PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910473

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910473
Industrial Grade Urea - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Industrial Grade Urea Market was valued at 195.37 Million tons in 2025 and estimated to grow from 198.87 Million tons in 2026 to reach 217.29 Million tons by 2031, at a CAGR of 1.79% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
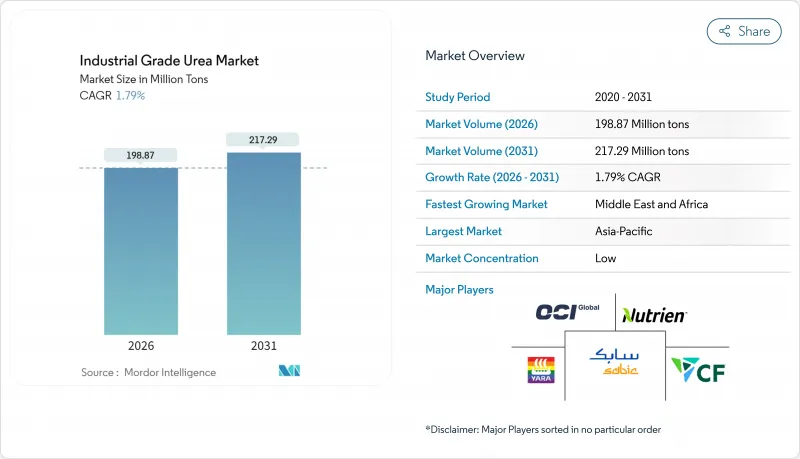
The market's modest trajectory reflects a mature landscape balancing cost-driven production economics with rising sustainability expectations. Demand growth flows mainly from agriculture, yet a new pull from diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) and engineered-wood resins diversifies the revenue base. Energy-price volatility, consolidation among large producers, and stricter emissions targets dominate strategic conversations, while process innovations aimed at green ammonia integration promise longer-term competitiveness.
Global Industrial Grade Urea Market Trends and Insights
Rising Diesel Exhaust Fluid Adoption Transforms Technical Grade Demand
Commercial vehicle emission standards underpin a robust uptake of DEF, with China's National VI regulations alone expected to lift DEF consumption to 25 million tons in 2025. European players are integrating DEF lines into existing ammonia-urea complexes, illustrated by CF Industries' Blue Point project that will add 1.4 million tpy low-carbon ammonia from 2029. This defensively hedges against seasonal fertilizer swings and supports premium pricing. North American fleets following EPA 2027 rules further reinforce a medium-term demand floor, while off-road machinery in construction and mining extends the addressable market. Overall, DEF's rise shifts a portion of the industrial-grade urea market toward higher-purity products, indirectly raising margins and encouraging investments in purification infrastructure.
Green Ammonia Integration Reshapes Production Economics
The European Union's RED III requirement for 42% renewable hydrogen by 2030 accelerates low-carbon ammonia adoption, turning electrolyzer costs and renewable power availability into new profit levers. Stamicarbon's NX Stami Green Ammonia modules slash CAPEX 25-30% at 50-500 t per day scale, enabling regional supply hubs that shorten freight routes and curb scope 3 emissions. Pilot projects in the Middle East aim to couple solar-powered electrolysis with urea synthesis, signaling a shift away from single-site mega-plants. Early adopters gain compliance advantages in carbon-regulated export markets and secure offtake agreements from food and beverage firms seeking lower-footprint supply chains. Over the long term, these developments could moderate the industrial-grade urea market's exposure to natural-gas price spikes and carbon costs.
Natural Gas Price Volatility Threatens Production Viability
Spot gas swung from USD 6.54/MMBtu in 2022 to USD 2.66/MMBtu in 2023, exposing producers whose feedstock can constitute 70-90% of cash costs. European plants curtailed utilization to 75% amid the 2022 energy crisis, redirecting trade flows toward Middle Eastern suppliers. U.S. operators with shale-based gas benefit from structural cost advantages, whereas net-importing areas confront negative margins during price spikes. Hedging strategies, dual-fuel capabilities, and green ammonia investments are emerging defenses but require substantial capital and policy support.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Technical Grade Applications Drive Premium Segment Growth
- Emerging Asia Fertilizer Demand Sustains Long-term Growth
- Environmental Regulations Constrain Application Growth
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Fertilizer grade accounted for 84.65% of the industrial grade urea market in 2025 and is forecast to expand at a 1.83% CAGR to 2031. The technical grade slice, while smaller, accelerates on DEF demand, potentially lifting its share by 130 basis points within the outlook period. Feed grade addresses ruminant nutrition niches with stringent purity needs. Process innovations such as pool-condenser reactors lower CAPEX by up to 30%, enabling multiproduct configurations that respond swiftly to shifting margins.
Flexibility matters because DEF and melamine demand decouple from crop cycles, smoothing revenue seasonality. Producers certified for automotive-grade urea meet ISO 22241 quality thresholds, commanding sustained premiums. In contrast, fertilizer producers remain exposed to subsidy regimes and environmentally driven application caps. This divergence underlines why technical grade is the fastest growing component of the industrial grade urea market size across the forecast.
The Industrial Grade Urea Market Report is Segmented by Grade (Fertilizer Grade, Technical Grade, and Feed Grade), End-User Industry (Agriculture, Chemical, Automotive, Medical, and Other End-User Industries), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle-East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (Tons)
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific dominated the industrial-grade urea market size with a 66.10% share in 2025, driven by India's and China's crop inputs and rising DEF uptake. Local production expansion in India aims for self-sufficiency by 2025, potentially trimming import reliance.
The Middle East and Africa region posts the fastest 2.33% CAGR through 2031, fueled by low-cost gas feedstock and export-oriented capacity additions in Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Algeria. New complexes integrate green-hydrogen pilot lines to future-proof carbon competitiveness. Europe's share contracts amid high gas costs and decarbonization policies; several plants operate seasonally or under curtailment, increasing import reliance on North Africa and the United States.
North America maintains steady demand, benefiting from abundant shale gas and ongoing DEF adoption in heavy-duty fleets. Trade patterns continue shifting: China's H1 2024 export volumes fell 90% following policy restrictions, creating spot shortages in Southeast Asia and Latin America. Middle Eastern producers quickly captured these gaps, affirming their swing-supplier status. Over the long term, Asia-Pacific retains leadership, yet its growth moderates as sustainability policies and domestic supply priorities reshape external trade.
- Acron
- BASF
- CF Industries Holdings Inc.
- Chambal Fertilisers & Chemicals Ltd
- China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC)
- EuroChem Group
- Genesis Fertilizers
- IFFCO
- Industries Qatar
- Koch Fertilizer LLC
- National Fertilizers Limited
- Notore Chemical Industries PLC
- Nutrien Ltd
- OCI
- Paradeep Phosphates Ltd
- Petrobras
- PT Pupuk Kalimantan Timur (PKT)
- SABIC
- The Chemical Company (TCC)
- Uralchem JSC
- Yara
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 High applicability of technical-grade urea
- 4.2.2 Rising diesel exhaust fluid (DEF/AdBlue) adoption in on-road and off-road vehicles
- 4.2.3 Expanding fertilizer consumption in emerging Asia
- 4.2.4 Increased melamine and resin production for engineered wood
- 4.2.5 Shift toward green ammonia-based urea via low-carbon hydrogen
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Indiscriminate over-application in groundwater-stressed regions
- 4.3.2 Volatile natural-gas pricing impacting production cost
- 4.3.3 Stricter fertilizer subsidy reforms in major consuming countries
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Policy Analysis
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.6.1 Production Process
- 4.6.2 Patent Analysis
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Degree of Competition
- 4.8 Feedstock Analysis
- 4.9 Import-Export Trends
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Volume)
- 5.1 By Grade
- 5.1.1 Fertilizer Grade
- 5.1.2 Technical Grade
- 5.1.3 Feed Grade
- 5.2 By End-user Industry
- 5.2.1 Agriculture
- 5.2.2 Chemical
- 5.2.3 Automotive
- 5.2.4 Medical
- 5.2.5 Other End-user Industries
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.1.1 China
- 5.3.1.2 India
- 5.3.1.3 Japan
- 5.3.1.4 South Korea
- 5.3.1.5 ASEAN
- 5.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2 North America
- 5.3.2.1 United States
- 5.3.2.2 Canada
- 5.3.2.3 Mexico
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 France
- 5.3.3.3 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.4 Italy
- 5.3.3.5 Russia
- 5.3.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 South Africa
- 5.3.5.3 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Acron
- 6.4.2 BASF
- 6.4.3 CF Industries Holdings Inc.
- 6.4.4 Chambal Fertilisers & Chemicals Ltd
- 6.4.5 China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC)
- 6.4.6 EuroChem Group
- 6.4.7 Genesis Fertilizers
- 6.4.8 IFFCO
- 6.4.9 Industries Qatar
- 6.4.10 Koch Fertilizer LLC
- 6.4.11 National Fertilizers Limited
- 6.4.12 Notore Chemical Industries PLC
- 6.4.13 Nutrien Ltd
- 6.4.14 OCI
- 6.4.15 Paradeep Phosphates Ltd
- 6.4.16 Petrobras
- 6.4.17 PT Pupuk Kalimantan Timur (PKT)
- 6.4.18 SABIC
- 6.4.19 The Chemical Company (TCC)
- 6.4.20 Uralchem JSC
- 6.4.21 Yara
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




