PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836512

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836512
France Residential Real Estate - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The France residential real estate market size is valued at USD 528.33 billion in 2025 and is forecast to expand to USD 697.52 billion by 2030, reflecting a 5.92% CAGR.
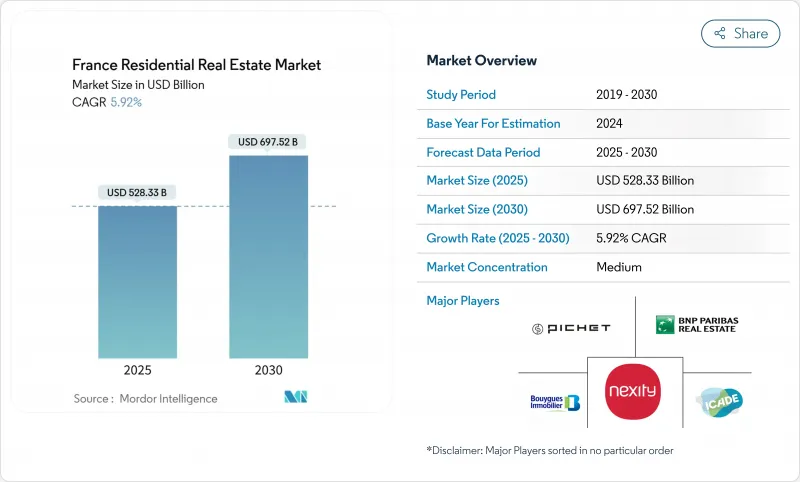
This recovery follows the 35.6% collapse in transaction volumes that occurred between August 2021 and October 2024, underlining the market's resilience as lending standards, mortgage costs, and demographic trends realign to new post-pandemic realities. Mortgage rates have eased from 4.21% in late 2023 to near 3.1% in 2025, and credit production is already 71% higher than the preceding year, signaling renewed purchasing power and liquidity. Structural housing shortages, regulatory energy-efficiency timelines, and remote-work migration to southern and western regions are adding durable tailwinds. At the same time, institutional capital is accelerating the rental-focused build-to-rent cycle, while energy regulations are accelerating upgrades in the existing stock, anchoring long-term value for compliant assets. Developers are pivoting toward recurring-income models and integrated investment services to shield margins from rising construction costs and policy-driven compliance outlays.
France Residential Real Estate Market Trends and Insights
Housing Deficit & Supply Imbalance Amid Declining Building Permits
New building permits fell 23.7% in 2023, deepening an estimated structural shortfall that underpins the France residential real estate market's long-run price floor. The deficit is most severe where net in-migration persists, such as Ile-de-France, which still adds roughly 50,000-60,000 residents per year despite accelerated outflows to southern regions. Costly materials and layered regulations slow new supply, so institutional investors target build-to-rent programs that lock in long leases and modern energy standards. Government ownership initiatives acknowledge the shortage's role in stabilizing prices, rewarding developers that can maneuver within compliance constraints and swiftly deliver stock
First-Time Buyer Incentives & PTZ+ Extension Fueling Entry-Level Demand
France extended the zero-interest Pret a Taux Zero (PTZ+) to December 2027 and widened eligibility nationwide from April 2025, lifting entry-level purchase capacity. Lower mortgage costs around 3.1% in 2025 have coincided with PTZ+ uptake, and banks indicate longer 20-plus-year loan maturities that keep monthly burdens manageable. By mitigating equity gaps, the program funnels activity toward secondary cities previously outside high-tension zones, diversifying regional demand and re-energizing first-time buyer traffic.
Rising Mortgage Rates & Tighter Lending Standards Squeezing Affordability
Although costs retreated from 4.2% peaks, the current 3.1% average still triples the record-low 1.05% rate of late 2021. Stricter prudential norms cap indebtedness, curbing access for mid-income borrowers, and outstanding housing loans slipped 0.65% y/y to EUR 1.424 trillion in July 2024 BNP-Paribas. Longer 253-month amortizations offset some pressure but highlight affordability strain in premium markets and defer ownership for younger households.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Remote-Work Driven Migration to Suburban & Rural Areas
- Energy-Efficiency Regulations Accelerating Renovation & New-Build Demand
- Stagnant Real Wage Growth Dampening Purchasing Power in Core Urban Areas
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Apartments captured 65% of France residential real estate market share in 2024, reflecting the dominance of higher-density living formats in metropolitan areas. Villas and landed houses account for a smaller base but are projected to expand at a 6.18% CAGR, benefiting from post-pandemic space preferences and remote-work flexibility. Energy mandates impose heavier per-unit retrofit costs on aging apartment blocks, whereas detached homes offer owners more control over upgrade timelines. Apartments nevertheless gain scale advantages in large urban regeneration projects such as Clichy-Batignolles, which is delivering 3,400 units including a 50% social-housing component. Rental-focused investors increasingly target suburban single-family assets to secure yield premiums above dense-core apartments, especially in Occitanie and Nouvelle-Aquitaine.
In the medium term, the France residential real estate market size of villa transactions is forecast to rise faster than apartment sales as household relocation to lower-density zones persists. Yet apartments will remain the backbone of urban portfolios, supported by inbound student and migrant populations, and by developer-led modernizations that lift energy labels to meet 2030 standards. Institutional buyers show growing appetite for mixed-use buildings that integrate residential floors atop commercial podiums, leveraging apartments' steady cash flows to balance office-market volatility.
Mid-market properties represented 46% of France residential real estate market size in 2024, providing the broadest match between buyer budgets and available stock. Affordable units, while smaller in value terms, are poised for 6.11% CAGR growth through 2030 as PTZ+ and MaPrimeRenov' lower entry hurdles. Regional dispersion is visible: demand for affordable homes clusters in secondary towns offering below-median prices and quality-of-life advantages, whereas high-income purchasers still dominate Parisian prime and luxury segments.
Energy-efficiency rules also shape price-band dynamics. Owners in lower-priced brackets may struggle to finance mandatory upgrades, risking accelerated disposals that tighten supply and elevate residual values of renovated affordable stock. Meanwhile, developers supported by institutional mandates funnel capital toward intermediate housing priced for public-sector employees, addressing a structural gap highlighted by a EUR 200 million residential program from pension fund ERAFP.
The France Residential Real Estate Market is Segmented by Property Type (Apartments & Condominiums and Villas & Landed Houses), Price Band (Affordable, Mid-Market and Luxury), Mode of Sale (Primary and Secondary), Business Model (Sales and Rental) and Region (Ile-De-France, Provence-Alpes-Cote D'Azur, Auvergne-Rhone-Alpes, Nouvelle-Aquitaine and Rest of France). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Nexity
- Bouygues Immobilier
- Vinci Immobilier
- Icade
- Groupe Pichet
- Promogim
- Linkcity
- Sogeprom
- BNP Paribas Real Estate
- Eiffage Immobilier
- VINGT Paris
- iad France
- BSK Immobilier
- Kaufman & Broad
- Altarea Cogedim
- CDC Habitat
- Foncia
- Century 21 France
- Orpi
- SeLoger
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Overview of the Economy and Market
- 4.2 Real Estate Buying Trends - Socioeconomic and Demographic Insights
- 4.3 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.4 Technological Outlook
- 4.5 Insights into Rental Yields in Real Estate Segment
- 4.6 Real Estate Lending Dynamics
- 4.7 Insights Into Affordable Housing Support Provided by Government and Public-private Partnerships
5 Market Landscape
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Housing Deficit & Supply Imbalance Amid Declining Building Permits
- 5.1.2 First-Time Buyer Incentives & PTZ+ Extension Fueling Entry-Level Demand
- 5.1.3 Remote-Work Driven Migration to Suburban & Rural Areas
- 5.1.4 Energy-Efficiency Regulations Accelerating Renovation & New-Build Demand
- 5.1.5 Growing Single-Person Households Increasing Demand for Smaller Units
- 5.1.6 Build-to-Rent Institutional Investment Growth Boosting Rental Supply
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 Rising Mortgage Rates & Tighter Lending Standards Squeezing Affordability
- 5.2.2 Stagnant Real Wage Growth Dampening Purchasing Power in Core Urban Areas
- 5.2.3 Ageing Housing Stock Requiring High Retrofit Costs
- 5.2.4 Price Volatility & Market Correction Creating Buyer Uncertainty
- 5.3 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 5.3.1 Overview
- 5.3.2 Real estate developers & Contractors - Key Quantitative and Qualitative insights
- 5.3.3 Real estate brokers and agents - Key Quantitative and Qualitative insights
- 5.3.4 Property management companies - Key Quantitative and Qualitative insights
- 5.3.5 Insights on Valuation Advisory and Other Real Estate Services
- 5.3.6 State of the building materials industry and partnerships with kep developers
- 5.3.7 Insights on key strategic real estate investors/buyers in the market
- 5.4 Porter's Five Forces
- 5.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 5.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 5.4.5 Competitive Rivalry
6 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (France Residential Real Estate Market Value)
- 6.1 By Property Type
- 6.1.1 Apartments & Condominiums
- 6.1.2 Villas & Landed Houses
- 6.2 By Price Band
- 6.2.1 Affordable
- 6.2.2 Mid-Market
- 6.2.3 Luxury
- 6.3 By Mode of Sale
- 6.3.1 Primary (New-Build)
- 6.3.2 Secondary (Existing Home Resale)
- 6.4 By Business Model
- 6.4.1 Sales
- 6.4.2 Rental
- 6.5 By Region
- 6.5.1 Ile-de-France
- 6.5.2 Provence-Alpes-Cote d'Azur
- 6.5.3 Auvergne-Rhone-Alpes
- 6.5.4 Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- 6.5.5 Rest of France
7 Competitive Landscape
- 7.1 Market Concentration
- 7.2 Strategic Moves
- 7.3 Market Share Analysis
- 7.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 7.4.1 Nexity
- 7.4.2 Bouygues Immobilier
- 7.4.3 Vinci Immobilier
- 7.4.4 Icade
- 7.4.5 Groupe Pichet
- 7.4.6 Promogim
- 7.4.7 Linkcity
- 7.4.8 Sogeprom
- 7.4.9 BNP Paribas Real Estate
- 7.4.10 Eiffage Immobilier
- 7.4.11 VINGT Paris
- 7.4.12 iad France
- 7.4.13 BSK Immobilier
- 7.4.14 Kaufman & Broad
- 7.4.15 Altarea Cogedim
- 7.4.16 CDC Habitat
- 7.4.17 Foncia
- 7.4.18 Century 21 France
- 7.4.19 Orpi
- 7.4.20 SeLoger
8 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 8.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




