PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851478

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851478
Gastric Cancer Therapy - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The gastric cancer treatment market size touched USD 5.99 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 10.86 billion by 2030 on the back of a firm 12.63% CAGR throughout the forecast period, underscoring vigorous demand expansion across care settings.
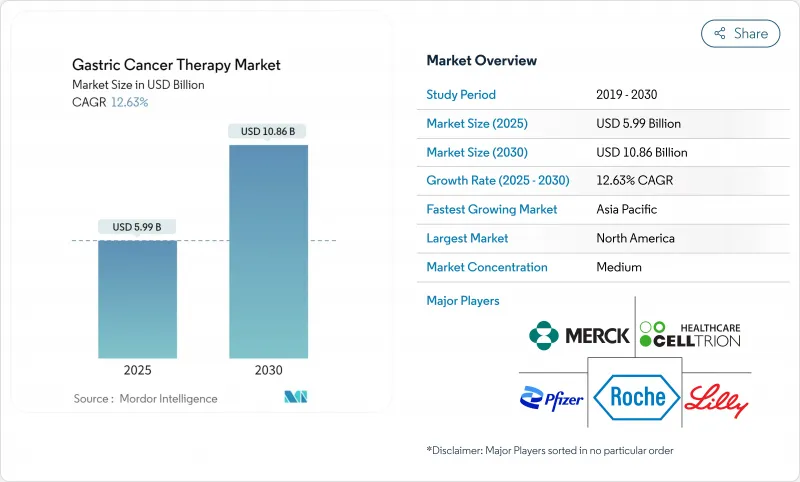
Accelerating incidence among aging cohorts, rapid immunotherapy adoption, earlier biomarker testing, and China's high-volume procurement reforms together underpin growth momentum in every major region. Artificial-intelligence-supported endoscopic screening is shifting detection toward curable stages, while companion diagnostics now inform a widening set of precision regimens that improve outcomes and extend treatment duration. Five breakthrough approvals secured United States clearance between October 2024 and March 2025, and parallel fast-track systems in Japan and the European Union are narrowing launch timelines for late-stage candidates, reinforcing revenue visibility for innovators. Conversely, high post-surgical complication costs and uneven biomarker reimbursement across emerging economies still place friction on optimal care, tempering near-term adoption curves for premium drugs in some markets.
Global Gastric Cancer Therapy Market Trends and Insights
Aging Population & H. pylori Prevalence Upswing
Demographic aging combines with lingering H. pylori infection to keep baseline incidence on an upward slope, particularly across Japan, South Korea, China, and southern Europe where historic exposure persists despite eradication programs. Hospital discharge databases in Tokyo show that people >=65 years account for more than 70% of new gastric cancer diagnoses, confirming the demand wave entering oncology clinics. Because remission often requires lengthy multimodal therapy and frequent follow-up, older patients typically consume higher cumulative drug volumes, a dynamic that inflates lifetime spend per case inside the gastric cancer treatment market. In addition, real-world analyses indicate that geriatric toxicity management protocols have improved markedly over the past two years, enabling clinicians to sustain systemic regimens longer without dose reductions, thereby raising average selling volumes for checkpoint inhibitors and targeted agents. Payors nonetheless struggle with the budget impact of treating larger elderly cohorts, prompting a shift toward value-based reimbursement schemes that tether payment to outcomes over multiyear horizons. Although preventive measures continue to expand, their epidemiologic benefit will materialize only gradually, securing a long runway of sustained therapy demand within the gastric cancer treatment market.
Uptake of PD-1/PD-L1 Checkpoint Inhibitors
First-line adoption of pembrolizumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy, approved in March 2025, raised median progression-free survival from 7.3 to 10.9 months, altering front-of-card treatment algorithms in North America and Europe. Health-technology-assessment dossiers submitted in France and Italy indicate an incremental cost per quality-adjusted life-year that falls below national willingness-to-pay thresholds when the drug is used in biomarker-positive patients, propelling formulary inclusion and anchoring revenue growth across the gastric cancer treatment market. Similarly, the perioperative use of durvalumab combinations slashed recurrence risk by 29% in randomized trials presented at ASCO 2025, prompting guideline committees to recommend immune modulation earlier in the disease course. Importantly, response durability for patients with low PD-L1 scores has improved when checkpoint blockade is paired with trastuzumab or cytotoxic agents, expanding the treatable cohort by as much as one-third according to pooled Phase 3 data.
High Post-Surgical Complication Costs
Major gastrectomy complications occur in 15-25% of cases and cost USD 15,000-25,000 per readmission, burdening payers and delaying adjuvant therapy, which can worsen survival outcomes by 10-15% for affected patients. Data from public hospitals in Brazil, South Africa, and Indonesia show that complication care absorbs up to 30% of total in-patient oncology budgets, crowding out funds for modern systemic agents. Enhanced recovery after surgery and laparoscopic approaches are trimming complication rates to near 10% in high-volume centers, yet capital expenditure for robotics remains prohibitive for many middle-income countries. Until broader surgical standardization is achieved, payers may cap spending on premium adjuvant drugs for high-risk candidates, dampening uptake potential across parts of the gastric cancer treatment market. Consortiums involving device makers, surgical training bodies, and multilateral lenders are exploring outcome-based financing to lower entry barriers for minimally invasive platforms, but tangible impact will take several budget cycles to manifest.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Earlier HER2-Positive Testing Protocols
- China's Volume-Based Procurement Price Drops
- Limited Biomarker Reimbursement Outside Tier-1 Cities
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Immunotherapy generated roughly USD 1.2 billion in revenue within the gastric cancer treatment market in 2025, representing the segment with the fastest 13.45% CAGR and confirming its foundational role in modern care algorithms. Chemotherapy nonetheless kept a formidable 42.19% share during 2024 because it remains the backbone of first-line regimens, particularly in metastatic settings, and retains price advantages that make it the default in budget-constrained hospitals. Surgical resection volumes are climbing on the back of enhanced perioperative protocols, but systemic therapy cycles per patient continue to rise as immunologic agents extend survival, thereby sustaining repeat dosing. Radiation therapy holds a modest niche, largely confined to locally advanced tumors where organ preservation strategies augment resection margins.
The rapid pivot toward multidrug protocols blurs historical categorizations: checkpoint inhibitors now launch concurrently with cytotoxic backbones, and trastuzumab deruxtecan plus nivolumab combinations have progressed into Phase 3 testing for adjuvant settings, indicating that "combination therapy" will soon eclipse single-agent categories. Targeted therapy uptake accelerates whenever HER2 or FGFR2 testing is reimbursed, while palliative and supportive care regimens start earlier as improved survival prolongs symptom-management needs. Owing to these interlocking lines of therapy, specialist oncologists increasingly view drug selection through an integrated platform lens rather than discrete classes, a perspective that favors companies able to bundle immunotherapy, ADCs, and supportive agents into coordinated offerings across the gastric cancer treatment market.
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors registered the single-largest 20.23% share of 2024 drug-class revenue, reflecting their entrenchment as standard of care across multiple lines. Yet their annual growth is moderating as penetration in high-income markets nears saturation. In contrast, FGFR2 inhibitors are projected to log the most rapid 12.55% CAGR, driven by striking response rates near 42% in FGFR2-amplified tumors and expected approvals in Japan and South Korea by 2026. On the horizon, bispecific antibodies that fuse PD-1 blockade with FGFR2 targeting are entering early clinical evaluations, setting the stage for step-change efficacy that could boost class share further.
Cytotoxic agents retain relevance by anchoring novel regimens and maintaining reimbursement advantages, especially in markets where biosimilar doxorubicin or oxaliplatin cost pennies on the dollar compared with branded biologics. HER2 antagonists strengthened footholds after the FDA's tumor-agnostic approval for trastuzumab deruxtecan in April 2024, which prompted universal HER2 screening for all metastatic presentations. VEGF/VEGFR inhibitors and ADCs supply important adjunct activity: vascular normalization improves immune infiltration, while ADCs deliver lethal payloads to marker-rich cells, amplifying synergy with immune checkpoint blockade. Collectively, the mosaic of drug classes underscores that sustained differentiation arises from precise patient targeting and modular combination potential, reinforcing multiplatform strategies across the gastric cancer treatment market.
The Gastric Cancer Treatment Market Report is Segmented by Therapy Type (Surgery, Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy, and More), Drug Class (Cytotoxic Agents, HER2 Antagonists, and More), Route of Administration (Intravenous, Oral), Disease Stage (Early Stage 0-IA, Resectable IB-III, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America generated 42.23% of global revenue in 2024 on the strength of broad insurance coverage, high drug pricing power, and expedited FDA review routes such as breakthrough therapy and real-time oncology review that speed access by six to eight months versus standard pathways. Yet growth deceleration is visible as payers layer value-based formularies: Canada's May 2025 time-limited reimbursement for trastuzumab deruxtecan links payment continuation to interim real-world outcomes, foreshadowing broader outcome-based contracts.
Asia-Pacific leads growth with a 15.56% CAGR, fueled by China's volume-based procurement, India's expanding oncology infrastructure, and Japan's near-automatic reimbursement for approved agents within 90 days. Chinese hospital claims show nivolumab usage tripled in lower-tier cities after inclusion in the 2024 procurement round, highlighting volume elasticity. India's government cancer hospital network added eight new tertiary centers in 2025, each equipped with molecular diagnostics labs that fast-track biomarker screening. Japanese regulators approved a new AI-guided endoscopy system in April 2025, positioning the country to sustain leadership in early detection that feeds case volumes into systemic therapy pipelines.
Europe remains a mature yet cautious adopter, with health-technology-assessment rigor pushing companies to amass real-world evidence fast to secure national reimbursements. Germany's statutory insurers widely reimburse perioperative immunotherapy after positive IQWiG appraisal, whereas Italy requires price-volume agreements that cap public spending. South America and the Middle East/Africa together account for just under 7% of the gastric cancer treatment market but hold latent upside as multinationals pilot patient-assistance schemes that subsidize biomarker testing and co-pay support. Broadly, geographic diversification reduces overexposure to any single reimbursement environment and adds resilience to the global gastric cancer treatment market.
- Roche
- Merck
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd.
- Ono Pharmaceutical
- Pfizer
- AstraZeneca
- BeiGene Ltd.
- Astellas Pharma
- Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
- CARsgen Therapeutics
- MacroGenics
- Seagen
- Eisai
- Zai Lab Limited
- Innovent Biologics, Inc.
- Amgen
- Abbvie
- Chugai Pharmaceutical
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Aging population & H. pylori prevalence upswing
- 4.2.2 Uptake of PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors
- 4.2.3 Earlier HER2-positive testing protocols
- 4.2.4 China's volume-based procurement price drops
- 4.2.5 AI-driven endoscopic screening pilots
- 4.2.6 mRNA neo-antigen vaccine pipelines
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High post-surgical complication costs
- 4.3.2 Limited biomarker reimbursement outside Tier-1 cities
- 4.3.3 Shortage of GI oncology specialists in LATAM
- 4.3.4 Supply-chain fragility for liposomal formulations
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.6.1 Companion-diagnostic co-development
- 4.6.2 AI-enhanced endoscopy & pathology
- 4.6.3 Drug-delivery innovations (ADCs, liposomes, BiTEs)
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7.2 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.5 Threat of Substitutes
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD Bn)
- 5.1 By Therapy Type
- 5.1.1 Surgery
- 5.1.2 Chemotherapy
- 5.1.3 Radiation Therapy
- 5.1.4 Targeted Therapy
- 5.1.5 Immunotherapy
- 5.1.6 Combination Therapy
- 5.1.7 Palliative & Supportive Care
- 5.2 By Drug Class
- 5.2.1 Cytotoxic Agents
- 5.2.2 HER2 Antagonists
- 5.2.3 PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors
- 5.2.4 VEGF / VEGFR Inhibitors
- 5.2.5 FGFR2 Inhibitors
- 5.2.6 ADCs (Antibody-Drug Conjugates)
- 5.2.7 Others
- 5.3 By Route of Administration
- 5.3.1 Intravenous
- 5.3.2 Oral
- 5.4 By Disease Stage
- 5.4.1 Early Stage (0-IA)
- 5.4.2 Resectable (IB-III)
- 5.4.3 Unresectable Locally Advanced
- 5.4.4 Advanced / Metastatic
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Australia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 GCC
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- 6.3.2 Merck & Co., Inc.
- 6.3.3 Bristol Myers Squibb Company
- 6.3.4 Eli Lilly and Company
- 6.3.5 Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.6 Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.7 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.8 AstraZeneca PLC
- 6.3.9 BeiGene Ltd.
- 6.3.10 Astellas Pharma Inc.
- 6.3.11 Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.12 CARsgen Therapeutics
- 6.3.13 MacroGenics, Inc.
- 6.3.14 Seagen Inc.
- 6.3.15 Eisai Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.16 Zai Lab Limited
- 6.3.17 Innovent Biologics, Inc.
- 6.3.18 Amgen Inc.
- 6.3.19 AbbVie Inc.
- 6.3.20 Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




