PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1937367

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1937367
Prefabricated Housing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
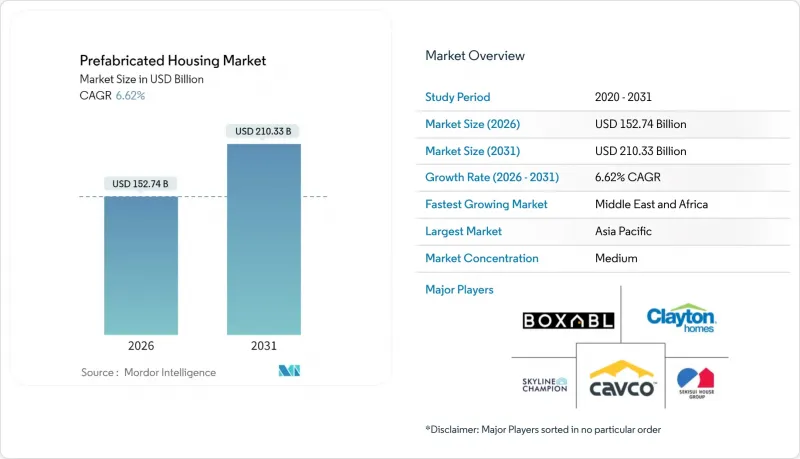
The prefabricated housing market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 152.74 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 143.3 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 210.33 billion, growing at 6.62% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Rapid adoption of off-site manufacturing, policy incentives that shorten approval cycles, and steady material innovation are expanding the prefabricated housing market across income bands and geographies. Governments in Canada, Australia, and the United States are channeling public funds and code updates toward standardized factory-built homes that trim build times and cut life-cycle energy use. Labor shortages, estimated to affect 68% of construction firms, and higher interest in net-zero structures continue to shift demand from site-built to plant-assembled units. Technology adoption-from Building Information Modeling (BIM) through LiDAR-guided inspection-further solidifies quality control and cost predictability, reinforcing the competitive edge of the prefabricated housing market.
Global Prefabricated Housing Market Trends and Insights
Government Push for Affordable & Sustainable Housing
Targeted public funding is reshaping market adoption, shifting prefab from a cost-driven option to a policy-backed priority. Canada's Build Canada Homes program earmarks USD 25 billion in loans and USD 1 billion in equity, leveraging bulk orders that lower unit costs by 20%. The United States now ties Federal Housing Administration financing to the 2021 International Energy Conservation Code, adding USD 7,229 per unit in upfront costs yet saving USD 963 annually on energy. Australia committed USD 54 million to close a 62,000-home gap while standardizing certification, accelerating plant output. Sweden's 84% prefab penetration shows how incentives and capacity building can synchronize supply and demand. Together these measures illustrate a durable shift toward factory-assembled units that meet strict sustainability targets.
Accelerating Urbanization & Housing Shortfall
Rapid urban growth compresses project timelines, intensifying demand for factory-assembled homes that can be erected in half the time of site-built equivalents. Vermont's requirement for up to 36,000 new homes by 2029 mirrors wider North American shortages and positions modular solutions as a scalable fix that cuts construction costs by 20%. At the production level, Onx Homes' Florida plant delivers components for 1,000 dwellings a year, shrinking site schedules from eight months to 30 days. In disaster-hit Los Angeles, modular micro-units helped wildfire victims return faster than conventional rebuilds. Hong Kong's Transitional Housing Programme, with more than 21,000 units built via Modular Integrated Construction, underscores prefab's advantage where land is scarce. These examples reveal how urban density and urgency are reinforcing demand for the prefabricated housing market.
High Logistics Cost for Oversized Modules
Transporting large modules adds 15-25% to project budgets when shipping dimensions exceed standard limits. Specialized trailers, permits, and escort requirements raise costs, particularly across borders where divergent road standards complicate routing. Australia's dependence on Chinese imports shows supply risks; 70% of prefab inflow faces extra handling and compliance checks that slow delivery. Infrastructure gaps, such as low bridge clearances or weight restrictions in emerging regions, force manufacturers to down-size modules, eroding economies of scale. For remote areas, freight expenses can outstrip manufacturing savings, making localized micro-factories or panelized systems more viable. Unless route optimization and regional fabrication expand, logistics will restrain the prefabricated housing market's full potential.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cost-Efficient Off-Site Manufacturing vs. Conventional Build
- Tech Leap: BIM, 3-D Printing & Automated Factories
- Scarcity of Skilled Prefab Fabricators & Installers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Timber held a 32.62% share of the prefabricated housing market in 2025, outpacing all other materials and expanding at a 7.18% CAGR through 2031. Mass-timber panels show high seismic resilience, proven in laboratory shake-table tests that kept rocking frames intact under major earthquake loads. Regulatory roadmaps such as the United Kingdom's Timber in Construction 2025 plan reinforce adoption by linking carbon targets to wood-based systems. Concrete retains a solid position through precast innovation that slashes curing times, while steel benefits from robotic welding that enhances dimensional accuracy. Glass and composite panels cater to specialized use-cases like hurricane-rated facades that must satisfy FEMA debris-impact guidelines.
Growth in the timber segment aligns with green-building certificates that reward low-embodied carbon, prompting developers to embrace Design for Manufacturing and Assembly principles that optimize panel sizing for factory output. The Nordic Swan Ecolabel extends this push by stipulating non-toxic ingredients across the building life cycle, strengthening consumer confidence. Continuous R&D in hybrid systems that pair timber with light-gauge steel or recycled composites illustrates how manufacturers can meet structural, fire, and acoustic codes without handicapping speed or cost. These synchronous advances ensure that wood remains the benchmark for sustainable solutions in the prefabricated housing industry.
The Prefabricated Housing Market Report is Segmented by Material Type (Concrete, Glass, Metal, Timber and Other Materials), by Type (Single-Family and Multi-Family), by Product Type (Modular Homes, Panelised & Componentised Systems, Manufactured Homes and Other Prefab Types), and by Geography (North America, South America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific led with 35.88% share in 2025, underpinned by China's large-scale factories and Japan's mature consumer acceptance. Compliance barriers-for instance, aligning Chinese imports with Australian standards-spark investments in local certification labs that smooth cross-border trade. India's incentive packages, which rank government financing as the most potent driver of prefab uptake, add long-term volume by encouraging domestic resource manufacture. Australia's USD 54 million federal stimulus, coupled with a new national approval framework, streamlines pipeline visibility and lifts builder confidence.
Middle East & Africa is poised for the fastest 7.29% CAGR thanks to disaster recovery, youth-heavy demographics, and mega-infrastructure corridors that favor quick-turn developments. Post-earthquake Turkey illustrates scale economics, as centrally procured modular villages delivered communal services at lower per-unit costs than site-built shelters. Gulf Cooperation Council states embrace prefab labor-saving advantages amidst tighter visa quotas, integrating smart cooling skins to meet stringent thermal codes.
North America and Europe remain innovation hubs. Sweden maintains 84% prefab adoption in detached homes, and the United Kingdom is embedding off-site solutions into housing-supply targets via parliamentary advocacy. In the United States, state-level modern-methods-of-construction standards-enacted in Virginia and on deck in California-accelerate convergence. South America, led by Brazil, tests modular pilot projects in social-housing programs but contends with fragmented regulation. Across all regions, policy alignment and local fabrication capacity prove decisive for continued prefabricated housing market expansion.
- Clayton Homes (Berkshire Hathaway)
- Skyline Champion Corporation
- Cavco Industries Inc.
- Sekisui House Ltd (North America arm)
- Boxabl Inc.
- Plant Prefab Inc.
- Method Homes
- Modular Home Builder LLC
- BluHomes Inc.
- Module Housing
- Indie Dwell Inc.
- Connect Homes
- FullStack Modular
- Weyerhaeuser NR Co. (Engineered Wood Prefab)
- MiTek Inc. (Berkshire subsidiary - PEB)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Government push for affordable & sustainable housing
- 4.2.2 Accelerating urbanisation & housing shortfall shrink build-times
- 4.2.3 Cost-efficient off-site manufacturing vs. conventional build
- 4.2.4 Tech leap: BIM, 3-D printing & automated precast factories
- 4.2.5 ESG-linked green-building mandates favour low-carbon prefab
- 4.2.6 Disaster-rebuild & remote-work demand spur modular micro-units
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High logistics cost for oversized modules
- 4.3.2 Scarcity of skilled prefab fabricators & installers
- 4.3.3 Fragmented cross-border building codes slow approvals
- 4.3.4 Seismic- & cyclone-resilience perception gaps
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Brief on Different Structures Used in Prefabricated Housing
- 4.9 Cost Structure Analysis of Prefabricated Housing
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Material Type
- 5.1.1 Concrete
- 5.1.2 Glass
- 5.1.3 Metal
- 5.1.4 Timber
- 5.1.5 Other Materials
- 5.2 By Type
- 5.2.1 Single-Family
- 5.2.2 Multi-Family
- 5.3 By Product Type
- 5.3.1 Modular Homes
- 5.3.2 Panelised & Componentised Systems
- 5.3.3 Manufactured Homes
- 5.3.4 Other Prefab Types
- 5.4 By Region
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Chile
- 5.4.2.4 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4.1 China
- 5.4.4.2 India
- 5.4.4.3 Japan
- 5.4.4.4 South Korea
- 5.4.4.5 Australia
- 5.4.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.5 Middle East & Africa
- 5.4.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.3 South Africa
- 5.4.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.4.5.5 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Clayton Homes (Berkshire Hathaway)
- 6.4.2 Skyline Champion Corporation
- 6.4.3 Cavco Industries Inc.
- 6.4.4 Sekisui House Ltd (North America arm)
- 6.4.5 Boxabl Inc.
- 6.4.6 Plant Prefab Inc.
- 6.4.7 Method Homes
- 6.4.8 Modular Home Builder LLC
- 6.4.9 BluHomes Inc.
- 6.4.10 Module Housing
- 6.4.11 Indie Dwell Inc.
- 6.4.12 Connect Homes
- 6.4.13 FullStack Modular
- 6.4.14 Weyerhaeuser NR Co. (Engineered Wood Prefab)
- 6.4.15 MiTek Inc. (Berkshire subsidiary - PEB)
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




