PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939099

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939099
Diesel Generator - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Diesel Generator market is expected to grow from USD 25.30 billion in 2025 to USD 26.86 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 36.24 billion by 2031 at 6.18% CAGR over 2026-2031.
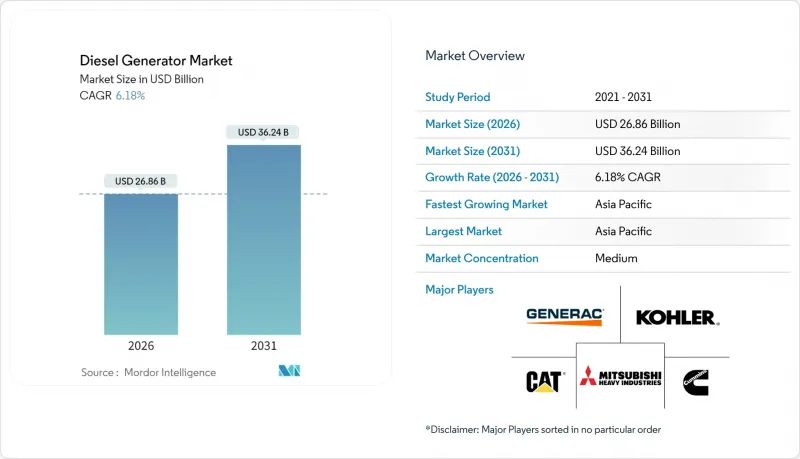
The forecast underscores the market's continued relevance even as grids add more renewables and regulators tighten emission limits. Demand pivots on three structural forces: the need for resilient power to protect digitalized operations, the rapid industrial build-out in regions where grids cannot keep pace, and the availability of advanced Tier 4 Final engines that sharply cut particulate matter and nitrogen oxides. At the same time, hybrid microgrids combine batteries and photovoltaics with diesel generation, enabling operators to limit fuel consumption without compromising availability. Mid-range 75-375 kVA sets now incorporate remote monitoring, aftertreatment, and parallel-ready switchgear once reserved for megawatt-class units, widening the addressable user base.
Global Diesel Generator Market Trends and Insights
Rising Demand for Uninterrupted Power in Critical Infrastructure
Hospitals, financial exchanges, and semiconductor fabs now categorise power loss as a business-continuity risk on par with cyberattacks. The Walsh Data Center in California installed 96 MW of diesel backup to protect cloud workloads, an investment illustrating how operators equate generator capacity with revenue protection. Predictive analytics embedded in controller firmware schedule maintenance around live loads, lowering lifecycle costs and turning generators into active facility assets. As average downtime costs exceed USD 100,000 per hour for many digital businesses, procurement teams increasingly prioritize proven diesel reliability over capital expenditure savings. This trend supports premium pricing for Tier 4 Final sets that combine remote diagnostics with 99% lower particulate emissions, preserving the diesel generator industry's value proposition even under stricter regulations.
Rapid Industrialisation and Infrastructure Build-out in APAC & Africa
Factory output in Southeast Asia and Africa rises faster than utilities can reinforce transmission. Industrial parks frequently integrate 10-20 MW of on-site generation that synchronises with weak grids or runs islanded during outages. Turnkey rental fleets supplied by Aggreko and Cummins keep green-field mines in Sub-Saharan Africa operational until permanent lines arrive, shortening project schedules by several years. Diesel generators are delivered, commissioned, and load-tested in months, compared with multi-year grid-extension timelines. This speed advantage fuels a virtuous cycle where industrial growth demands more generation capacity, enabling further expansion and keeping the diesel generator industry on a steady upward trajectory in emerging economies.
Stricter Emission Norms Favouring Gas & Hybrid Sets
California's Air Resources Board is pushing diesel particulate and NOx thresholds below Tier 4 Final, motivating some fleet owners to switch to natural-gas units or hybrid microgrids. The European Stage V rule set mandates the use of selective catalytic reduction and particulate filters on engines exceeding 19 kW, thereby increasing acquisition costs and complicating maintenance schedules. While these standards pose a headwind, engine manufacturers have responded with cooled-EGR combustion strategies, advanced fuel injection, and renewable diesel compatibility that meet compliance without eroding performance. Facilities with mission-critical loads continue to value diesel's energy density, thereby preserving the diesel generator industry's relevance in premium segments.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Grid Instability Caused by Extreme Weather Events
- Edge Data-Centre Roll-outs in Tier-2 Cities
- Growing Penetration of Battery-Storage-Backed UPS
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The below-75 kVA class retained the largest 43.25% slice of the diesel generator industry share in 2025, reflecting strong uptake in residential, small commercial, and telecom sites where modest loads warrant compact sets. Yet the 375-750 kVA band is advancing at a 7.55% CAGR to 2031, outpacing every other bracket as factories, data-processing hubs, and large retail footprints migrate to solutions that balance cost and resiliency. Mid-range models now ship with Tier 4-Final aftertreatment, hybrid-ready controls, and cloud telemetry once reserved for multi-megawatt units.
Caterpillar's compact architecture reduces installation space by 31% while maintaining full EPA compliance, a design leap that lowers total installed costs and accelerates adoption in brownfield facilities. At the top end, 750-2,000 kVA and >2,000 kVA sets power mines and hyperscale data centers, which require extended runtime with utility-grade voltage regulation. The widening performance gap between entry-level and feature-rich models signals a maturing diesel generator industry, in which application demands, rather than price alone, dictate buying criteria and open premium positioning for OEMs.
The Diesel Generator Market Report is Segmented by Capacity (Below 75 KVA, 75 To 375 KVA, 375 To 750 KVA, 750 To 2, 000 KVA, and Above 2, 000 KVA), Application (Stand-by/Backup Power, Prime/Continuous Power, and Peak-shaving/Load Management), End User (Residential, Commercial, and Industrial), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
The Asia-Pacific region holds a leading 48.55% share of the diesel generator industry in 2025 and is projected to expand at a 7.12% CAGR through 2031. Strong factory output, new transport links, and a sharp rise in cloud spending keep demand well ahead of local grid upgrades. China and India account for the majority of installations, as manufacturers rely on on-site sets to protect production from voltage fluctuations. Regional data-center capacity now totals 12,206 MW, with another 14,338 MW under construction, each megawatt of IT load matched by roughly one megawatt of standby power. Singapore's moratorium on new server farms has redirected investment to Johor and Greater Jakarta, widening the geographic spread of generator sales. A rapid 5G rollout requires the addition of thousands of telecom towers, which necessitate small but reliable units. Meanwhile, remote mine sites in Australia and Southeast Asia specify larger hybrid diesel-solar packages to avoid costly grid extensions.
North America is the second-largest region by revenue and exhibits steady growth as utilities enhance their networks to mitigate weather-driven outages. Residential shipments rise 5.82% CAGR to 2027 because homeowners buy protection from longer blackouts caused by hurricanes, wildfires, and ice storms. California's strict emission rules favor Tier 4 Final engines and renewable diesel blends, creating premium sub-segments that value compliance as much as price. The diesel generator industry also benefits from rising demand in Virginia, Texas, and Northern California. They host clusters of hyperscale data centers, and a single campus, such as the 96 MW Walsh facility, can order dozens of medium-speed generators to guarantee uptime for cloud services. In Europe, carbon-reduction goals are prompting buyers to opt for hybrid sets and Stage V-compliant aftertreatment systems that reduce particulate matter and NOx emissions.
The Middle East and Africa are experiencing high single-digit growth as governments invest in building airports, rail corridors, and mines that are far from reliable grids. Developers often pair diesel with solar arrays and batteries to trim fuel costs and simplify logistics in desert or high-altitude terrain. South America mirrors this pattern: copper and lithium miners in Chile, Peru, and Argentina deploy containerized, prime-rated units because grid connections often lag behind project timelines. The diesel generator industry in Brazil and Argentina also adds capacity for food processing and petrochemicals, widening the customer base beyond extractive industries. A stable outlook for global diesel supply, outlined in the International Energy Agency's 2025 report, supports generator availability and pricing across emerging regions. Together, these factors create a diverse demand landscape where integrated solutions that combine diesel reliability with renewable inputs gain traction.
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Cummins Inc.
- Generac Holdings Inc.
- Kohler Co.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd.
- Rolls-Royce Holdings plc (MTU)
- Atlas Copco AB
- Doosan Corp.
- Kirloskar Oil Engines Ltd
- Aggreko plc
- FG Wilson (Caterpillar)
- Perkins Engines Co. Ltd
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Wartsila Oyj Abp
- Yanmar Holdings Co. Ltd
- MTU Onsite Energy
- SDMO Industries (KOHLER-SDMO)
- Weichai Power Co. Ltd
- Baudouin Engines
- Mahindra Powerol
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising demand for uninterrupted power in critical infrastructure
- 4.2.2 Rapid industrialisation & infrastructure build-out in APAC & Africa
- 4.2.3 Grid instability caused by extreme weather events
- 4.2.4 Edge-data-centre roll-outs in Tier-2 cities
- 4.2.5 Surge in telecom tower deployments for 5G
- 4.2.6 Diesel-hybrid micro-grid adoption in off-grid mining
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Stricter emission norms favouring gas & hybrid sets
- 4.3.2 Growing penetration of battery-storage backed UPS
- 4.3.3 Rare-earth supply bottlenecks for Tier-4 engines
- 4.3.4 Higher urban insurance premiums for diesel exhaust risks
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Capacity (kVA)
- 5.1.1 Below 75 kVA
- 5.1.2 75 to 375 kVA
- 5.1.3 375 to 750 kVA
- 5.1.4 750 to 2000 kVA
- 5.1.5 Above 2000 kVA
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Stand-by/Backup Power
- 5.2.2 Prime/Continuous Power
- 5.2.3 Peak-shaving/Load Management
- 5.3 By End User
- 5.3.1 Residential
- 5.3.2 Commercial
- 5.3.3 Industrial
- 5.4 Geographic Analysis
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 NORDIC Countries
- 5.4.2.6 Russia
- 5.4.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 South Korea
- 5.4.3.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.3 South Africa
- 5.4.5.4 Egypt
- 5.4.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Caterpillar Inc.
- 6.4.2 Cummins Inc.
- 6.4.3 Generac Holdings Inc.
- 6.4.4 Kohler Co.
- 6.4.5 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Rolls-Royce Holdings plc (MTU)
- 6.4.7 Atlas Copco AB
- 6.4.8 Doosan Corp.
- 6.4.9 Kirloskar Oil Engines Ltd
- 6.4.10 Aggreko plc
- 6.4.11 FG Wilson (Caterpillar)
- 6.4.12 Perkins Engines Co. Ltd
- 6.4.13 MAN Energy Solutions
- 6.4.14 Wartsila Oyj Abp
- 6.4.15 Yanmar Holdings Co. Ltd
- 6.4.16 MTU Onsite Energy
- 6.4.17 SDMO Industries (KOHLER-SDMO)
- 6.4.18 Weichai Power Co. Ltd
- 6.4.19 Baudouin Engines
- 6.4.20 Mahindra Powerol
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




