PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911267

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911267
North America Prefabricated Housing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The North America prefabricated housing market was valued at USD 32.3 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 34.5 billion in 2026 to reach USD 47.98 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 6.82% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
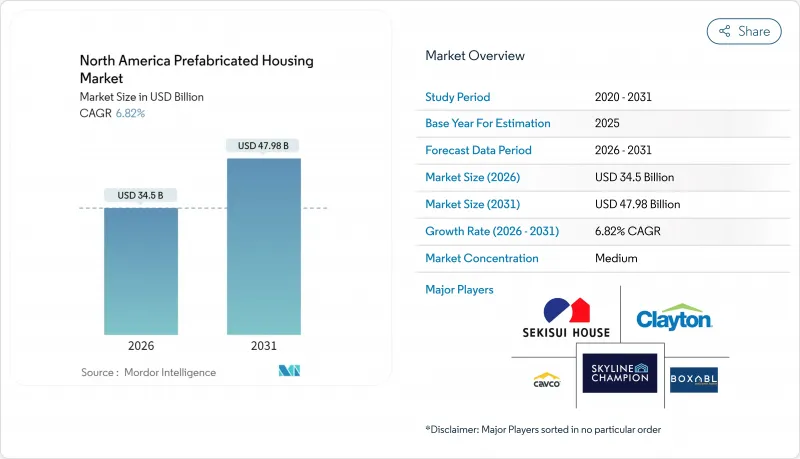
The uptick mirrors ongoing efforts to close an estimated 4-to-7 million-unit housing gap, which has intensified price inflation across the region. Strong federal and provincial incentives, rapid urban in-migration, and widening labor shortages are steering developers toward factory-built solutions that shorten build cycles and control cost volatility. Energy-efficiency mandates are another growth lever; HUD's adoption of the 2021 International Energy Conservation Code for all federally backed homes is forecast to cut annual utility bills by at least USD 400 million while curbing 2 million tons of carbon dioxide emissions. At the same time, technology convergence, from BIM to large-format 3-D printing, is squeezing waste, boosting precision, and allowing mass customization. Competitive intensity remains high as legacy manufacturers expand capacity while venture-backed disruptors introduce robotics-powered micro-factories that promise sub-USD 120-per-square-foot delivered costs.
North America Prefabricated Housing Market Trends and Insights
Government's Push for Affordable Housing Programs Reshapes Market Dynamics
Fresh capital, streamlined codes, and risk-sharing incentives are tilting project economics toward the North America prefabricated housing market. HUD's new Manufactured Home Community loan gives FHA-backed financing to cooperative resident groups, unlocking ownership for 5,000 families over five years. Canada's USD 50 million Regional Homebuilding Innovation Initiative prioritizes modular and 3-D printed housing, while Virginia's statewide adoption of ICC/MBI off-site standards has already shaved permit lead times by up to 30%. Mexico's National Housing Plan earmarks land parcels and low-interest INFONAVIT loans, injecting volume into emerging prefab corridors. Collectively, these measures fill financing gaps and speed entitlements, providing the dependable demand backdrop manufacturers need for multi-shift plant utilization.
Rapid Urbanization Drives Accelerated Construction Timelines
Metro areas from Phoenix to Toronto are scrambling to meet surging household formation, pushing municipalities to favor factory-built housing that can halve onsite schedules. Canada must add 3.5 million units by 2030 to restore affordability, and sees modular delivery trimming project duration by 50%. Vermont's housing agency lists off-site fabrication as a prerequisite to hit its 36,000-unit goal, noting that factory output mitigates labor deficits and winter weather delays. AI-enabled projects such as West Oakland's 300-unit Phoenix complex illustrate how digital twins and robotic assembly can erect super-energy-efficient structures in under two weeks. Shorter build windows translate directly into faster lease-up, improved IRRs, and trimmed carrying costs, underpinning broader adoption.
High Logistics Cost for Oversized Module Transportation
Module widths beyond 12 feet require specialized carriers, police escorts, and restricted travel windows, inflating transport bills by 20-40% and eroding plant-level savings. Tariffs imposed on Canadian lumber in 2024 kept cross-border material costs elevated, while the 80,000-driver deficit in the U.S. long-haul sector tightened freight capacity and boosted spot rates. Mexico's 2021 subcontracting reform adds another paperwork layer for cross-border installers, further straining timelines. Even with multi-plant networks, manufacturers face circuitous routing to avoid low bridges and stringent state permitting, nudging the market toward panelized and flat-pack kits that better utilize trailer cube.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cost-Efficient Off-Site Manufacturing Transforms Construction Economics
- Tech Leap: BIM, 3-D Printing, and Automated Manufacturing
- Scarcity of Skilled Prefab Fabricators & Installers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Timber commanded a 60.35% revenue share in 2025 as most production lines and framing crews remain optimized for wood, yet the segment recorded only mid-single-digit growth while concrete marked a robust 9.44% CAGR. Wildfire-prone states such as California and Oregon are driving a pivot toward insulated concrete panels that withstand flame exposure and qualify owners for 10-15% lower insurance premiums. The North America prefabricated housing market size attributed to concrete solutions is poised to almost double by 2031 as mortgage lenders increasingly factor climate-risk scoring into underwriting. Builders also see value in the thermal-mass benefits of concrete, which cut HVAC tonnage requirements and boost point values in green-building rating systems. Over the next five years, hybridized mass-timber superstructures topped with 3-D printed concrete shear cores are expected to enter pilot production, blending sustainability credentials with structural robustness. Carbon capture additives, coupled with low-temperature kiln technologies, aim to deflate concrete's embodied carbon by another 30%, aligning with incoming Scope 3 disclosure rules. Meanwhile, cross-laminated-timber factories continue to chase incremental gains through optimized finger-jointing and resin substitutions that lower VOC emissions and accelerate cure times.
Concrete's rise stems from a widening array of pre-stressed panel assemblies, some formed adjacent to the jobsite, that dramatically cut trucking distances and set times. Pre-tensioned panels reach 4,000 psi within hours, allowing cranes to install full structural walls the same day, compressing project schedules by 20%. Bulk bag mixes infused with graphene or volcanic ash are also improving tensile strength, letting designers reduce rebar density and save material weight. Insurance carriers are lobbying state regulators to recognize concrete's superior fire-resistance ratings, an adjustment that could unlock more credit for homebuyers and developers. The mass-timber camp counters with life-cycle analysis, citing 39-51% lower global warming potential than concrete, yet adoption momentum now heavily factors in regional disaster profiles. Over the projection horizon, both material streams will coexist, with builders matching material choice to lot location, code requirements, and climate-risk scoring criteria.
The North America Prefabricated Housing Market Report is Segmented by Material Type (Concrete, Glass, Metal, Timber, Other Materials), by Type (Single Family, Multi Family), by Product Type (Modular Homes, Panelized & Componentized Systems, Manufactured Homes, Other Prefab Types), and by Country (United States, Canada, Mexico). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Clayton Homes (Berkshire Hathaway)
- Skyline Champion Corporation
- Cavco Industries Inc.
- Sekisui House Ltd (North America arm)
- Boxabl Inc.
- Plant Prefab Inc.
- Method Homes
- Modular Home Builder LLC
- BluHomes Inc.
- Module Housing
- Indie Dwell Inc.
- Connect Homes
- FullStack Modular
- Weyerhaeuser NR Co. (Engineered Wood Prefab)
- MiTek Inc. (Berkshire subsidiary - PEB)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Government push for affordable housing (FHA, HUD, CMHC programs)
- 4.2.2 Rapid urbanisation & housing shortfall accelerate build-times
- 4.2.3 Cost-efficient off-site manufacturing vs conventional build
- 4.2.4 Tech leap: BIM, 3-D printing & automated precast factories
- 4.2.5 ESG-linked green-building mandates favour low-carbon prefab
- 4.2.6 Warehousing & data-centre boom needs large-span PEBs
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High logistics cost for oversized modules
- 4.3.2 Scarcity of skilled prefab fabricators & installers
- 4.3.3 Fragmented state- & provincial codes delay project approvals
- 4.3.4 Seismic-safety perception gaps in earthquake-prone zones
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Brief on Different Structures Used in Prefabricated Housing
- 4.9 Cost Structure Analysis of Prefabricated Housing
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Material Type
- 5.1.1 Concrete
- 5.1.2 Glass
- 5.1.3 Metal
- 5.1.4 Timber
- 5.1.5 Other Materials
- 5.2 By Type
- 5.2.1 Single Family
- 5.2.2 Multi Family
- 5.3 By Product Type
- 5.3.1 Modular Homes
- 5.3.2 Panelized & Componentized Systems
- 5.3.3 Manufactured Homes
- 5.3.4 Other Prefab Types
- 5.4 By Region
- 5.4.1 United States
- 5.4.2 Canada
- 5.4.3 Mexico
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Clayton Homes (Berkshire Hathaway)
- 6.4.2 Skyline Champion Corporation
- 6.4.3 Cavco Industries Inc.
- 6.4.4 Sekisui House Ltd (North America arm)
- 6.4.5 Boxabl Inc.
- 6.4.6 Plant Prefab Inc.
- 6.4.7 Method Homes
- 6.4.8 Modular Home Builder LLC
- 6.4.9 BluHomes Inc.
- 6.4.10 Module Housing
- 6.4.11 Indie Dwell Inc.
- 6.4.12 Connect Homes
- 6.4.13 FullStack Modular
- 6.4.14 Weyerhaeuser NR Co. (Engineered Wood Prefab)
- 6.4.15 MiTek Inc. (Berkshire subsidiary - PEB)
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




