PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940752

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940752
United States Seafood - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The US seafood market is expected to grow from USD 24.70 billion in 2025 to USD 25.02 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 26.65 billion by 2031 at 1.28% CAGR over 2026-2031.
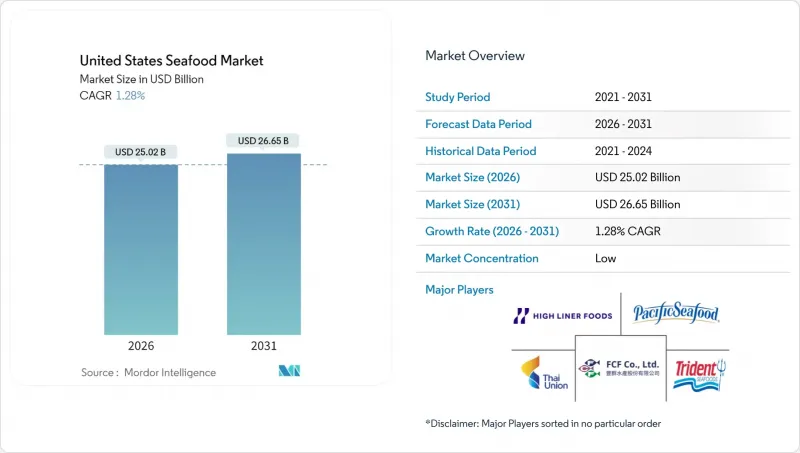
This growth is steady and reflects several key factors. Per-capita seafood consumption remains stable, while there is a noticeable shift toward higher-quality and premium seafood options. However, rising regulatory costs are slowing down the growth in overall volume. When looking at seafood types, fish continues to dominate the market, but shrimp is becoming more popular due to growing consumer demand. In terms of product form, frozen seafood remains the largest segment. However, innovations in processing are challenging this position, as more consumers are opting for ready-to-cook and value-added products that save time and effort. Regarding sourcing, wild-caught seafood has traditionally been the preferred choice, but farmed seafood is gaining momentum. Advances in aquaculture technology and a focus on sustainability are driving the growth of farmed seafood. For distribution channels, foodservice outlets, such as restaurants and hotels, continue to lead the market. However, retail channels are transforming, with online platforms becoming increasingly popular for seafood purchases. The United States seafood market is highly fragmented, with many small-scale harvesters and processors competing for market share. This results in a low concentration profile, where no single player dominates the market.
United States Seafood Market Trends and Insights
Rising consumer demand for protein-rich foods and omega-3 diets
Demand for protein-rich foods and omega-3 diets is a major factor, as seafood is an excellent source of high-quality protein, with about 20-30% of its total weight made up of protein, as per PubMed Central. The American Heart Association advises consuming 2 servings of fatty fish, such as salmon and tuna, each week due to their heart-health benefits. Salmon and tuna are particularly popular because they are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and can be used in a wide range of dishes, from grilled meals to sushi, making them attractive to health-conscious consumers. There is a rising preference for sustainable and clean-label seafood products, which is encouraging consumers to choose premium options. Many people are moving away from traditional meat sources like beef and pork, which have a larger environmental impact. To meet this growing demand, retailers and foodservice providers are introducing initiatives that focus on nutrition. These include clearly labeling health benefits on packaging and offering chef-designed meal kits.
Consumer demand for fresh and quality seafood
Consumer demand for fresh and high-quality seafood is a major factor driving the United States seafood market. According to the Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute in 2024, about 90% of United States consumers eat seafood, and many are now focusing more on freshness and quality rather than the quantity of seafood they consume. Sales of fresh and chilled seafood are increasing, even though frozen products still hold the largest share of the market. This growth is largely due to shorter supply chains, which allow domestic fishers to deliver seafood within 24-48 hours. This quick delivery ensures the seafood meets consumer expectations for freshness and justifies higher prices. Direct-to-consumer models are becoming more popular. These models use insulated packaging and real-time temperature tracking to ensure that even customers living far from coastal areas receive high-quality, restaurant-grade seafood. Regional preferences also play a significant role in shaping the market.
Competition from alternative proteins
Competition from alternative proteins is becoming a significant challenge for the United States seafood market. Plant-based seafood alternatives, such as those offered by brands like Good Catch and Ocean Hugger, are gaining popularity. These products mimic the texture and taste of traditional seafood, such as tuna and salmon, while promoting sustainability as a key selling point. Flexitarian consumers, who occasionally eat meat or fish but are open to plant-based options, are increasingly drawn to these alternatives. Foodservice providers are also experimenting with plant-based seafood by incorporating it into popular dishes like tacos and sushi without needing to change recipes, which is gradually reducing the market share of traditional frozen seafood. Although plant-based options currently lack the same levels of omega-3 fatty acids found in real seafood, advancements in algae-based DHA additives are expected to close this gap in the near future.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Technology and farming innovation
- Demand for sustainable, certified, ethical, traceable seafood
- Supply chain and cold chain limitations
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Fish remained the largest segment in the United States seafood market in 2025, accounting for 51.02% of the market share. This dominance is primarily due to the popularity of salmon and tuna, which are widely consumed for their health benefits, convenience, and versatility in cooking. Salmon is highly valued for its rich omega-3 content, while tuna is favored for its long shelf life and ease of use in various dishes. Retailers and restaurants continue to promote these fish through ready-to-cook options, pre-seasoned fillets, and meal kits, making them accessible to a broad range of consumers. The growing demand for sustainably sourced and clean-label seafood further strengthens the position of fish in the market.
Shrimp is emerging as the fastest-growing segment in the United States seafood market, with an expected CAGR of 2.32% through 2031. Its growth is fueled by its versatility in cooking, quick preparation time, and increasing domestic production through advanced aquaculture systems like recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS). Shrimp is widely used in various cuisines, from Asian stir-fries to Western-style salads, making it a favorite among consumers. The availability of value-added shrimp products, such as pre-seasoned or ready-to-cook options, has also expanded its appeal in both retail and foodservice channels. These factors are driving shrimp's growth, positioning it as a key contributor to the overall expansion of the United States seafood market in the coming years.
Frozen seafood products led the United States seafood market in 2025, accounting for 41.15% of the market share. This dominance is largely due to the heavy reliance on imports and the flexibility frozen products offer for storage and inventory management. Frozen seafood provides a longer shelf life and consistent quality, making it a preferred option for retailers and foodservice providers. Popular items like tuna, salmon, and shrimp drive this segment, supported by advancements in packaging and freezing technologies that maintain freshness and flavor. The convenience and cost-effectiveness of frozen seafood ensure its continued importance in the United States seafood supply chain.
Processed seafood is expected to grow the fastest among all formats, with a projected CAGR of 2.61% through 2031. This growth is driven by increasing consumer demand for convenient, ready-to-eat options that save time and effort. Products such as seasoned fillets, pre-cooked bowls, snack packs, and portioned servings are becoming more popular, catering to busy households and restaurants. These innovations make seafood more accessible and versatile, encouraging consumption across various occasions. By combining convenience with quality, processed seafood is set to become a key growth area in the United States seafood market over the coming years.
The United States Seafood Market Report is Segmented by Seafood Type (Fish, Shrimp, and More), Form (Canned, Frozen, and More), Source (Farmed and Wild-Caught), and Distribution Channel (On-Trade and Off-Trade). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Tons).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Inland Seafood Inc.
- Aqua Star Corp
- Tropic Seafood
- American Seafoods Group
- Mowi ASA
- Clearwater Seafoods
- Maruha Nichiro Corp. (Umios Corp.)
- Nissui Corporation (UniSea Corp.)
- Beaver Street Fisheries
- Trident Seafoods Corp.
- Leroy Seafood Group
- Pacific Seafood Group
- FCF Co. Ltd. (Bumble Bee)
- Thai Union (Chicken of the Sea)
- NaturalShrimp Inc.
- Dulcich Inc.
- Dongwon Industries
- Harvest Select Seafood
- Cooke Inc.
- High Liner Foods Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising consumer demand for protein-rich foods and omega-3 diets
- 4.2.2 Technology and farming innovation
- 4.2.3 Consumer demand for fresh and quality seafood
- 4.2.4 Consumer demand for seafood that is sustainable, certified, ethical, and traceable sourced
- 4.2.5 Culinary globalization and foodservice demand
- 4.2.6 Growth of aquaculture and improved import supply
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Competition from alternative proteins
- 4.3.2 Supply chain and cold chain limitations
- 4.3.3 Stringent regulatory and quality standards
- 4.3.4 Environmental risks and climate change
- 4.4 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.5 Consumer Behaviour Analysis
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE AND VOLUME)
- 5.1 By Seafood Type
- 5.1.1 Fish
- 5.1.1.1 Salmon
- 5.1.1.2 Tuna
- 5.1.1.3 Other Fish Type
- 5.1.2 Shrimp
- 5.1.3 Other Seafood
- 5.1.1 Fish
- 5.2 By Form
- 5.2.1 Canned
- 5.2.2 Fresh/Chilled
- 5.2.3 Frozen
- 5.2.4 Processed
- 5.3 By Source
- 5.3.1 Farmed
- 5.3.2 Wild-Caught
- 5.4 By Distribution Channel
- 5.4.1 Off-Trade
- 5.4.1.1 Supermarkets/Hypermarkets
- 5.4.1.2 Online Retail Stores
- 5.4.1.3 Convenience Stores
- 5.4.1.4 Others
- 5.4.2 On-Trade
- 5.4.2.1 Hotels
- 5.4.2.2 Restaurants
- 5.4.2.3 Catering
- 5.4.1 Off-Trade
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials (if available), Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Inland Seafood Inc.
- 6.4.2 Aqua Star Corp
- 6.4.3 Tropic Seafood
- 6.4.4 American Seafoods Group
- 6.4.5 Mowi ASA
- 6.4.6 Clearwater Seafoods
- 6.4.7 Maruha Nichiro Corp. (Umios Corp.)
- 6.4.8 Nissui Corporation (UniSea Corp.)
- 6.4.9 Beaver Street Fisheries
- 6.4.10 Trident Seafoods Corp.
- 6.4.11 Leroy Seafood Group
- 6.4.12 Pacific Seafood Group
- 6.4.13 FCF Co. Ltd. (Bumble Bee)
- 6.4.14 Thai Union (Chicken of the Sea)
- 6.4.15 NaturalShrimp Inc.
- 6.4.16 Dulcich Inc.
- 6.4.17 Dongwon Industries
- 6.4.18 Harvest Select Seafood
- 6.4.19 Cooke Inc.
- 6.4.20 High Liner Foods Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




