PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1907329

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1907329
Germany Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Germany freight and logistics market is expected to grow from USD 221.37 billion in 2025 to USD 227.99 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 264.17 billion by 2031 at 2.99% CAGR over 2026-2031.
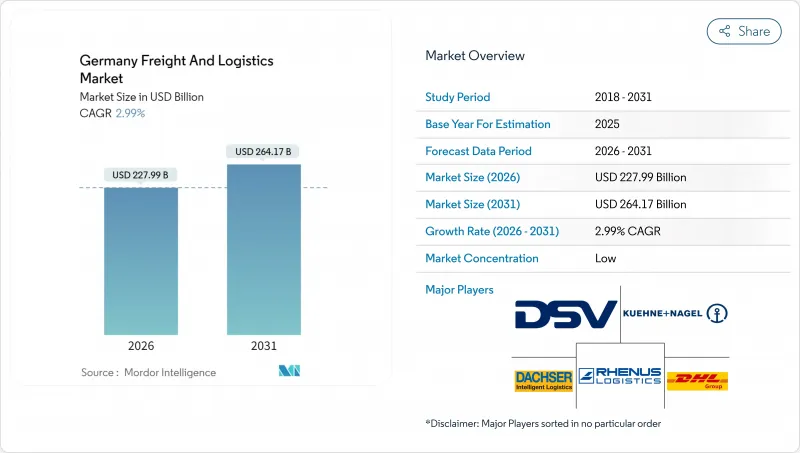
The moderate growth pace reflects an already-mature ecosystem that is repositioning around e-commerce fulfillment, export-oriented manufacturing corridors, and European Green Deal rules that raise carbon costs for road haulage. Rail incentive packages worth EUR 1.7 billion (USD 1.9 billion) through 2030, coupled with steadily climbing carbon prices of EUR 55 (USD 60.7) per tonne, are steering shippers toward intermodal solutions while still relying on road for flexible, short-haul moves. At the same time, the courier, express, and parcel (CEP) wave gains momentum from 87% consumer online-shopping penetration, pushing parcel density past 54 items per capita and accelerating automation investments in urban depots. Rising driver vacancies-70,000 open positions in 2025-tighten trucking capacity and elevate wages, motivating carriers to adopt route-optimization software and test autonomous yard tractors. Amid these structural shifts, the Germany freight and logistics market continues to leverage its central European location, 41,000 km highway grid, and world-class ports to anchor continental trade flows.
Germany Freight And Logistics Market Trends and Insights
E-commerce B2C Parcel Boom
Germany's e-commerce penetration hit 87% in 2024, translating into 4.5 billion annual parcels and driving a dense last-mile network that now averages 54 deliveries per resident. Grocery platforms grew 23% year over year as Amazon Fresh and Rewe expanded same-day services, prompting operators to pilot tram-based drop-offs in Frankfurt and micro-depots in parking structures across Berlin, Hamburg, and Munich. Parcel integrators responded by installing high-speed sorters capable of 30,000 items per hour and by adding electric delivery vans to comply with low-emission-zone rules. Seasonal peaks such as Singles' Day and Christmas overloaded city streets, making urban consolidation schemes a priority for municipalities. The sustained flow of small parcels reinforces the strategic value of robotics, AI-driven demand forecasting, and flexible shift scheduling for CEP networks.
Manufacturing Export Resilience
German factories shipped EUR 1.56 trillion (USD 1.72 trillion) worth of goods in 2024 despite global volatility, thanks to diversified destination markets and near-shoring of critical inputs. Automakers clustered tier-1 suppliers within 500 km of final-assembly plants in Bavaria and Baden-Wurttemberg, trimming transport lead times and stabilizing just-in-sequence flows. Machinery and chemical exporters locked in long-term rail contracts on the Hamburg-Munich and Rhine-Ruhr corridors, improving wagon-turnaround rates by 15% and shielding margins from diesel price spikes. The predictable freight corridors enable logistics providers to run high-capacity shuttles and negotiate volume-based discounts with terminal operators. Export reliability continues to underpin the Germany freight and logistics market, sustaining demand for temperature-controlled containers, specialized project cargo gear, and customs compliance services.
Driver Shortage and Aging Workforce
Vacancies hit 70,000 in 2025, with 39% of licensed truckers older than 55, eroding fleet utilization and forcing companies to park 7-10% of tractors during peak weeks. Training schools graduate only 18,000 new drivers annually, against retirement outflows above 25,000, widening the skills gap. Carriers raised wages 10% and offered sign-on bonuses, but lifestyle deterrents-night work, days away from home, dense regulation-limit attraction. As a stop-gap, shippers stagger delivery windows, charter rail blocks, and trial autonomous shuttles inside warehouse yards to free humans for open-road segments. The shortage constrains the Germany freight and logistics market's growth potential until automation or immigration solutions emerge.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing 3PL Outsourcing Among Mittelstand
- EU Green Deal-Linked Modal Shift Incentives
- Rising Motorway Tolls and Carbon Pricing
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Manufacturing accounted for 28.37% of Germany freight and logistics market share in 2025, translating into USD 62.81 billion in logistics spend. The segment's robustness derives from Germany's deep specialization in autos, machinery, and process industries that rely on sequenced just-in-time flows. Outsized inventory values and plant uptime requirements foster long-term, multi-service contracts for line-side delivery, returnable packaging, and sub-assembly. In contrast, wholesale and retail trade, while smaller at present, registers a 3.18% CAGR (2026-2031) as omnichannel models force rapid replenishment between stores, dark stores, and direct-to-consumer channels.
Construction logistics hinges on heavy-lift trucking and on-site sequencing for prefabricated modules, creating a steady if slower-growing slice of activity. Agriculture, Fishing & Forestry calls for cold chain capacity and time-critical windows during harvest peaks, bolstering reefer trailer demand and multimodal fresh-produce corridors to urban markets. Oil, Gas, Mining & Quarrying edges downward as Germany's Energiewende moves tonnage toward components for wind and solar installations. Emerging verticals, from medical technology to hydrogen fuel-cell components, add complexity and temperature-controlled micro-flows that favor specialized 3PLs.
Freight Transport remained the cornerstone at 59.29% share in 2025; however, the Courier, Express, and Parcel arm is forecast to post the quickest expansion at 3.44% CAGR between 2026-2031, propelled by residential delivery volumes tied to the e-commerce habit. Growth also favors Warehousing & Storage, which absorbs safety stocks as firms hedge against supplier shocks. Freight Forwarding adapts by bundling digital booking portals with multimodal visibility tools, enabling smaller exporters to tap premium air and rail services without owning transportation assets.
The Germany freight and logistics market continues to prioritize value-added services such as kitting, light assembly, and returns processing under the Others banner, all of which complement manufacturers' lean-production mandates. Domestic CEP registered a 66.56% share thanks to Germany's dense consumer base, yet cross-border CEP lanes inside the European single market post stronger growth as merchants court Polish, French, and Nordic shoppers. Freight Transport sub-segments show diverging fortunes: bulk trucking feels the brunt of carbon taxes, while specialized automotive milk-runs deliver stable contract revenue. Opportunistic consolidation among 3PLs, exemplified by DSV's purchase of DB Schenker, amplifies bargaining power over parcel integrators and port terminals.
The Germany Freight and Logistics Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry, Construction, Manufacturing, Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and Others) and by Logistics Function (Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP), Freight Forwarding, Freight Transport, Warehousing and Storage, and Other Services). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- A. Hartrodt
- A.P. Moller - Maersk
- Amazon
- BLG Logistics Group AG & Co. KG
- CMA CGM Group (Including CEVA Logistics)
- DACHSER
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- Emons Services GmbH
- FedEx
- Fiege Logistik Holding Stiftung and Co. KG
- GEODIS
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- Hermes Europe GmbH
- International Distributions Services (Including GLS)
- Kuehne+Nagel
- La Poste Group
- Rhenus Group
- ROHLIG SUUS Logistics SA
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.12 Trucking Fleet Size by Type
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Logistics Performance
- 4.15 Modal Share
- 4.16 Maritime Fleet Load Carrying Capacity
- 4.17 Liner Shipping Connectivity
- 4.18 Port Calls and Performance
- 4.19 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.20 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.21 Infrastructure
- 4.22 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.23 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.24 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.25 Market Drivers
- 4.25.1 E-Commerce B2C Parcel Boom
- 4.25.2 Manufacturing Export Resilience
- 4.25.3 Growing 3PL Outsourcing Among Mittelstand
- 4.25.4 EU Green Deal-Linked Modal Shift Incentives
- 4.25.5 On-Demand Warehousing Platforms Scaling Up
- 4.25.6 OEM-Backed Battery-Logistics Corridors for EV Supply Chains
- 4.26 Market Restraints
- 4.26.1 Driver Shortage and Ageing Workforce
- 4.26.2 Rising Motorway Tolls and Carbon Pricing
- 4.26.3 Limited Urban Consolidation Hubs
- 4.26.4 Inland Waterway Low-Water Disruptions
- 4.27 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.28 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.28.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.28.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.28.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.28.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.28.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 A. Hartrodt
- 6.4.2 A.P. Moller - Maersk
- 6.4.3 Amazon
- 6.4.4 BLG Logistics Group AG & Co. KG
- 6.4.5 CMA CGM Group (Including CEVA Logistics)
- 6.4.6 DACHSER
- 6.4.7 DHL Group
- 6.4.8 DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.9 Emons Services GmbH
- 6.4.10 FedEx
- 6.4.11 Fiege Logistik Holding Stiftung and Co. KG
- 6.4.12 GEODIS
- 6.4.13 Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- 6.4.14 Hermes Europe GmbH
- 6.4.15 International Distributions Services (Including GLS)
- 6.4.16 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.17 La Poste Group
- 6.4.18 Rhenus Group
- 6.4.19 ROHLIG SUUS Logistics SA
- 6.4.20 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment




