PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940690

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940690
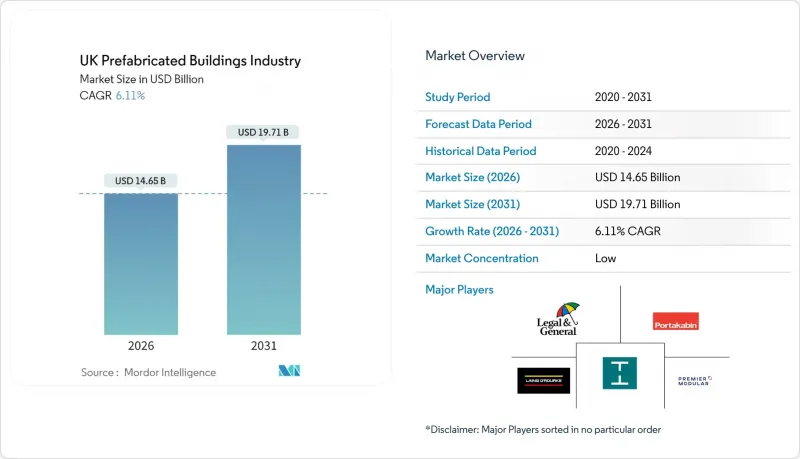
UK Prefabricated Buildings Industry - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The UK prefabricated buildings market is expected to grow from USD 13.81 billion in 2025 to USD 14.65 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 19.71 billion by 2031 at 6.11% CAGR over 2026-2031.
This expansion stems from urgent housing-supply targets, post-Brexit labor shortages, and aggressive net-zero mandates that collectively push builders toward factory-based solutions. Government funding of USD 49.6 billion (£39 billion) for social and affordable homes, coupled with streamlined planning approvals, improves visibility for manufacturers and encourages capacity investments.
Traditional contractors are partnering with modular specialists to mitigate site costs and secure ESG-linked finance, while institutional investors raise allocations to Build-to-Rent schemes that favor repeatable volumetric designs. Scotland's housing-emergency reforms accelerate order pipelines beyond England, and the Department for Education's six-year, USD 19.5 billion construction framework embeds off-site classifications that guarantee sustained demand for classrooms, colleges, and community assets. Simultaneously, public-sector frameworks for healthcare infrastructure spur volumetric bids that reduce project timelines and embodied carbon versus conventional builds.
UK Prefabricated Buildings Industry Trends and Insights
Government Housing Targets Drive MMC Acceleration
Mandatory delivery of 1.5 million homes by 2030 anchors a predictable pipeline that lets factories optimize throughput and cut unit costs. The USD 49.6 billion Social and Affordable Homes Programme prioritizes modular bids, while the Planning & Infrastructure Bill trims approval times that once stalled volumetric projects. Education procurement reinforces demand, with a six-year framework that embeds CPV 44211000 for prefabricated buildings and guarantees multi-lot opportunities for compliant suppliers.
SMEs secure financing through the Levelling Up Home Building Fund, which assigns USD 1.35 billion net-present social value to modern methods, translating to as many as 51,700 modular homes by 2027. Regional execution varies: England leads adoption, and Scotland's National Planning Framework 4 now mirrors these accelerative measures after declaring a housing emergency.
Post-Brexit Labor Shortages Inflate Traditional Construction Costs
The industry needs 225,000 additional workers by 2027, but immigration restrictions tighten supply, pushing London site wages beyond historic peaks. Government training grants of USD 756 million are helpful yet slow to solve acute shortages, leading to a 15-20% rise in construction costs since 2020, especially for specialist trades.
Factory settings reduce manual exposure and centralize skilled labor, insulating project budgets from volatile site rates. Laing O'Rourke's dedicated MMC training hub illustrates the pivot toward manufacturing-style skills aligned with off-site production. The widening cost differential between on-site and factory-built strengthens the UK prefabricated buildings market's appeal to developers navigating thin margins.
High Upfront Capital Requirements Challenge Factory Utilization
Fixed overheads for automated lines make utilization rates the make-or-break metric for modular firms. Ilke Homes' USD 397 million collapse underscored how weak pipelines turn world-class factories into loss centers, resulting in 1,150 job losses and shaking investor confidence. TopHat paused its Corby super-factory-planned for 4,000 units annually-illustrating sector-wide caution amid mortgage volatility and inflationary pressures. A House of Lords inquiry linked inconsistent public-sector demand to under-utilized lines, creating a vicious cycle where investors defer capital until volumes stabilize. Even Legal & General shuttered its modular arm despite deep pockets, proving scale alone does not guarantee break-even when orders dip. Insolvency rates in 2023 led the entire construction sector, pushing lenders to tighten working-capital terms and raising entry barriers for new players.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Net-Zero Mandates Favor Low-Waste Off-Site Methods
- Public Procurement Frameworks Favor Volumetric Solutions
- Mortgage and Valuation Hurdles Constrain End-User Financing
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Timber captured 33.40% of the UK prefabricated buildings market share in 2025, riding on government afforestation goals and well-established domestic supply chains that shorten lead times. The segment benefited from Vistry Group's 16,118 unit output, 67% of which used timber frames that align with partner-funded housing strategies. Timber's strength also lies in regulatory preference, as EPC scoring and net-zero pathways reward carbon-sequestering materials. Still, price sensitivity to global lumber supply and fire-safety compliance necessitate hybrid detailing, blending steel cores with cross-laminated panels to meet urban fire codes without eroding speed advantages.
Glass ranks as the fastest-growing material, forecast to expand at a 6.74% CAGR, propelled by advanced curtain-wall systems for high-rise volumetric towers like Ten Degrees, which achieved a 40% embodied-carbon reduction. Developers prize glass for daylighting, airtightness, and aesthetics that counter stigma around "pre-fab" looks, especially in premium Build-to-Rent schemes. Meanwhile, metal frames and concrete panels preserve steady demand for structural stability and acoustic ratings in dense city centers. Composite and hybrid formulations serve niche applications where balcony cantilevers or extreme span requirements outstrip single-material performance limits.
The UK Prefabricated Buildings Market Report is Segmented by Material Type (Concrete, Glass, Metal, Timber, and Other Material Types), Application (Residential, Commercial, and Others), Product Type (Modular Buildings, Panelized & Componentized Systems, Other Prefab Types), and Region (England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Laing O'Rourke (Explore Manufacturing)
- Vision Modular Systems
- Legal & General Modular Homes
- TopHat
- Portakabin Limited
- Premier Modular
- Elements Europe
- McAvoy Group
- Algeco UK / Elliott Group
- Urban Splash House Holdings
- Berkeley Modular
- M-AR Offsite
- Reds10
- Modulek
- Metek Modular
- Rollalong
- Balfour Beatty (Offsite Solutions)
- Bouygues UK (Modular)
- Kier Integrated Offsite
- Ilke Homes
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Government '300 k-homes' target accelerating MMC adoption
- 4.2.2 Post-Brexit skilled-labour crunch inflating on-site costs
- 4.2.3 Net-zero & circular-economy mandates favour low-waste off-site methods
- 4.2.4 Public-procurement frameworks (DfE MMC, NHS P23) favour volumetric bids
- 4.2.5 Institutional investors chasing ESG scores via modular BTR assets
- 4.2.6 Idle pandemic ICU-module lines repurposed for school classrooms
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront CAPEX & uncertain factory utilisation
- 4.3.2 Mortgage & valuation hurdles for non-traditional dwellings
- 4.3.3 Insolvency shocks (e.g., ilke) eroding supply-chain confidence
- 4.3.4 UK road-width limits constraining shippable module size
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Brief on Different Structures Used in Prefabricated Buildings
- 4.9 Cost Structure Analysis of Prefabricated Buildings
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Material Type
- 5.1.1 Concrete
- 5.1.2 Glass
- 5.1.3 Metal
- 5.1.4 Timber
- 5.1.5 Other Materials
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Residential
- 5.2.2 Commercial
- 5.2.3 Others
- 5.3 By Product Type
- 5.3.1 Modular Buildings
- 5.3.2 Panelized & Componentized Systems
- 5.3.3 Other Prefab Types
- 5.4 By Region
- 5.4.1 England
- 5.4.2 Scotland
- 5.4.3 Wales
- 5.4.4 Northern Ireland
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Laing O'Rourke (Explore Manufacturing)
- 6.4.2 Vision Modular Systems
- 6.4.3 Legal & General Modular Homes
- 6.4.4 TopHat
- 6.4.5 Portakabin Limited
- 6.4.6 Premier Modular
- 6.4.7 Elements Europe
- 6.4.8 McAvoy Group
- 6.4.9 Algeco UK / Elliott Group
- 6.4.10 Urban Splash House Holdings
- 6.4.11 Berkeley Modular
- 6.4.12 M-AR Offsite
- 6.4.13 Reds10
- 6.4.14 Modulek
- 6.4.15 Metek Modular
- 6.4.16 Rollalong
- 6.4.17 Balfour Beatty (Offsite Solutions)
- 6.4.18 Bouygues UK (Modular)
- 6.4.19 Kier Integrated Offsite
- 6.4.20 Ilke Homes
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




