Rising Global Cancer Incidence & Aging Population
India forecasts 2 million annual cases by 2040, and Europe saw diagnoses climb from 2.1 million in 1995 to 3.2 million in 2022. These shifts pressure health systems to adopt both high-complexity genomics for precision therapy in older cohorts and low-cost rapid tests for populous markets. Vendors capable of scaling test menus across disparate infrastructures are well placed to capture outsized gains.
High Cost of Advanced Molecular Diagnostics
Median out-of-pocket charges for AI radiology exceed USD 1,000, deterring uptake where insurance lags. Although the AMA has drafted AI CPT codes, evidence hurdles delay broad coverage. Emerging economies face import duties and currency headwinds that elevate device prices well beyond local affordability, stalling the diffusion of genomics despite clinical value.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid Adoption of Liquid Biopsy & ctDNA Tests
- Point-Of-Care Imaging & Diagnostics Expansion
- Limited Reimbursement in Low-Income Nations
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Genomic/Liquid Biopsy Tests are projected to log an 18.4% CAGR, the highest within the cancer diagnostics market, as pan-tumor companion diagnostics gain FDA clearance. The FDA green-lighted Illumina's TruSight Oncology Comprehensive assay in 2024, supporting broad genomic profiling for solid tumors. Meanwhile, Diagnostic Imaging Tests preserved a 46.2% foothold in 2024 due to AI overlays that cut interpretation time and mitigate radiologist shortages. Biopsy & Cytology remain indispensable for histology confirmation, yet non-invasive blood tests inch closer to tissue accuracy, particularly when combined with multi-omic analytics. Tumor Biomarker panels see steady demand through their role in therapy selection. IVD Immunoassays thrive in decentralized sites where laboratory infrastructure is scarce, aligning with the push to expand basic oncology services in middle-income settings. Other platforms, such as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, with 94.75% accuracy in large cohorts, signal future competitive threats.
The Cancer Diagnostics Market is Segmented by Diagnostic Type (Diagnostic Imaging Tests, Biopsy & Cytology Tests, Tumor Biomarkers, and More), Cancer Type (Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer, Colorectal Cancer, and More), End User (Hospitals, Diagnostic Laboratories, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Sizes and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America led revenue with a 38.9% share in 2024, supported by Medicare's inclusion of blood-based colorectal tests in the 2025 fee schedule and frequent FDA breakthrough device designations. A mature payer system and widespread adoption of electronic health records ease integration of AI analytics, positioning the region as an early-adopter hub. U.S. academic networks are running multi-state trials that validate multi-cancer detection platforms, accelerating time-to-reimbursement once analytical validity is proven. Canada benefits from pan-provincial genomic initiatives that underwrite sequencing for therapy guidance, further buoying test volumes.
Europe holds the second-largest revenue pool. Updated EU screening guidelines now encompass lung, prostate, and gastric cancers, generating demand for both low-dose CT and liquid biopsy alternatives. The European Liquid Biopsy Society is standardizing sample handling, which should harmonize clinical adoption across member states. Reimbursement, however, varies widely: Germany's DRG system promptly covers NGS panels, while southern Europe lags, creating a two-speed uptake environment. Data-privacy regulation under GDPR raises compliance costs for cloud-based AI vendors, but investment in in-country data centers is easing adoption.
Asia Pacific delivers the fastest expansion at a 10.9% CAGR. China's NMPA approved 61 innovative devices in 2023, reflecting regulatory pragmatism that accelerates time to market for local innovators. Public-private partnerships are building molecular pathology labs across Tier-2 cities, expanding sample-processing capacity. India's National Cancer Grid is rolling out digital pathology and tele-oncology, enabling rural facilities to access urban expertise. Japan's fast-track approvals for pan-lung PCR panels exemplify how mature markets in the region continue to embrace precision diagnostics.
In Latin America, decentralized policies are nascent, but sequencing costs are declining, paving the way for targeted screening of high-incidence cancers like gastric and gallbladder. Middle East and Africa remain hampered by reimbursement gaps anda limited oncology workforce. Medical tourism underscores the deficit: more than 90% of Sub-Saharan oncologists report patients traveling abroad for diagnostics. International agencies are piloting portable imaging and point-of-care assays to bridge these inequities, but uptake hinges on sustainable funding models.
- Abbott Laboratories
- Roche
- Siemens Healthineers
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- GE Healthcare
- Hologic
- Illumina
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- Agilent Technologies
- bioMerieux
- QIAGEN
- Guardant Health
- Exact Sciences
- Beckton Dickinson
- Danaher
- PerkinElmer
- Myriad Genetics
- Sysmex
- Foundation Medicine
- NanoString Technologies
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing Government-Funded Screening Programs
- 4.2.2 Rising Global Cancer Incidence & Aging Population
- 4.2.3 Rapid Adoption Of Liquid-Biopsy & ctDNA Tests
- 4.2.4 Point-Of-Care Imaging & Diagnostics Expansion
- 4.2.5 AI-Driven Multi-Omics Early Detection Platforms
- 4.2.6 Value-Based Companion Diagnostics Reimbursement
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Cost Of Advanced Molecular Diagnostics
- 4.3.2 Limited Reimbursement In Low-Income Nations
- 4.3.3 Shortage Of Trained Molecular Pathologists
- 4.3.4 Data-Privacy Concerns In AI Cloud Workflows
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Diagnostic Type
- 5.1.1 Diagnostic Imaging Tests
- 5.1.2 Biopsy & Cytology Tests
- 5.1.3 Tumor Biomarkers
- 5.1.4 Genomic / Liquid-Biopsy Tests
- 5.1.5 IVD Immunoassays
- 5.1.6 Other Diagnostic Types
- 5.2 By Cancer Type
- 5.2.1 Breast Cancer
- 5.2.2 Lung Cancer
- 5.2.3 Colorectal Cancer
- 5.2.4 Cervical Cancer
- 5.2.5 Prostate Cancer
- 5.2.6 Kidney Cancer
- 5.2.7 Liver Cancer
- 5.2.8 Pancreatic Cancer
- 5.2.9 Ovarian Cancer
- 5.2.10 Other Cancer Types
- 5.3 By End User
- 5.3.1 Hospitals
- 5.3.2 Diagnostic Laboratories
- 5.3.3 Academic & Research Institutes
- 5.3.4 POC / Ambulatory Centres
- 5.4 By Region
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 South Korea
- 5.4.3.5 Australia
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.4.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.4.1 GCC
- 5.4.4.2 South Africa
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5 South America
- 5.4.5.1 Brazil
- 5.4.5.2 Argentina
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Abbott Laboratories
- 6.3.2 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- 6.3.3 Siemens Healthineers
- 6.3.4 Thermo Fisher Scientific
- 6.3.5 GE HealthCare
- 6.3.6 Hologic Inc.
- 6.3.7 Illumina Inc.
- 6.3.8 Bio-Rad Laboratories
- 6.3.9 Agilent Technologies
- 6.3.10 bioMerieux SA
- 6.3.11 Qiagen
- 6.3.12 Guardant Health
- 6.3.13 Exact Sciences Corporation
- 6.3.14 Becton, Dickinson and Company
- 6.3.15 Danaher Corporation (Cepheid)
- 6.3.16 PerkinElmer
- 6.3.17 Myriad Genetics
- 6.3.18 Sysmex Corporation
- 6.3.19 Foundation Medicine
- 6.3.20 NanoString Technologies
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




