PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911781

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911781
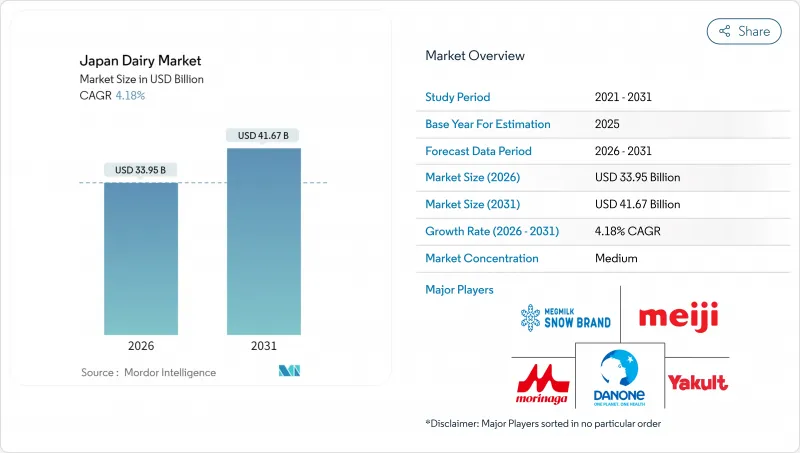
Japan Dairy - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Japan dairy market was valued at USD 32.59 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 33.95 billion in 2026 to reach USD 41.67 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 4.18% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
Structural labor shortages, increasing feed costs, premium product positioning, and advancements in functional foods are shaping demand trends. Growing health consciousness and a focus on preventive nutrition are boosting the consumption of low-fat, probiotic, fortified, and lactose-free dairy products, with yogurt and functional drinks leading this growth. Yogurt's probiotic benefits and milk's shelf-stable formats are driving greater household adoption. At the same time, cheese and dairy desserts are gaining popularity for their indulgent appeal. Retailers are focusing on chilled convenience formats to cater to urban commuters, while rural consumers are increasingly opting for ambient-stable UHT milk. In Hokkaido, farm automation is enhancing yields and partially addressing labor shortages. Concurrently, investments in precision fermentation and bifidobacteria strains are positioning Japan as a leader in functional dairy innovation, particularly under the Foods with Function Claims regime.
Japan Dairy Market Trends and Insights
Growing demand for premium cheese and yogurt
In Japan, cheese consumption has been steadily increasing, with natural cheese experiencing faster growth compared to processed cheese. The ongoing urbanization and the integration of Western culinary practices into Japanese cuisine have transformed cheese from a niche import into a widely accepted cooking ingredient and snack option. Yogurt, however, is experiencing an even more pronounced growth trajectory. Probiotic formulations, which focus on promoting immune health and digestive wellness, have become integral to breakfast routines and post-meal consumption habits. The trend of premiumization is also gaining momentum, as consumers demonstrate a willingness to pay higher prices for dairy products that are grass-fed and traceable. Multinational companies are seizing this opportunity by emphasizing origin storytelling and obtaining sustainability certifications to appeal to this growing preference. This shift is significantly reshaping retail assortments. Convenience stores are increasingly allocating chilled-case space to artisan and imported cheeses, while yogurt product lines have expanded to include a diverse range of options such as drinkable yogurts, spoonable varieties, and frozen dessert hybrids.
Health-conscious shift to functional dairy
Functional dairy products, enriched with probiotics, vitamins, or bioactive peptides, are increasingly appealing to consumers seeking preventive health solutions. Kirin's LC-Plasma lactobacillus strain enhances plasmacytoid dendritic cell activity. Japan's regulatory framework supports such advancements: The Foods with Function Claims system enables self-certification of health benefits backed by scientific evidence, expediting the process compared to the stricter Foods for Specified Health Uses pathway. This favorable environment is attracting pharmaceutical and nutraceutical companies to collaborate in dairy product development, blurring sector boundaries and driving research and development efforts. Japan's aging population emphasizes the importance of bone health, immunity, and gut wellness, fueling demand for probiotic yogurts and fortified milks as daily wellness staples. According to the Consumer Affairs Agency, 15.5% of Japanese consumers had tried health foods certified as "foods for specified health uses" (FOSHU) as of March 2024 . Urban professionals and younger consumers prefer convenient options, such as single-serve drinkable yogurts, which cater to their busy lifestyles while offering scientifically proven benefits like improved metabolism and digestive health.
Aging dairy-farmer population
Japan's dairy workforce is aging rapidly, with over 70% of workers now 65 or older. This demographic trend is reducing production capacity and increasing operational risks. Many producers, burdened by rising feed, particularly in compound feed and stagnant farmgate milk prices, are operating at a loss and considering exiting the market. According to the Japan Dairy Association, raw milk production in Japan declined from 7.53 million tons in 2022 to 7.32 million tons in 2023 . In June 2024, the government introduced a revised foreign labor policy, which includes a three-year development program to transition technical interns into Specified Skilled Workers. Although the program explicitly covers livestock farming, its implementation is delayed until 2027 and is expected to result in only a modest annual intake. Succession mechanisms, such as the Hokkaido Agricultural Public Corporation's five-year lease-to-own program and the Zenraku Academy's three-year training pathway, have supported the establishment of approximately 400 new farms since 1982. However, these initiatives address only a small portion of the annual retirements. The demographic challenges are driving consolidation, with herd sizes gradually increasing and corporate entities acquiring retired farms. Despite these efforts, the rate of consolidation lags behind the rate of exits, creating a structural supply deficit that imports and productivity improvements can only partially mitigate.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising awareness of nutritional benefits of dairy in aging population
- Advances in dairy processing technology improving shelf life and variety
- Gen-z shift toward plant-based options
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
In 2025, yogurt accounted for 36.08% of Japan's dairy market, reinforcing its role as a breakfast essential, a popular snack, and a health-focused product. Meanwhile, milk is expected to grow at the fastest rate among dairy products, with a forecasted CAGR of 4.72% through 2031. Probiotic advancements drive yogurt's leadership: Kirin's LC-Plasma strain, Meiji's R-1 series, and Morinaga's bifidobacteria formulations have elevated yogurt from a basic commodity to a preventive health product. Manufacturers have also obtained "Foods with Function Claims" certifications, enabling them to promote immune-support benefits on packaging. Drinkable yogurt formats appeal to on-the-go consumers, while spoonable options are preferred for sit-down breakfasts and post-meal consumption. Milk's growth is supported by ultra-high-temperature processing, which extends its shelf life to 150 days and facilitates room-temperature distribution. This innovation reduces cold-chain expenses and increases accessibility, particularly in rural areas and among single-person households. Flavored milk options, such as coffee, matcha, and strawberry, are gaining popularity with younger consumers, and UHT milk is also experiencing growth.
Cheese ranks as the third-largest segment, with natural cheese showing significant growth. This expansion in natural cheese is driven by its adoption in Western-style cooking and a shift toward premium products. Consumers are increasingly choosing Cheddar, Parmesan, and artisanal varieties for cooking and charcuterie boards. Cream, including fresh, cooking, and whipping variants, serves both foodservice and home-baking needs, with demand peaking during holiday seasons. Dairy desserts, such as ice cream, cheesecakes, and frozen treats, are growing as indulgence categories. Notable flavor innovations include Morinaga's Pino Matcha and Meiji's collaborative desserts. Sour milk drinks, a niche category, attract consumers seeking tangy, fermented flavors and probiotic benefits. This segmentation reveals a dual market structure: yogurt and milk drive volume, while cheese and desserts boost margins. As a result, processors are strategically managing their portfolios to optimize both revenue and profitability.
The Japan Dairy Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Butter, Cheese, Cream, Dairy Desserts, Milk, Yogurt, Sour Milk Drinks) and Distribution Channel (On-Trade, Off-Trade). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Tons).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Bel Japon KK
- Danone SA
- Megmilk Snow Brand Co. Ltd
- Meiji Dairy Corp.
- Morinaga Milk Industry Co. Ltd
- NH Foods Ltd
- Rokko Butter Co. Ltd
- Takanashi Dairy Co. Ltd
- Yakult Honsha Co. Ltd
- Yotsuba Milk Products Co. Ltd
- Koiwai Dairy Products Co. Ltd
- Arla Foods Japan K.K.
- Fonterra Japan Ltd
- Savencia Fromage and Dairy Japan
- Kraft Heinz Japan Co. Ltd
- Asahi Group Foods Ltd
- Ezaki Glico Co. Ltd
- Kyodo Milk Industry Co. Ltd
- Lacto Japan Co. Ltd
- Hokkaido Dairy Co-op
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing demand for premium cheese and yogurt
- 4.2.2 Health-conscious shift to functional dairy
- 4.2.3 Rising awareness of nutritional benefits of dairy in aging population
- 4.2.4 Advances in dairy processing technology improving shelf life and variety.
- 4.2.5 Strong domestic dairy brands with extensive product innovation
- 4.2.6 Robotic milking adoption in Hokkaido
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Ageing dairy-farmer population
- 4.3.2 Gen-Z shift toward plant-based options
- 4.3.3 Limited availability of grazing land in Japan
- 4.3.4 Consumer concerns over lactose intolerance and dairy allergies
- 4.4 Consumer Behaviour Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE AND VOLUME)
- 5.1 Product Type
- 5.1.1 Butter
- 5.1.1.1 Salted Butter
- 5.1.1.2 Unsalted Butter
- 5.1.2 Cheese
- 5.1.2.1 Natural Cheese
- 5.1.2.1.1 Cheddar
- 5.1.2.1.2 Cottage
- 5.1.2.1.3 Ricotta
- 5.1.2.1.4 Parmesan
- 5.1.2.1.5 Others
- 5.1.2.2 Processed Cheese
- 5.1.2.1 Natural Cheese
- 5.1.3 Cream
- 5.1.3.1 Fresh Cream
- 5.1.3.2 Cooking Cream
- 5.1.3.3 Whippng Cream
- 5.1.3.4 Others (Clottted, Sour Cream)
- 5.1.4 Dairy Desserts
- 5.1.4.1 Ice Cream
- 5.1.4.2 Cheesecakes
- 5.1.4.3 Frozen Desserts
- 5.1.4.4 Others (Puddings/desserts, trifles, fools)
- 5.1.5 Milk
- 5.1.5.1 Condensed milk
- 5.1.5.2 Flavored Milk
- 5.1.5.3 Fresh Milk
- 5.1.5.4 UHT Milk (Ultra-high temperature milk)
- 5.1.5.5 Powdered Milk
- 5.1.6 Yogurt
- 5.1.6.1 Drinkable
- 5.1.6.2 Spoonable
- 5.1.7 Sour Milk Drinks
- 5.1.1 Butter
- 5.2 Distribution Channel
- 5.2.1 On-trade
- 5.2.2 Off-trade
- 5.2.2.1 Convenience Stores
- 5.2.2.2 Specialist Retailers
- 5.2.2.3 Supermarkets and Hypermarkets
- 5.2.2.4 On-line Retail
- 5.2.2.5 Others (Warehouse clubs, gas stations, etc.)
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Bel Japon KK
- 6.4.2 Danone SA
- 6.4.3 Megmilk Snow Brand Co. Ltd
- 6.4.4 Meiji Dairy Corp.
- 6.4.5 Morinaga Milk Industry Co. Ltd
- 6.4.6 NH Foods Ltd
- 6.4.7 Rokko Butter Co. Ltd
- 6.4.8 Takanashi Dairy Co. Ltd
- 6.4.9 Yakult Honsha Co. Ltd
- 6.4.10 Yotsuba Milk Products Co. Ltd
- 6.4.11 Koiwai Dairy Products Co. Ltd
- 6.4.12 Arla Foods Japan K.K.
- 6.4.13 Fonterra Japan Ltd
- 6.4.14 Savencia Fromage and Dairy Japan
- 6.4.15 Kraft Heinz Japan Co. Ltd
- 6.4.16 Asahi Group Foods Ltd
- 6.4.17 Ezaki Glico Co. Ltd
- 6.4.18 Kyodo Milk Industry Co. Ltd
- 6.4.19 Lacto Japan Co. Ltd
- 6.4.20 Hokkaido Dairy Co-op
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




