PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1852018

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1852018
Philippines Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Philippines freight and logistics market size stands at USD 15.26 billion in 2025 and is projected to advance to USD 20.41 billion by 2030, reflecting a 5.99% CAGR (2025-2030).
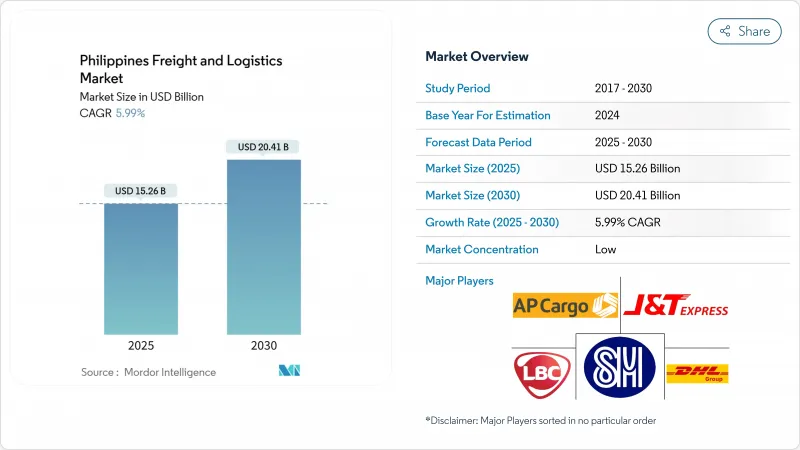
The expansion gains momentum from the PHP 8.8 trillion (USD 158.19 billion) "Build, Better, More" program, liberalized foreign-ownership rules, and increased e-commerce demand. Road freight remains the backbone of the network, yet port automation and air-cargo upgrades are reshaping modal decisions. Foreign investors are entering through joint ventures that pair global expertise with local reach, accelerating technology adoption across warehousing, freight forwarding, and last-mile delivery. Government-led digital connectivity policies, including a USD 750 million World Bank loan, complement physical infrastructure and allow smaller operators to adopt platform business models.
Philippines Freight And Logistics Market Trends and Insights
Infrastructure "Build, Better, More" Program Boosting Road and Port Capacity
The PHP 8.8 trillion (USD 158.19 billion) flagship pipeline has completed 11,945 km of road projects and is constructing 15,769 km more, slashing Luzon travel times by up to 50% and linking Batangas, Manila, Clark, and Subic into a unified corridor. Harmonized road, port, and rail upgrades promise lower transit times, tighter supply-chain scheduling, and higher truck turns. Investors are fast-tracking distribution hubs near the new expressways to secure first-mover advantages. Contract logistics providers are aligning network designs with the expressway map to cut empty back-haul miles. As multimodal nodes emerge, operators that integrate trucking with coastal shipping gain cost leverage over single-mode rivals.
Port Modernization and Automation PPPs (e.g., MICT) Cutting Vessel Turn-Around Time
Manila International Container Terminal (MICT) applied an N4 3.4 operating system and yard upgrades worth PHP 15 billion (USD 269.64 million), slicing berth time by 35% and raising Manila's 2023 throughput to 5.06 million TEUs. Quicker clearances reduce demurrage penalties and lower inventory buffers for shippers. Forwarders embed real-time port data in booking tools, letting exporters choose sailings with minimal congestion. Equipment automation unlocks longer gate hours, which supports night-time drayage and eases daytime traffic, benefiting last-mile fleets working tight delivery windows.
Under-Developed Rail Freight Network Limiting Multimodal Efficiency
Freight rail remains negligible despite a PHP 135.4 billion (USD 2.43 billion) transport budget, of which only PHP 1.17 billion (USD 21.03 million) targets rail transport in 2024. Heavy industries lose scale benefits when bulk cargo must shift to trucks. Logistics costs run 20-30% higher than regional peers, the World Bank notes. Private consortia are evaluating dedicated cargo spurs between economic zones and ports, but land-acquisition hurdles persist. Operators experimenting with road-rail containers position themselves for first-mover gains once corridors break ground.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Foreign-Ownership Liberalization Attracting FDI in 3PLs
- Surging B2C E-Commerce Requiring Same-/Next-Day Logistics Across Luzon Urban Corridors
- Severe Road Congestion in Metro Manila Inflating Last-Mile Costs
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Wholesale and retail trade represented 30.79% of 2024 revenue with a projected CAGR (2025-2030) of 6.59%, mirroring the nation's consumption-driven economy. Manufacturing is linked to the expansion of semiconductor back-end plants, personal-care production, and beverage lines that depend on predictable inbound raw-material streams. Construction absorbed the infrastructure push, buoyed demand for bulk aggregates, steel, and cement. Agriculture, fishing, and forestry are expected to grow with cold chain upgrades, facilitating longer shelf life and better farm-gate revenue.
Retailers and factories alike now seek real-time inventory snapshots and coordinated replenishment, prompting logistics partners to embed IoT sensors and API gateways. Maersk's fulfilment-center investments under CREATE MORE tax incentives illustrate how integrated ocean-to-warehouse services resonate with multinational manufacturers. Oil, gas, and mining require specialized heavy-haul rigs and hazardous-cargo compliance, while the fast-growing "others" band, healthcare, education, and reverse logistics, creates opportunities for operators proficient in high-value, high-service niches within the Philippines freight and logistics market.
Freight transport generated 63.34% of the 2024 total revenue, underscoring its role as the backbone of the Philippines freight and logistics market. Trucking, coastal shipping, air cargo, and pipelines underpin national supply-chain continuity across more than 7,600 islands. Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) segment, though a smaller slice today, is clocking a 6.89% CAGR between 2025-2030 as social-commerce sellers and marketplace giants promise next-day delivery nationwide. The warehousing and storage segment and freight forwarding form critical links that synchronize upstream production with downstream retail intake.
Momentum inside CEP is redrawing competitive boundaries: pure-play parcel firms are integrating digital wallets, while traditional 3PLs adopt crowdsourced rider models to protect share. Warehouse operators deploy robotics and construct multi-temperature zones to attract pharmaceutical and agrifood tenants. Forwarders leverage port automation and foreign-capital partnerships to bundle customs brokerage with value-added services such as kitting and reverse logistics. Collectively, these shifts confirm an ecosystem moving toward end-to-end orchestration rather than siloed execution in the Philippines freight and logistics market.
The Philippines Freight and Logistics Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry, Construction, Manufacturing, Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and More) and by Logistics Function (Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP), Freight Forwarding, Freight Transport, Warehousing and Storage, and Other Services). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- A.P. Moller - Maersk
- AAI Worldwide Logistics
- AP Cargo
- Ayala Corporation (Including Airfreight 2100, Inc.)
- CMA CGM Group (Including CEVA Logistics)
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- Fast Logistics
- FedEx
- J&T Express (Including PH Global Jet Express, Inc.)
- JRS Business Corporation
- Kuehne+Nagel
- LBC Express Holdings, Inc.
- LF Global Logistics Solutions, Inc.
- Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd.
- Ninja Van Group (Including Ninja Van Philippines)
- NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- Orient Freight
- Royal Cargo
- SM Investments Corporation (Including 2GO Group, Inc.)
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Logistics Performance
- 4.12 Modal Share
- 4.13 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.14 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.15 Infrastructure
- 4.16 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.17 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.18 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.19 Market Drivers
- 4.19.1 Infrastructure "Build Build Build 2" Program Boosting Road and Port Capacity
- 4.19.2 Expansion of Cold-Chain Capacity for Fisheries and Agrifood Exports
- 4.19.3 Port Modernization and Automation PPPs (e.g., MICT) Cutting Vessel Turn-Around Time
- 4.19.4 Foreign-Ownership Liberalization (Public Service Act Amendments) Attracting FDI in 3PLs
- 4.19.5 Surging B2C E-commerce Requiring Same-/Next-Day Logistics Across Luzon Urban Corridors
- 4.19.6 Growing Manufacturing Sector Driving Industrial Logistics Demand
- 4.20 Market Restraints
- 4.20.1 Under-developed Rail Freight Network Limiting Multimodal Efficiency
- 4.20.2 Severe Road Congestion in Metro Manila Inflating Last-Mile Costs
- 4.20.3 Fragmented SME-Dominated Sector with Low Digitalization
- 4.20.4 High Typhoon and Seismic Risk Disrupting Supply Chains
- 4.21 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.22 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.22.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.22.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.22.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.22.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.22.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Road
- 5.2.3.1.4 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 A.P. Moller - Maersk
- 6.4.2 AAI Worldwide Logistics
- 6.4.3 AP Cargo
- 6.4.4 Ayala Corporation (Including Airfreight 2100, Inc.)
- 6.4.5 CMA CGM Group (Including CEVA Logistics)
- 6.4.6 DHL Group
- 6.4.7 DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.8 Fast Logistics
- 6.4.9 FedEx
- 6.4.10 J&T Express (Including PH Global Jet Express, Inc.)
- 6.4.11 JRS Business Corporation
- 6.4.12 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.13 LBC Express Holdings, Inc.
- 6.4.14 LF Global Logistics Solutions, Inc.
- 6.4.15 Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd.
- 6.4.16 Ninja Van Group (Including Ninja Van Philippines)
- 6.4.17 NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- 6.4.18 Orient Freight
- 6.4.19 Royal Cargo
- 6.4.20 SM Investments Corporation (Including 2GO Group, Inc.)
- 6.4.21 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment




