PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910518

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910518
Indonesia Foodservice - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Indonesia Foodservice Market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 70.41 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 62.40 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 128.76 billion, growing at 12.84% CAGR over 2026-2031.
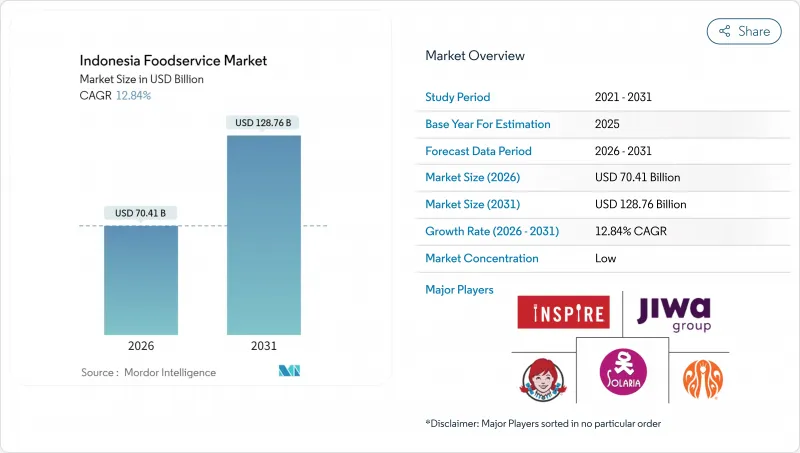
This growth trajectory positions Indonesia as Southeast Asia's largest foodservice market, driven by the convergence of full-service and quick service restaurants with emerging digital delivery ecosystems and evolving consumer preferences . The upward trajectory of the Indonesia foodservice market is underpinned by resilient household consumption, rapid digital delivery adoption, and the steady recovery of hospitality and tourism activity. Full-service restaurants command over half of current sales, while cafes and bars, propelled by specialty coffee chains, register the fastest expansion. Independent operators still dominate outlet counts, yet chained brands are scaling quickly through standardized formats and franchise financing. Stand-alone locations remain the primary venue type, but hotel-based dining is benefiting from strengthening visitor arrivals and new lodging supply. Ongoing halal certification reforms and front-of-pack nutrition labeling rules are reshaping menus, procurement, and branding, reinforcing trust among increasingly health-aware urban consumers.
Indonesia Foodservice Market Trends and Insights
Rapid Cafe Culture and Coffee-Chain Proliferation
Indonesia's coffee culture transformation is reshaping the foodservice landscape through rapid specialty chain expansion and premiumization trends. Local coffee chains like Kopi Kenangan have scaled to over 900 outlets while Tomoro Coffee operates approximately 600 stores, demonstrating the market's appetite for differentiated coffee experiences beyond traditional warung kopi, according to the USDA Foreign Agricultural Service. This proliferation extends beyond domestic players, with international brands like Flash Coffee and Fore Coffee establishing significant footprints through franchise models and strategic partnerships. The segment's growth is amplified by Indonesian consumers' increasing willingness to pay premium prices for artisanal coffee experiences, with specialty coffee shops commanding higher average transaction values than traditional food outlets. This trend creates opportunities for equipment suppliers, specialty ingredient importers, and real estate developers targeting high-traffic urban locations.
Menu Localization by Global Chains
International foodservice brands are accelerating localization strategies to compete effectively against Indonesia's deeply embedded culinary traditions and price-sensitive consumer segments. Global chains are incorporating Indonesian flavors, ingredients, and cooking methods into their core offerings, moving beyond superficial adaptations to fundamental menu restructuring that resonates with local palates. This localization extends to pricing strategies, with international brands developing value-tier products specifically for Indonesian markets while maintaining premium positioning for aspirational consumers. The approach reflects lessons learned from successful regional players who have built market share by combining international operational standards with authentic local flavors. Menu localization also addresses Indonesia's diverse regional preferences, with chains adapting offerings for Javanese, Sumatran, and other regional taste profiles to maximize market penetration. The strategy becomes particularly critical as Indonesian consumers demonstrate strong loyalty to familiar flavors, making authentic localization a competitive necessity rather than a marketing enhancement.
Intense Competition from Independent and Street Food
Indonesia's vast network of independent restaurants and street food vendors creates persistent pricing pressure that limits formal foodservice operators' ability to capture market share in price-sensitive segments. Traditional warung and street food stalls operate with minimal overhead costs, enabling them to offer authentic local dishes at price points that formal restaurants cannot match while maintaining profitability. This competitive dynamic is particularly challenging in urban areas where street food density is highest and consumer familiarity with local vendors runs deepest. The competition extends beyond pricing to authenticity perceptions, with many Indonesian consumers viewing street food as a more genuine representation of local culinary traditions compared to formal restaurant offerings. Street food operators also benefit from flexible operating models that allow rapid menu adjustments, location changes, and seasonal adaptations that formal restaurants cannot replicate due to regulatory and operational constraints. The challenge intensifies as street food vendors increasingly adopt digital payment systems and delivery partnerships, reducing the convenience advantages that previously differentiated formal foodservice operators.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Strong 'Dine-Out' and Socializing Culture
- Dark / Cloud Kitchen Expansion
- Inconsistent Food Safety and Hygiene Standards
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Full-service restaurants maintain market dominance with a 52.67% share in 2025, reflecting Indonesian consumers' preference for comprehensive dining experiences that accommodate social gatherings and family meals. However, the cafe and bars segment demonstrates the strongest growth trajectory at 15.23% CAGR through 2031, driven by urbanization trends and evolving lifestyle preferences among younger demographics. Quick service restaurants occupy a significant but stable position, benefiting from convenience demands and delivery integration, while cloud kitchens represent an emerging category that leverages delivery platforms without traditional front-of-house investments. The segment dynamics reflect Indonesia's economic development, with full-service establishments serving established middle-class consumers while cafe concepts capture emerging affluent segments seeking premium experiences.
Specialty coffee and tea shops within the cafe segment are experiencing particularly robust expansion through aggressive franchising and strategic location selection. This growth reflects Indonesian consumers' increasing sophistication in coffee consumption, moving beyond traditional kopi tubruk to specialty brewing methods and premium bean varieties. The bars and pubs subcategory faces regulatory constraints in some regions but demonstrates strong performance in tourism-focused areas like Bali and Jakarta's entertainment districts. Juice, smoothie, and dessert bars are capitalizing on health consciousness trends, particularly among urban millennials and Gen Z consumers who prioritize wellness-oriented food choices.
Independent outlets command 62.41% market share in 2025, reflecting Indonesia's entrepreneurial food culture and the prevalence of family-owned restaurants, warungs, and street food operations. This dominance stems from independent operators' ability to offer authentic local flavors at competitive price points while maintaining operational flexibility that enables rapid menu adjustments and location changes. Independent establishments also benefit from deep community connections and customer loyalty that chain operators struggle to replicate, particularly in smaller cities and rural areas where personal relationships drive dining decisions.
Chained outlets, despite holding a smaller market share, demonstrate superior growth momentum at 13.76% CAGR through 2031, indicating ongoing market consolidation and professionalization trends. The Ministry of Trade reports that food and beverage franchises represent 47.92% of all franchised businesses in Indonesia, highlighting the sector's appeal for structured expansion models . Chain growth is driven by superior access to capital, standardized operational systems, and marketing capabilities that enable rapid geographic expansion and brand recognition development. International chains benefit from proven business models and supply chain efficiencies, while domestic chains leverage local market knowledge and cultural authenticity to compete effectively against global brands.
The Indonesia Foodservice Market is Segmented by Foodservice Type (Cafes and Bars, Cloud Kitchen, Full-Service Restaurants, Quick Service Restaurants), Outlet (Chained Outlets, and Independent Outlets), Location (Leisure, Lodging, Retail, Standalone, Travel), and Service Type (Dine-In, Takeaway, Delivery). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- PT Rekso Nasional Food
- PT Map Boga Adiperkasa Tbk
- PT Sarimelati Kencana Tbk
- Inspire Brands, Inc.
- PT Dom Pizza Indonesia (Domino's)
- PT Bumi Berkah Boga (Kopi Kenangan)
- Jiwa Group
- PT Pesta Pora Abadi (Mie Gacoan)
- PT JCO Donut & Coffee
- Restaurant Brands Asia Ltd (Popeyes, BK)
- PT BABA RAFI ENTERPRISE (Kebab Turki Baba Rafi)
- PT Richeese Kuliner Indonesia
- The Wendy's Company
- Fore Coffee (PT Fore Kopi Indonesia)
- Flash Coffee
- PT Pesta Pora Abadi (Mie Gacoan)
- Chatime Indonesia ( La Kaffa International Co. Ltd.)
- Solaria Indonesia
- PT Fast Food Indonesia Tbk
- Hot Palette Pte Ltd. (Pepper Lunch Indonesia's)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Number of Outlets
- 4.2 Average Order Value
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
5 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 5.1 Market Overview
- 5.2 Market Drivers
- 5.2.1 Rapid cafe culture and coffee-chain proliferation
- 5.2.2 Menu localization by global chains
- 5.2.3 Strong 'Dine-Out' and socializing culture
- 5.2.4 Dark/cloud kitchen expansion
- 5.2.5 Rise of halal-assurance branding
- 5.2.6 High mobile-app ordering literacy
- 5.3 Market Restraints
- 5.3.1 Intense competition from independent and street food
- 5.3.2 Inconsistent food safety and hygiene standards
- 5.3.3 Menu copycatting and concept fatigue
- 5.3.4 Cold-chain and perishables reliability gaps
- 5.4 Porter's Five Forces
- 5.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 5.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 5.4.5 Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 6.1 By Foodservice Type
- 6.1.1 Cafe and Bars
- 6.1.1.1 By Cuisine
- 6.1.1.1.1 Bars and Pubs
- 6.1.1.1.2 Cafe
- 6.1.1.1.3 Juice/Smoothie/Desserts Bars
- 6.1.1.1.4 Specialist Coffee and Tea Shops
- 6.1.1.1 By Cuisine
- 6.1.2 Cloud Kitchen
- 6.1.3 Full Service Restaurants
- 6.1.3.1 By Cuisine
- 6.1.3.1.1 Asian
- 6.1.3.1.2 European
- 6.1.3.1.3 Latin American
- 6.1.3.1.4 Middle Eastern
- 6.1.3.1.5 North American
- 6.1.3.1.6 Other FSR Cuisines
- 6.1.3.1 By Cuisine
- 6.1.4 Quick Service Restaurants
- 6.1.4.1 By Cuisine
- 6.1.4.1.1 Bakeries
- 6.1.4.1.2 Burger
- 6.1.4.1.3 Ice Cream
- 6.1.4.1.4 Meat-based Cuisines
- 6.1.4.1.5 Pizza
- 6.1.4.1.6 Other QSR Cuisines
- 6.1.4.1 By Cuisine
- 6.1.1 Cafe and Bars
- 6.2 By Outlet
- 6.2.1 Chained Outlets
- 6.2.2 Independent Outlets
- 6.3 By Locations
- 6.3.1 Leisure
- 6.3.2 Lodging
- 6.3.3 Retail
- 6.3.4 Sandalone
- 6.3.5 Travel
- 6.4 By Service Type
- 6.4.1 Dine-in
- 6.4.2 Takeaway
- 6.4.3 Delivery
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Market Concentration
- 7.2 Strategic Moves
- 7.3 Market Share Analysis
- 7.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 7.4.1 PT Rekso Nasional Food
- 7.4.2 PT Map Boga Adiperkasa Tbk
- 7.4.3 PT Sarimelati Kencana Tbk
- 7.4.4 Inspire Brands, Inc.
- 7.4.5 PT Dom Pizza Indonesia (Domino's)
- 7.4.6 PT Bumi Berkah Boga (Kopi Kenangan)
- 7.4.7 Jiwa Group
- 7.4.8 PT Pesta Pora Abadi (Mie Gacoan)
- 7.4.9 PT JCO Donut & Coffee
- 7.4.10 Restaurant Brands Asia Ltd (Popeyes, BK)
- 7.4.11 PT BABA RAFI ENTERPRISE (Kebab Turki Baba Rafi)
- 7.4.12 PT Richeese Kuliner Indonesia
- 7.4.13 The Wendy's Company
- 7.4.14 Fore Coffee (PT Fore Kopi Indonesia)
- 7.4.15 Flash Coffee
- 7.4.16 PT Pesta Pora Abadi (Mie Gacoan)
- 7.4.17 Chatime Indonesia ( La Kaffa International Co. Ltd.)
- 7.4.18 Solaria Indonesia
- 7.4.19 PT Fast Food Indonesia Tbk
- 7.4.20 Hot Palette Pte Ltd. (Pepper Lunch Indonesia's)
8 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




