PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906090

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906090
Southeast Asia Tourism - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Southeast Asia tourism market is expected to grow from USD 35.52 billion in 2025 to USD 39.52 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 67.41 billion by 2031 at 11.27% CAGR over 2026-2031.
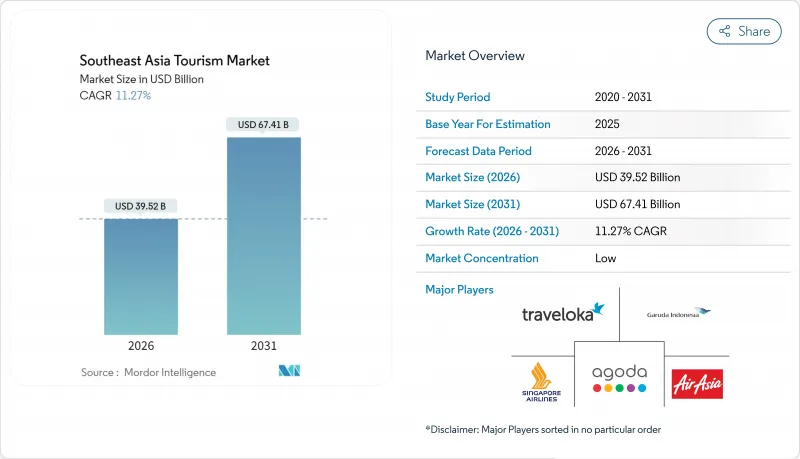
This pace firmly places the Southeast Asia tourism market among the world's fastest-expanding visitor economies, outstripping the growth rates in most other regions. The momentum in Southeast Asia's tourism market is driven by three key factors: streamlined visa reforms that have minimized travel barriers, the strategic network expansion by low-cost carriers resulting in reduced airfares, and the consistent growth in disposable incomes across a substantial consumer base. These drivers collectively enhance both origin and destination options, diversify revenue channels, and reinforce confidence in the market's ability to withstand future disruptions. Accommodation services remain the primary revenue generator; however, digital travel services, particularly dynamic packaging and in-destination activities, are capturing an increasing share of consumer spending as mobile platforms dominate the search, booking, and review processes. The MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences, and Exhibitions) segment is witnessing a resurgence, with corporate planners finalizing long-delayed events. Simultaneously, leisure tourism continues to serve as the foundation, supporting employment within the hospitality sector across the region.
Southeast Asia Tourism Market Trends and Insights
Visa Liberalization & E-Visa Roll-outs Drive Regional Integration
Southeast Asian policymakers now treat seamless entry as the linchpin of competitiveness, and the recent wave of exemptions illustrates collective intent. Thailand doubled visa-free stays to 60 days for 93 nationalities and introduced the Destination Thailand Visa that grants 180-day renewable residence to remote workers. Vietnam has enhanced its business environment by extending 45-day visa waivers for 12 European countries until 2028 and implementing digital systems to streamline approval processes for other markets. Malaysia has strategically enhanced its tourism inflow by implementing long-term visa waivers for Chinese visitors, while the Philippines has introduced a digital-nomad permit aimed at attracting the global remote workforce. These policy measures have streamlined application processes and reduced compliance costs, resulting in extended visitor stays and increased expenditure. Collectively, these initiatives strengthen Southeast Asia's position as a leading and accessible multi-country tourism destination.
Expansion of Low-Cost Carrier Networks Transforms Regional Connectivity
Ten budget airlines secured Thai operating certificates in 2024, multiplying city-pair frequencies and linking previously isolated locales such as Mae Sot and Trang. AirAsia Group inaugurated cross-border routes that bypass capital hubs, Cebu Pacific partnered with Traveloka to penetrate mobile-first consumers, and Singapore Airlines deepened joint scheduling with Scoot to fill off-peak slots. Airlines in Southeast Asia are strategically responding to shifting traveler preferences, resulting in notable market changes. A substantial reduction in average round-trip fares, coupled with increased passenger traffic at secondary airports, highlights the region's expanding network density and enhanced geographic accessibility. The establishment of dedicated low-cost carrier (LCC) terminals in key cities such as Bangkok, Jakarta, and Ho Chi Minh City has optimized operational efficiency by reducing turnaround times. This operational improvement enables tighter scheduling, maintaining profitability despite lower fare yields. The availability of cost-effective and frequent flights provides the Southeast Asia tourism market with the flexibility to capitalize on demand driven by spontaneous travel decisions, particularly among millennials and first-time travelers.
Political Instability Creates Regional Tourism Disruption
Myanmar's dramatic visitor collapse after the 2021 coup eliminated a once-promising destination and disrupted Mekong multi-country circuits. Cruise lines rerouted to avoid off-limit ports, and insurers raised premiums on regional itineraries that traverse contested waters. Sporadic protests in Malaysia and Indonesia occasionally trigger foreign travel advisories, leading to last-minute cancellations that squeeze small operators with thin cash reserves. Political risk, therefore, remains an unpredictable drag on the Southeast Asia tourism market, prompting businesses to invest in scenario planning and diversified source markets.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Disposable Income of the Intra-Regional Middle Class Fuels Domestic Demand
- Digital-Nomad Visa Schemes Capture Long-Stay Tourism Premium
- Infrastructure Bottlenecks Constrain Secondary-Destination Development
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The domestic channel retains a 63.72%, proving a shock absorber when borders closed. Stimulus vouchers in Thailand and Indonesia funded hotel discounts and free attraction passes, sustaining labour in provincial economies. Vietnam reported 110 million domestic trips in 2024, with a significant shift observed in consumer behaviour. Mid-scale hotels experienced an increase in occupancy rates, indicating a trend where local travellers are opting for higher-quality accommodations. This development highlights a growing preference among domestic tourists to upgrade their lodging choices, reflecting an evolution in spending patterns and travel preferences within the market. A similar pattern emerged in Malaysia, where domestic trips to Penang and Kota Kinabalu doubled quarter-on-quarter, pushing room rates up despite moderate volumes. The Southeast Asia tourism market thus benefits from a vast internal customer base that backstops employment and public revenues.
International travel, though currently smaller, advances faster on an 11.05% trajectory. China's tourism sector has demonstrated a significant recovery, approaching pre-pandemic performance levels. Concurrently, extended visa waivers have encouraged European travelers to prolong their stays, contributing to increased tourism revenue. Long-haul travelers are generating higher daily expenditures compared to domestic tourists, thereby enhancing foreign-exchange inflows and strengthening the economic impact of international tourism. The introduction of digital-nomad visas is mitigating the effects of seasonality by transforming peak-period visitors into consistent, year-round contributors to the tourism economy. Furthermore, the adoption of simplified e-visa platforms is reducing customer acquisition costs for marketers, improving operational efficiency. By 2031, the Southeast Asia tourism market is expected to achieve greater financial stability through a balanced mix of domestic and international tourist flows, ensuring more predictable cash cycles and sustainable growth.
The Southeast Asia Tourism Market Report Segments the Industry Into by Origin (Domestic and International), by Type (Accommodation Services and Travel Services), by Purpose (Leisure, Business, and Other), and by Geography (Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, and Other). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Singapore Airlines
- AirAsia Group
- Agoda (Booking Holdings)
- Traveloka
- Garuda Indonesia
- Thai Airways International
- Vietnam Airlines
- Cebu Pacific
- Malaysia Airlines
- Jetstar Asia
- Trip.com Group
- Expedia Group
- Marriott International
- AccorHotels
- Hilton Worldwide
- Hyatt Hotels Corporation
- Banyan Tree Holdings
- Genting Group
- TUI Group
- Minor Hotels
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Visa liberalization & e-visa roll-outs
- 4.2.2 Expansion of low-cost carrier (LCC) networks
- 4.2.3 Rising disposable income of intra-regional middle class
- 4.2.4 Digital-nomad visa schemes and long-stay demand
- 4.2.5 Heritage-conservation PPPs catalyzing cultural tourism
- 4.2.6 Early adoption of crypto-payments in select destinations
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Political instability & travel advisories
- 4.3.2 Infrastructure bottlenecks in Tier-2/3 cities
- 4.3.3 Overtourism-driven visitor caps at heritage sites
- 4.3.4 Climate-risk insurance cost spikes for airlines & resorts
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7.2 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.5 Threat of Substitutes
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Origin
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 By Type
- 5.2.1 Accommodation Services
- 5.2.2 Travel Services
- 5.3 By Purpose
- 5.3.1 Leisure
- 5.3.2 Business
- 5.3.3 Visiting Friends & Relatives (VFR)
- 5.3.4 Religious
- 5.3.5 Meetings-Incentives-Conferences-Exhibitions (MICE)
- 5.3.6 Other Purposes
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 Indonesia
- 5.4.2 Thailand
- 5.4.3 Malaysia
- 5.4.4 Singapore
- 5.4.5 Philippines
- 5.4.6 Vietnam
- 5.4.7 Rest of Southeast Asia
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Singapore Airlines
- 6.4.2 AirAsia Group
- 6.4.3 Agoda (Booking Holdings)
- 6.4.4 Traveloka
- 6.4.5 Garuda Indonesia
- 6.4.6 Thai Airways International
- 6.4.7 Vietnam Airlines
- 6.4.8 Cebu Pacific
- 6.4.9 Malaysia Airlines
- 6.4.10 Jetstar Asia
- 6.4.11 Trip.com Group
- 6.4.12 Expedia Group
- 6.4.13 Marriott International
- 6.4.14 AccorHotels
- 6.4.15 Hilton Worldwide
- 6.4.16 Hyatt Hotels Corporation
- 6.4.17 Banyan Tree Holdings
- 6.4.18 Genting Group
- 6.4.19 TUI Group
- 6.4.20 Minor Hotels
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 Cross-border eco-tourism circuits along the Mekong Basin
- 7.2 Integrated esports-tourism packages tied to regional gaming events




