PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910873

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910873
Philippines Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Philippines courier, express, and parcel market is expected to grow from USD 1.33 billion in 2025 to USD 1.42 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 1.98 billion by 2031 at 6.81% CAGR over 2026-2031.
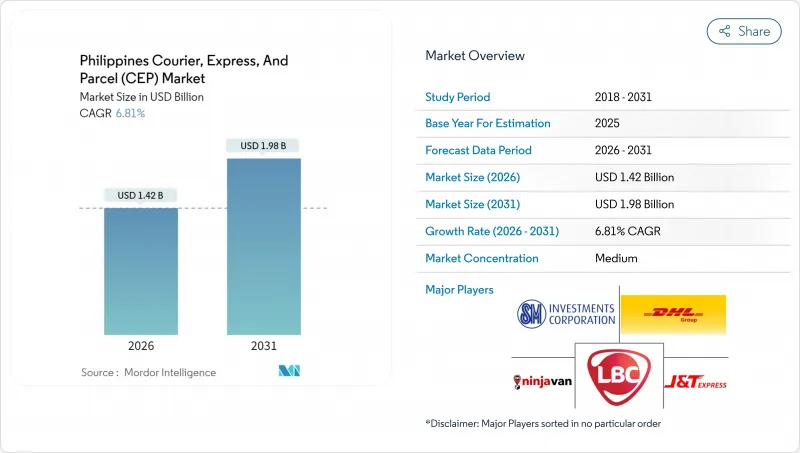
This growth is propelled by surging e-commerce volumes, sustained infrastructure investment, and the country's archipelagic geography, which together create a large addressable base for island-to-island delivery solutions. Intensifying competition, regulatory modernization, and rising consumer expectations for real-time visibility are prompting operators to upgrade technology stacks and redesign hub-and-spoke models. Consolidation pressure is growing as fuel price volatility and asset-heavy network requirements strain smaller fleets, while scale players leverage automation to protect margins. As a result, the Philippines courier, express, and parcel market is evolving from a volume-oriented model toward a technology-enabled, service-differentiated landscape that prizes speed, reliability, and geographic reach.
Philippines Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) Market Trends and Insights
Explosive E-Commerce Order Volumes
Transaction values are expected to represent 5.5% of national GDP in 2025, tripling the average parcel frequency per consumer and stretching existing sortation capacity. Operators are pivoting to high-throughput automation and dynamic routing tools that can orchestrate multiple transport modes across 7,641 islands. Modular hubs, scalable software, and data-driven capacity planning are enabling the Philippines courier, express, and parcel market to absorb a wave of small, frequent shipments without proportionate cost increases. Retail categories led by consumer electronics and fashion are compressing average parcel revenue yet boosting overall volume, rewarding carriers that achieve densification at the route level. E-commerce platforms increasingly condition tender awards on guaranteed delivery windows, pushing carriers toward predictive analytics and real-time visibility. Investments in robotic sorters and application-programming-interface integrations are becoming table stakes for relevance in the Philippines courier, express, and parcel industry.
Same-Day / Instant Delivery Preference in Metro Manila
Metro Manila houses 13 million residents within a dense road network where traffic congestion paradoxically favors nimble motorcycle fleets over vans. Same-day arrival has shifted from premium to baseline expectation, prompting couriers to roll out micro-fulfillment nodes inside the metropolis. These nodes shorten stem mileage, lower failed-delivery risk, and enable tighter two-hour delivery windows. Real-time tracking, automated proof-of-delivery, and proactive customer notifications are now standard features across leading platforms. Carriers that fail to meet visibility benchmarks risk customer churn as app-based challengers capture share with transparent, GPS-enabled service. To meet the capital intensity of same-day service, larger players are experimenting with asset-light franchise models that blend company-owned hubs with crowd-sourced rider supply, reinforcing the network density that underpins express profitability within the Philippines courier, express, and parcel market.
Port Congestion and Inter-Island Shipping Bottlenecks
Manila and Cebu ports routinely operate at 40-50% above designed throughput during peak periods, creating two-day average dwell overruns that ripple into downstream delivery commitments. Limited berthing slots and manual container handling extend vessel turnaround, while weather-driven RORO cancellations disrupt the sailing cadence vital for inventory-light models. Until port automation and berth expansion projects reach completion, carriers must maintain buffer inventory, multi-port contingency routes, and customer communication protocols to protect service levels in the Philippines courier, express, and parcel market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- MSME Digital-Selling Boom Outside NCR
- Government "Build Better More" Logistics Corridors
- Rising Fuel Surcharges Pressuring Last-Mile Margins
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
E-commerce commanded 42.10% share in 2025 as online marketplaces, direct-to-consumer brands, and social sellers collectively fueled daily shipment spikes. Bundled warehousing, returns management, and omnichannel integration services enhance retention of large platform accounts. Healthcare logistics posts a robust 7.10% CAGR between 2026-2031 as telemedicine, vaccine distribution, and prescription-by-mail programs demand temperature integrity, chain-of-custody compliance, and rapid fulfillment. GDP-certified warehouses, validated packaging, and regulatory-aligned documentation become critical differentiators in the Philippines courier, express, and parcel industry.
Financial-services parcels credit-card statements, legal documents-continue a measured migration to digital channels but still require secure physical handover in certain regulatory workflows. Manufacturing and wholesale shipments incorporate heavier SKUs and scheduled bulk-order patterns. Primary industries including agriculture and mining rely on courier networks for time-sensitive samples, spare parts, and compliance paperwork, underscoring the sector's broad-based relevance to national economic modernization.
Domestic flow anchored 64.40% of 2025 revenue, reflecting concentrated trade along the Manila-Cebu-Davao triangle where network density lowers per-parcel cost. Operators leverage fixed-route trucking and modular micro-depots to hit sub-48-hour delivery for 70% of intra-Luzon origin-destination pairs. The Philippines courier, express, and parcel market size for domestic services is projected to grow steadily yet face thinning margins as app-based competitors intensify discounting. International parcels, although smaller in absolute volume, register a 7.05% CAGR between 2026-2031, driven by cross-border e-commerce purchases, balikbayan boxes, and export shipments from MSMEs tapping overseas buyers. Premium pricing for customs clearance, airfreight space, and regulatory compliance underpins higher unit economics, making cross-border a profit stabilizer within the wider Philippines courier, express, and parcel market.
Expanding bilateral trade agreements and electronic customs platforms are shaving up to 48 hours off clearance times, narrowing service-quality gaps with regional peers. As Clark and Cebu airports add integrated cargo terminals, north-south diversion reduces Manila hub pressure, enabling faster transit for perishables and high-value electronics. Market leaders now bundle international shipping with localized returns orchestration, capitalizing on the diaspora's remittance-linked purchases and expanding the Philippines courier, express, and parcel industry's global connectivity.
The Philippines Courier, Express, and Parcel Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (E-Commerce and More), Destination (Domestic and International), Speed of Delivery (Express and More), Shipment Weight (Heavy Weight Shipments and More), Mode of Transport (Air, Road, and Others), and Model (Business-To-Business, Business-To-Consumer, and Consumer-To-Consumer). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Ayala Corporation
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- J&T Express
- Lalamove
- LBC Express Holdings, Inc.
- Ninja Van
- Philippine Postal Corporation (PHLPost)
- SM Investments Corporation (including 2GO)
- United Parcel Service (UPS)
- Ximex Delivery Express Logistics Inc. (XDE)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Logistics Performance
- 4.12 Infrastructure
- 4.13 Regulatory Framework
- 4.14 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.15 Market Drivers
- 4.15.1 Explosive E-Commerce Order Volumes
- 4.15.2 Same-Day/Instant Delivery Preference in Metro Manila
- 4.15.3 MSME Digital-Selling Boom Outside NCR
- 4.15.4 Government "Build Better More" Logistics Corridors
- 4.15.5 Rider-Security Regulations Improving Workforce Supply
- 4.15.6 Drone and Autonomous Delivery Pilots in Island Provinces
- 4.16 Market Restraints
- 4.16.1 Port Congestion and Inter-Island Shipping Bottlenecks
- 4.16.2 Rising Fuel Surcharges Pressuring Last-Mile Margins
- 4.16.3 Fragmented Address System in Rural Barangays
- 4.16.4 Intensifying Price Wars Among App-Based Players
- 4.17 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.18 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.18.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.18.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.18.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.18.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.18.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Ayala Corporation
- 6.4.2 DHL Group
- 6.4.3 FedEx
- 6.4.4 J&T Express
- 6.4.5 Lalamove
- 6.4.6 LBC Express Holdings, Inc.
- 6.4.7 Ninja Van
- 6.4.8 Philippine Postal Corporation (PHLPost)
- 6.4.9 SM Investments Corporation (including 2GO)
- 6.4.10 United Parcel Service (UPS)
- 6.4.11 Ximex Delivery Express Logistics Inc. (XDE)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment




