PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910910

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910910
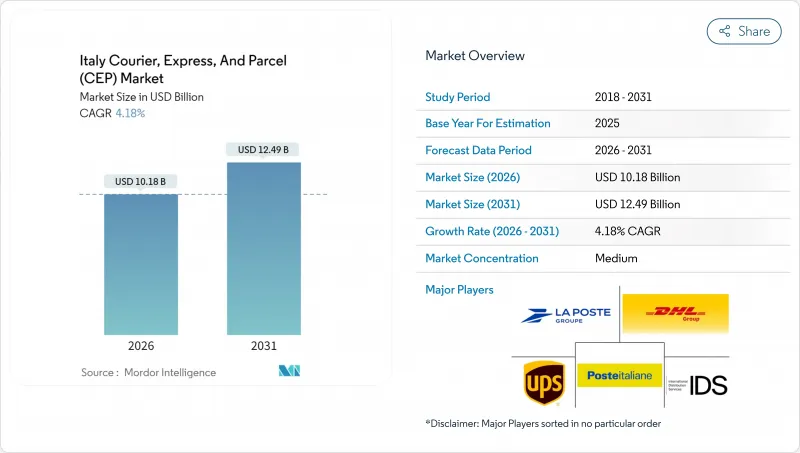
Italy Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Italy courier express parcel market is expected to grow from USD 9.77 billion in 2025 to USD 10.18 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 12.49 billion by 2031 at 4.18% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Italy holds a pivotal logistics role inside Europe because e-commerce spending hit EUR 58.8 billion (USD 64.89 billion) in 2024 and keeps expanding, while small-package demand from manufacturing exporters recovers in parallel. Route-dense urban areas such as Milan and Rome underpin high stop densities that support premium express services, even as national road toll hikes and driver shortages push operators toward cost-saving automation. International flows expand faster than domestic shipments, powered by cross-border e-commerce, pharmaceutical exports and simplified digital VAT refund processing for tourist purchases. Competitive intensity rises as Poste Italiane, DHL, UPS, FedEx and GLS invest in sortation automation, out-of-home collection networks and low-emission fleets, while impending EU Fit-for-55 rules accelerate fleet renewal and infrastructure electrification.
Italy Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) Market Trends and Insights
Strong Rebound of Italy's SME Exports Post-2024 Creates Higher B2B Parcel Density
Small and medium manufacturers lifted export volumes by 5.8% year on year in March 2025, concentrating activity along the A4 and A1 corridors that link Lombardy with key European markets. Dense export lanes generate superior stop economies for express carriers, allowing trucks to complete more premium deliveries per route. Machinery, textiles and specialty food producers increasingly rely on next-day CEP options so they can postpone inventory and still honor tight customer schedules. Northern logistics hubs around Milan and Bergamo attract investment in automated sort centers because carriers can justify higher capex where volumes cluster. International express margins rise as exporters pick premium products that guarantee customs clearance and late pickup windows, while domestic backhauls reduce repositioning costs.
Expansion of Micro-Fulfillment Centers by Grocery Chains Boosts Urban Same-Day Volumes
Grocery retailers accelerated micro-fulfillment roll-outs in 2024, with Esselunga spending EUR 5.8 million (USD 6.40 million) on compact facilities that can pick and dispatch orders inside two hours. These sub-10,000 ft2 nodes shorten last-mile distances, create same-day demand spikes, and favor parcels under five kilograms that fit light electric vans. Partnerships such as MD's alliance with Everli cover multiple cities and add predictable evening peak traffic, enabling carriers to deploy dedicated urban rounds that operate on strict delivery windows. Same-day grocery parcels carry premium surcharges which absorb the higher labor costs linked to dense stop frequency. Technology adoption rises as retailers test automated picking arms and temperature-segmented totes, raising requirements for data integration between store systems and CEP routing engines.
Driver Shortage Aggravated by Demographic Ageing
Only 2.2% of Italian truck drivers are under 25, while nearly one-half surpass 55, a gap wider than the European mean. Conftrasporto estimates 20,000 vacant driving jobs, and training costs near EUR 4,000 (USD 4,414.56) deter entrants. Logistics employers around Milan advertise monthly pay of EUR 3,392 (USD 3,743.55) but still struggle to fill shifts. Capacity tightness inflates subcontracting rates, forcing CEP networks to rebid linehaul contracts or lengthen transit windows. Policy responses include proposals to fast-track non-EU driver permits and co-fund license programs, yet uptake remains slow. Carriers trial double-deck trailers and AI routing tools to lift parcels per driver, but these gains do not fully offset workforce attrition.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- EU Fit-for-55 Regulation Accelerates Fleet Electrification Incentives
- Drone Corridor Pilot Between Milan and Bergamo Airports Slated for 2026
- 2025-27 Road-Toll Step-Ups on A4 And A14 Corridors
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
E-commerce commanded 34.60% share of 2025 volumes and sets service benchmarks that spill into other verticals. High return rates create extra reverse-logistics complexity, prompting carriers to deploy rules-based automation that sorts returns directly to refurbishment centers. Fashion brands pilot same-day try-at-home programs in Milan and Turin, extending parcel touches but lifting overall revenue per customer.
Healthcare parcels expand at a 4.33% CAGR between 2026-2031 because Italy's aging population increases medication throughput and biologic therapies demand strict cold-chain compliance. Carriers retrofit vans with GDP-validated chillers and install real-time temperature probes that send alerts to control towers. Pharmaceutical firms favor dedicated delivery windows that synchronize with hospital pharmacy schedules, ensuring priority access inside security zones.
Domestic deliveries accounted for 66.10% of the Italy courier express parcel market in 2025 because local sourcing and nationwide e-commerce anchor predictable daily volumes. Dense residential delivery points allow carriers to maximize stop efficiency, and familiarity with postal codes reduces address correction costs. Cross-border parcels, while smaller in count, expand at a 4.31% CAGR between 2026-2031 as fashion, pharmaceuticals, and industrial components rely on time-definite services for competitive differentiation. Customs simplification under the Import One-Stop Shop scheme lowers administrative frictions and supports growth.
International outbound growth is clustered around Milan, Turin and Bologna airports where exporters can access bonded facilities that speed clearance. Tourism-linked C2C parcels leverage duty-free thresholds, and operators market flat-rate boxes to capture souvenir traffic. The domestic network still underpins scale advantages, letting integrators redirect vehicles to international linehauls during off-peak domestic cycles. Alignment of domestic and European sortation windows will remain critical for maintaining overnight cut-off commitments without inflating hub staffing costs.
The Italy Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (E-Commerce and More), Destination (Domestic and More), Speed of Delivery (Express and Non-Express), Shipment Weight (Heavy Weight Shipments and More), Mode of Transport (Air, Road, and Others), and Model (Business-To-Business, Business-To-Consumer, and Consumer-To-Consumer). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Asendia
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- GEODIS
- International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- La Poste Group (including BRT)
- Poste Italiane
- Sailpost SpA
- Speedy SRL
- United Parcel Service (UPS)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Logistics Performance
- 4.12 Infrastructure
- 4.13 Regulatory Framework
- 4.14 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.15 Market Drivers
- 4.15.1 Strong Rebound of Italy's SME Exports Post-2024, Creating Higher B2B Parcel Density
- 4.15.2 Expansion of Micro-Fulfilment Centres by Grocery Chains, Boosting Urban Same-Day Volumes
- 4.15.3 EU Fit-for-55 Regulation Accelerating Fleet Electrification Incentives
- 4.15.4 Drone Corridor Pilot Between Milan-bergamo Airports Slated for 2026
- 4.15.5 Digital VAT Refund Platforms for Tourists Increasing C2C and Return Flows
- 4.15.6 Postal Bank Integration Unlocking Last-Mile Cash-on-delivery for Rural Areas
- 4.16 Market Restraints
- 4.16.1 Airport Slot Scarcity for Freighters at Milano-Malpensa
- 4.16.2 Driver Shortage Aggravated by Demographic Ageing
- 4.16.3 2025-27 Road-Toll Step-Ups on A4 and A14 Corridors
- 4.16.4 High Parcel Theft Rates in Southern Regions
- 4.17 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.18 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.18.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.18.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.18.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.18.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.18.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Asendia
- 6.4.2 DHL Group
- 6.4.3 FedEx
- 6.4.4 GEODIS
- 6.4.5 International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- 6.4.6 La Poste Group (including BRT)
- 6.4.7 Poste Italiane
- 6.4.8 Sailpost SpA
- 6.4.9 Speedy SRL
- 6.4.10 United Parcel Service (UPS)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment




