PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906995

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906995
Indonesia Solar Energy - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Indonesia Solar Energy Market is expected to grow from 2.15 gigawatt in 2025 to 2.97 gigawatt in 2026 and is forecast to reach 14.91 gigawatt by 2031 at 38.10% CAGR over 2026-2031.
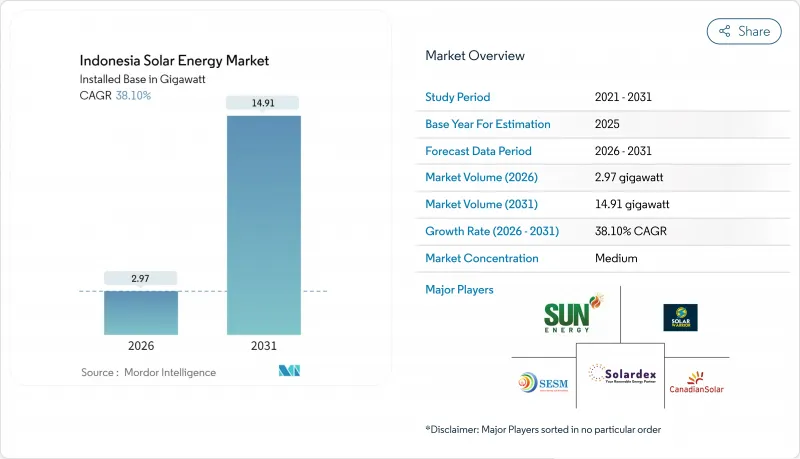
Jakarta's pivot from diesel subsidies toward grid-scale and distributed photovoltaic systems, the 5.746 GW rooftop quota framework, and PLN's commitment to 17.1 GW of solar capacity in its RUPTL 2025-2034 blueprint, together underpin this growth trajectory, signaling a decisive reallocation of capital away from coal baseload. Module average selling prices fell nearly 50% during 2024, shipping costs normalized, and Indonesian EPC bidders routinely met PLN's ceiling tariff of IDR 1,200 per kWh, which pushed the Indonesian solar energy market below grid-parity levels in high-irradiance provinces. Corporate renewable-power purchase agreements (RE-PPAs) surged as RE100 manufacturers in Java and Batam locked in twenty-year rooftop contracts that guarantee Scope 2 abatement and long-term price certainty. Utility-scale developers attracted by the archipelago's 207 GW technical potential, the USD 20 billion JETP commitment, and regulatory clarity under Presidential Regulation 112/2022 are queueing projects in Java, Sumatra, and Sulawesi despite grid-absorption quotas and foreign-exchange risks.
Indonesia Solar Energy Market Trends and Insights
Government Rooftop Incentives Accelerate Distributed Adoption
MEMR Regulation 2/2024 ended net-metering and replaced it with a 5.746 GW quota, clarifying interconnection rules and protecting PLN revenues while sustaining tax allowances for commercial systems. Jakarta's Governor Regulation 38/2024 now obliges the installation of rooftop solar on new commercial buildings exceeding 500 m2, a mandate mirrored in West Java and Bali. Together with the quota, this delivers a transparent pipeline that boosts developer visibility until 2028. The mechanism caps excess-generation credits, steering households toward self-consumption yet unlocking larger corporate installations that can absorb daytime output. Developers have accelerated engineering timelines to secure quota allocations early, anticipating tighter windows once the residential segment restarts in 2027. At the same time, municipal fines and permitting incentives ensure higher compliance, thereby expanding the Indonesian solar energy market in densely populated urban districts.
Module ASP Declines Compress Levelized Costs Below Grid Parity
Polysilicon spot prices declined from USD 30/kg in 2023 to USD 8/kg by Q4 2024, halving crystalline-silicon module ASPs and enabling EPC bids as low as IDR 1,050 per kWh in recent PLN tenders. Normalized freight rates shaved another 15-20% off landed costs for Chinese Tier-1 modules, pushing levelized electricity costs beneath coal benchmarks in East Nusa Tenggara and South Kalimantan. Developers responded by lodging unsolicited PPA proposals that already exceed PLN's 17.1 GW solar allocation for 2025-2034. Yet margin pressure remains as manufacturers offload high-priced inventory, compelling Indonesian firms to hedge order timing. Forward curves indicate that if Chinese factory utilization stays above 600 GW annually, the Indonesian solar energy market will benefit from sub-USD 0.07 kWh tariffs through 2026.
TKDN Local-Content Mandate Elevates Project Economics
MEMR Decree 191/2024 trimmed the TKDN threshold to 20%, yet developers still face 12-18% higher EPC costs because Indonesia lacks polysilicon and wafer plants, leaving PT Len Industri's 600 MW line as the chief compliant source. Queue times stretch to nine months, compelling utility-scale sponsors to renegotiate PPA schedules or accept partial-import penalties. PLN remains reluctant to uplift tariffs, forcing margin compression that cascades through the supply chain. Several IPPs now bundle balance-of-system gear from domestic suppliers to surpass the 20% threshold, although audits can delay commercial-operation certificates by up to 90 days. Unless new gigawatt-scale factories reach commercial operation before 2027, the TKDN rule will continue to hinder the Indonesian solar energy market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- RE100 Corporate Commitments Drive C&I PPA Volume
- Diesel Displacement in Eastern Archipelago Eases Fiscal Strain
- Grid-Absorption Constraints Trigger Curtailment Incidents
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Solar PV accounted for 100.00% of the Indonesian solar energy market size in 2025 and is forecast to advance at a 38.10% CAGR through 2031. CSP remains commercially unviable because most Indonesian sites record 1,400-1,600 kWh/m2 DNI, which is well below the 2,000 kWh/m2 threshold that CSP needs to remain competitive. PV capex of USD 800-1,200 kW undercuts CSP's USD 4,000-6,000 kW, so investors concentrate capital on crystalline-silicon routes. Bifacial and TOPCon modules captured 60% of 2024 imports as developers chase 10-15% yield gains in land-constrained Java. Compliance with IEC 61215 and IEC 61730 standards upholds bankability despite price compression, further reinforcing PV's exclusive status in the Indonesian solar energy market.
Second-generation cell technologies accelerate yield improvements, mitigating curtailment risks by enabling lower nameplate sizing for fixed quotas. LONGi and Trina each delivered over 500 MW of bifacial shipments in 2024, primarily for floating PV and hybrid diesel sites. As module energy density rises, developers forecast a 7% drop in land requirements by 2027, alleviating community-acceptance barriers in peri-urban Java while bolstering project IRRs.
The Indonesia Solar Energy Market Report is Segmented by Technology (Solar Photovoltaic and Concentrated Solar Power), Grid Type (On-Grid and Off-Grid), and End-User (Utility-Scale, Commercial and Industrial, and Residential). The Market Sizes and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Installed Capacity (GW).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- PT Surya Utama Nuansa (SUN Energy)
- PT TotalEnergies Eren Indonesia
- PT Sumber Energi Sukses Makmur (SES)
- PT Sumber Energi Surya Nusantara (SESNA)
- PT Solardex Energy Indonesia
- Canadian Solar Inc.
- Trina Solar Co. Ltd.
- LONGi Green Energy Technology Co. Ltd.
- First Solar Inc.
- JA Solar Technology Co. Ltd.
- Risen Energy Co. Ltd.
- PT Len Industri (Persero)
- PT PLN Nusantara Power
- Akuo Energy Indonesia
- ACWA Power Indonesia
- Vena Energy Indonesia
- Masdar Indonesia
- PT Xurya Daya Indonesia
- Enernet Global Indonesia
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Government rooftop-net-metering incentives strengthened (2023)
- 4.2.2 Declining global module ASPs and shipping costs
- 4.2.3 Corporate RE-PPA demand from RE100 manufacturers
- 4.2.4 Diesel-hybrid swaps on remote islands cut PLN subsidy burden
- 4.2.5 Jakarta & provincial mandatory-rooftop by-laws
- 4.2.6 Sulawesi nickel-smelter self-generation requirement
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 40 % TKDN local-content rule inflates costs
- 4.3.2 Grid-absorption quota & curtailment risk
- 4.3.3 Lack of sovereign guarantee for floating-PV PPAs
- 4.3.4 High IDR-FX hedging costs for IPPs
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porters Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Industry Rivalry
- 4.8 PESTLE Analysis
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Technology
- 5.1.1 Solar Photovoltaic (PV)
- 5.1.2 Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
- 5.2 By Grid Type
- 5.2.1 On-Grid
- 5.2.2 Off-Grid
- 5.3 By End-User
- 5.3.1 Utility-Scale
- 5.3.2 Commercial and Industrial (C&I)
- 5.3.3 Residential
- 5.4 By Component (Qualitative Analysis)
- 5.4.1 Solar Modules/Panels
- 5.4.2 Inverters (String, Central, Micro)
- 5.4.3 Mounting and Tracking Systems
- 5.4.4 Balance-of-System and Electricals
- 5.4.5 Energy Storage and Hybrid Integration
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 PT Surya Utama Nuansa (SUN Energy)
- 6.4.2 PT TotalEnergies Eren Indonesia
- 6.4.3 PT Sumber Energi Sukses Makmur (SES)
- 6.4.4 PT Sumber Energi Surya Nusantara (SESNA)
- 6.4.5 PT Solardex Energy Indonesia
- 6.4.6 Canadian Solar Inc.
- 6.4.7 Trina Solar Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.8 LONGi Green Energy Technology Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.9 First Solar Inc.
- 6.4.10 JA Solar Technology Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Risen Energy Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.12 PT Len Industri (Persero)
- 6.4.13 PT PLN Nusantara Power
- 6.4.14 Akuo Energy Indonesia
- 6.4.15 ACWA Power Indonesia
- 6.4.16 Vena Energy Indonesia
- 6.4.17 Masdar Indonesia
- 6.4.18 PT Xurya Daya Indonesia
- 6.4.19 Enernet Global Indonesia
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




