PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911708

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911708
Philippines Seed - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Philippines seed market was valued at USD 0.85 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 0.88 billion in 2026 to reach USD 1.08 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 4.03% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
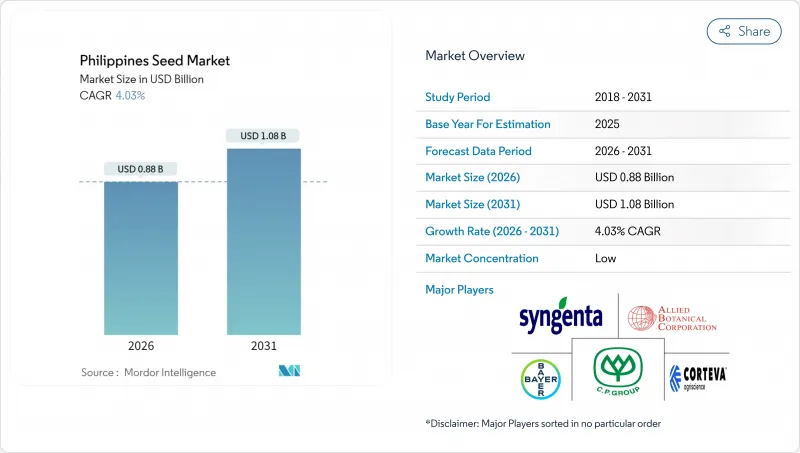
This expansion is propelled by the extension of the Rice Competitiveness Enhancement Fund through 2031, steady growth of contract farming schemes, and rising hybrid adoption across rice, corn, and vegetables. The government's annual budget for certified seeds is driving predictable demand, especially in Central Luzon and Cagayan Valley. Protected cultivation acreage is expanding at double-digit rates, creating new opportunities for high-value vegetable seed suppliers. Multinational and regional players are intensifying competition by adding climate-resilient hybrids, while gene-edited rice lines are positioned to reach farmers before the decade ends.
Philippines Seed Market Trends and Insights
Sustained Government Rice Self-Sufficiency Programs
Annual disbursement of PHP 30 billion (USD 540 million) for certified seed distribution through 2031 underpins stable demand and encourages breeders to scale hybrid production. The initiative's seed component accounts for 40% of total fund allocation, creating predictable demand for premium varieties while reducing farmer price sensitivity. Regional implementation focuses on Central Luzon and Cagayan Valley, where irrigated rice systems can maximize hybrid yield advantages. The program's extension signals long-term policy stability that encourages private sector investment in breeding programs and production capacity expansion.
Expansion of Contract Farming Models by Seed Firms
Contract farming arrangements between seed companies and agricultural cooperatives are reshaping market dynamics, with participating hectarage increasing 35% annually since 2022 across key production regions.. These partnerships reduce market intermediation costs and improve seed quality control, particularly for vegetable crops where post-harvest handling significantly impacts viability. Mindanao provinces lead adoption due to larger farm sizes and stronger cooperative structures, while Luzon regions are catching up through government-facilitated cluster farming initiatives. The model's success in reducing farmer financial risk while ensuring seed company supply chain reliability suggests continued expansion across crop segments.
Limited Cold-Chain Logistics
The Philippines' inadequate cold-chain infrastructure constrains seed quality maintenance and distribution efficiency, with only 12% of agricultural products having access to temperature-controlled storage and transport systems as of 2024. This limitation particularly affects hybrid vegetable seeds that require strict temperature and humidity control to maintain viability during the 6-month distribution cycle from production to planting. Government initiatives to develop cold-chain networks through public-private partnerships show promise but require 3-5 years for meaningful impact on seed distribution networks.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Consumer Demand for High-Value Vegetables
- Growth in Protected Cultivation Acreage
- High Fragmentation of Informal Seed Saving in Smallholders
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Open-pollinated varieties and hybrid derivatives retained 66.55% of the Philippines' seed market share in 2025, mirroring deep-seated farmer familiarity with saved seed systems. Yet hybrids are scaling at a 4.88% CAGR to 2031, buoyed by government subsidies, demonstration farms, and favorable credit lines. Hybrid rice delivers higher yields in irrigated plains, justifying its price premium, while hybrid corn's stacked insect resistance cuts chemical costs. Herbicide-tolerant hybrids now occupy commercial corn acreage, pointing to further upside.
The adoption of hybrids, however, remains uneven. Transgenic options remain limited to Bt corn owing to regulatory delays, whereas non-GM vegetable hybrids flourish in tunnels and highland zones. Younger producers embrace hybrids faster, and contract farming spreads the risk, prompting cooperatives to allocate larger hybrid budgets. As a result, the Philippines' seed market size for hybrids is set to close the gap with OPVs by decade-end.
The Philippines Seed Market Report is Segmented by Breeding Technology (Hybrids, Open Pollinated Varieties, and Hybrid Derivatives), Cultivation Mechanism (Open Field, Protected Cultivation), and Crop Type (Row Crops, Vegetables). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Metric Tons).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Charoen Pokphand Group Co., Ltd. (CP Group)
- Allied Botanical Corporation
- East-West Seed Group Co., Ltd.
- DCM Shriram Ltd (Bioseed)
- Harbest Agribusiness Corporation
- SeedWorks International Pvt. Ltd
- Ramgo International
- Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV
- Enza Zaden Beheer B.V.
- Syngenta Group
- Bayer AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- Vilmorin and Cie (Limagrain Group)
- Kaneko Seeds Co., Ltd.
- Sakata Seed Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
- 1.3 Research Methodology
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
3 REPORT OFFERS
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Area Under Cultivation
- 4.1.1 Row Crops
- 4.1.2 Vegetables
- 4.2 Most Popular Traits
- 4.2.1 Carrot & Peas
- 4.2.2 Rice & Corn
- 4.2.3 Tomato, Pumpkin & Squash
- 4.3 Breeding Techniques
- 4.3.1 Row Crops & Vegetables
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.6 Market Drivers
- 4.6.1 Sustained government rice self-sufficiency programs
- 4.6.2 Expansion of contract farming models by seed firms
- 4.6.3 Rising consumer demand for high-value vegetables
- 4.6.4 Growth in protected cultivation acreage
- 4.6.5 Filipino millennials' shift toward home gardening
- 4.6.6 Commercial adoption of CRISPR-edited rice lines
- 4.7 Market Restraints
- 4.7.1 Limited cold-chain logistics
- 4.7.2 High fragmentation of informal seed saving in smallholders
- 4.7.3 Persistent typhoon-related crop losses
- 4.7.4 Lengthy biosafety approval cycle for transgenics
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECAST (VALUE AND VOLUME)
- 5.1 Breeding Technology
- 5.1.1 Hybrids
- 5.1.1.1 Non-Transgenic Hybrids
- 5.1.1.2 Transgenic Hybrids
- 5.1.1.2.1 Herbicide Tolerant Hybrids
- 5.1.1.2.2 Insect Resistant Hybrids
- 5.1.1.2.3 Other Traits
- 5.1.2 Open Pollinated Varieties & Hybrid Derivatives
- 5.1.1 Hybrids
- 5.2 Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.2.1 Open Field
- 5.2.2 Protected Cultivation
- 5.3 Crop Type
- 5.3.1 Row Crops
- 5.3.1.1 Fiber Crops
- 5.3.1.1.1 Cotton
- 5.3.1.1.2 Other Fiber Crops
- 5.3.1.2 Forage Crops
- 5.3.1.2.1 Alfalfa
- 5.3.1.2.2 Forage Corn
- 5.3.1.2.3 Forage Sorghum
- 5.3.1.2.4 Other Forage Crops
- 5.3.1.3 Grains & Cereals
- 5.3.1.3.1 Corn
- 5.3.1.3.2 Rice
- 5.3.1.3.3 Sorghum
- 5.3.1.4 Oilseeds
- 5.3.1.4.1 Soybean
- 5.3.1.4.2 Other Oilseeds
- 5.3.1.5 Pulses
- 5.3.1.1 Fiber Crops
- 5.3.2 Vegetables
- 5.3.2.1 Brassicas
- 5.3.2.1.1 Cabbage
- 5.3.2.1.2 Carrot
- 5.3.2.1.3 Cauliflower & Broccoli
- 5.3.2.1.4 Other Brassicas
- 5.3.2.2 Cucurbits
- 5.3.2.2.1 Cucumber & Gherkin
- 5.3.2.2.2 Pumpkin & Squash
- 5.3.2.2.3 Other Cucurbits
- 5.3.2.3 Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.2.3.1 Garlic
- 5.3.2.3.2 Onion
- 5.3.2.3.3 Potato
- 5.3.2.3.4 Other Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.2.4 Solanaceae
- 5.3.2.4.1 Chilli
- 5.3.2.4.2 Eggplant
- 5.3.2.4.3 Tomato
- 5.3.2.4.4 Other Solanaceae
- 5.3.2.5 Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.2.5.1 Asparagus
- 5.3.2.5.2 Lettuce
- 5.3.2.5.3 Okra
- 5.3.2.5.4 Peas
- 5.3.2.5.5 Spinach
- 5.3.2.5.6 Other Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.2.1 Brassicas
- 5.3.1 Row Crops
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Charoen Pokphand Group Co., Ltd. (CP Group)
- 6.4.2 Allied Botanical Corporation
- 6.4.3 East-West Seed Group Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.4 DCM Shriram Ltd (Bioseed)
- 6.4.5 Harbest Agribusiness Corporation
- 6.4.6 SeedWorks International Pvt. Ltd
- 6.4.7 Ramgo International
- 6.4.8 Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV
- 6.4.9 Enza Zaden Beheer B.V.
- 6.4.10 Syngenta Group
- 6.4.11 Bayer AG
- 6.4.12 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.13 Vilmorin and Cie (Limagrain Group)
- 6.4.14 Kaneko Seeds Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Sakata Seed Corporation
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SEEDS CEOS




