PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850012

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850012
China Wound Care Management Devices - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The China wound care management devices market size stands at USD 0.98 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 1.33 billion by 2030, advancing at a 6.30% CAGR.
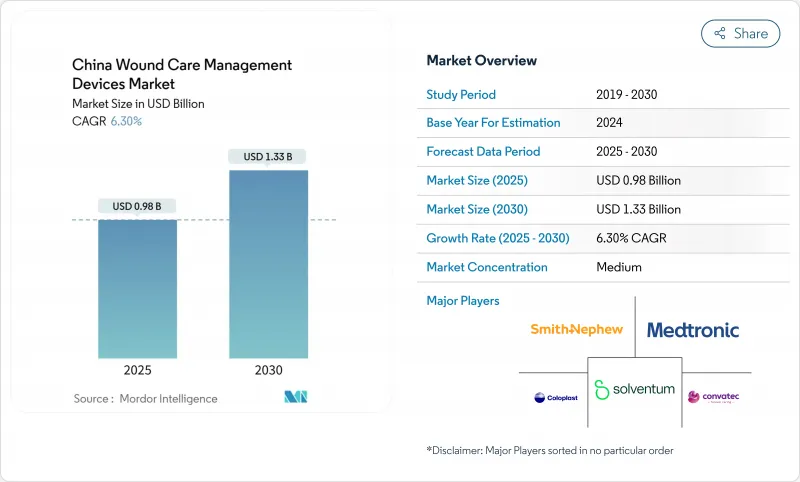
That trajectory reflects accelerating hospital capacity expansion, surging chronic disease prevalence, and government payment reforms that reward faster healing over procedure volume. China supports 233 million diabetes patients-15.88% of its adult population in 2023-and, without intervention, prevalence could rise to 29.1% by 2050 . Wound-healing centers multiplied, signaling institutional readiness for advanced therapies. At the same time, Volume-Based Procurement (VBP) is cutting average prices for high-value consumables by roughly 70%, forcing suppliers to prove clear economic value. Digital health policies-66 enacted in 2023 alone-further stimulate demand for connected dressings and remote monitoring solutions.
China Wound Care Management Devices Market Trends and Insights
Rising Incidence of Diabetes & Chronic Wounds
Diabetes prevalence increased from 7.53% in 2005 to 13.67% in 2023, inflating demand for the China wound care management devices market. Diabetic-foot treatment cost per patient jumped, while amputation rates almost tripled, prompting hospitals to shift toward preventive dressings and negative-pressure systems. Close to 100 million Chinese suffer chronic wounds every year, and diabetic ulcers have overtaken trauma as the primary cause. Evidence of superior healing in southern provinces drives region-specific adoption strategies. Collectively, these dynamics underpin sustained growth for the China wound care management devices market.
Demand for Faster Recovery & Reduced Hospital Stay
Complex-wound inpatients average 12 days of hospitalization versus seven for ordinary admissions, with median medical costs exceeding RMB 6,500. Hospitals therefore invest in technologies that shorten recovery. Modified negative-pressure therapy has trimmed healing time by almost three days and halved treatment expenses. Smart bandages such as the iCares system detect complications several days earlier than clinical observation. These solutions align with Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG) payment reforms that reward outcomes, helping expand the China wound care management devices market in metropolitan hubs.
Stringent Registration (NMPA Class III) & Reimbursement Hurdles
Advanced dressings classified as Class III must undergo extensive trials, often extending approval by up to two years. New 2024 procurement rules require local patents and manufacturing, effectively sidelining many multinationals. Price negotiations led by the National Healthcare Security Administration resulted in average 63% cuts for novel therapies, squeezing margins. Commercial insurance covers just 7.7% of innovative-device costs, forcing patients to pay nearly half out-of-pocket. These hurdles temper growth, especially for premium imports within the China wound care management devices market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Ageing Population & Higher Elective Surgeries
- Growing Technological Advancements in Wound Care Devices
- High Price Sensitivity in Public Tenders
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Advanced wound care retained a 63.23% share of the China wound care management devices market in 2024. Studies show negative-pressure therapy achieves 99.75% closure versus 94% for conventional methods, reinforcing clinical preference. Hospitals also favor antimicrobial hydrofibers such as Aquacel Ag+ for chronic ulcers, citing faster granulation. Advanced dressings' higher upfront cost is offset by shorter length-of-stay incentives under DRG payment reform, supporting wider adoption in tertiary centers.
The wound-closure segment, though smaller, is forecast to rise at a 6.91% CAGR. Tissue adhesives and absorbable sealants gain traction for minimally invasive surgery, and automated staplers improve operating-room efficiency. Liquid-diode smart bandages that channel exudate one way while reading pH levels represent the next leap. Taken together, product innovation underpins enduring expansion of the China wound care management devices market.
Chronic conditions accounted for 59.21% of the China wound care management devices market size in 2024, led by diabetic foot ulcers with an 8.1% annual incidence among diabetics. Specialized centers and city-level reimbursement pilots are scaling advanced dressings, although northern provinces still report slower healing. Pressure ulcers remain a costly inpatient problem, elevating demand for breathable silicone foams.
Acute wounds are projected to expand at 6.96% CAGR, reflecting increased elective surgery and improved emergency trauma care. Prophylactic negative-pressure systems reduce surgical-site infection by 74%, reinforcing hospital adoption. Dynamically phase-adaptive hydrogels that harden on impact but soften for remodeling shorten closure times in burn units. Such performance advantages sustain the acute segment's outsized contribution to incremental growth within the China wound care management devices market.
The China Wound Care Management Devices Market is Segmented by Product (Wound Care [Dressings, Wound-Care Devices, and More] and Wound Closure [Sutures, Surgical Staplers, and More]), Wound Type (Chronic Wounds and Acute Wounds), End User (Hospitals & Specialty Wound Clinics and More), and Mode of Purchase (Institutional Procurement and Retail / OTC Channel). The Market and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Johnson & Johnson
- Solventum
- Smiths Group
- Medtronic
- Coloplast
- Molnlycke Health Care
- Convatec
- Beiersdorf
- Winner Medical
- Zhende Medical
- Mindray (Negative-Pressure Therapy)
- SunMed Medical
- Acelity/KCI
- B. Braun
- Baxter
- DermaSci
- Kang Li Medical
- Lohmann & Rauscher
- Hartmann
- United-DS Medical
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising incidence of diabetes & chronic wounds
- 4.2.2 Demand for faster recovery & reduced hospital stay
- 4.2.3 Ageing population & higher elective surgeries
- 4.2.4 Growing technological advancements in Wound care devices
- 4.2.5 Government DRG payment reform accelerating adoption of advanced dressings
- 4.2.6 Rising e-commerce penetration of wound supplies in tier-3/4 cities
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Stringent registration (NMPA Class III) & reimbursement hurdles
- 4.3.2 High price sensitivity in public tenders
- 4.3.3 Emerging domestic OEMs triggering price wars in negative-pressure devices
- 4.3.4 Shortage of wound care specialists
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porters Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Product
- 5.1.1 Wound Care
- 5.1.1.1 Dressings
- 5.1.1.1.1 Traditional Gauze & Tape Dressings
- 5.1.1.1.2 Advanced Dressings
- 5.1.1.2 Wound-Care Devices
- 5.1.1.2.1 Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT)
- 5.1.1.2.2 Oxygen & Hyperbaric Systems
- 5.1.1.2.3 Electrical Stimulation Devices
- 5.1.1.2.4 Other Wound Care Devices
- 5.1.1.3 Topical Agents
- 5.1.1.4 Other Wound Care Products
- 5.1.2 Wound Closure
- 5.1.2.1 Sutures
- 5.1.2.2 Surgical Staplers
- 5.1.2.3 Tissue Adhesives, Strips, Sealants & Glues
- 5.1.1 Wound Care
- 5.2 By Wound Type
- 5.2.1 Chronic Wounds
- 5.2.1.1 Diabetic Foot Ulcer
- 5.2.1.2 Pressure Ulcer
- 5.2.1.3 Venous Leg Ulcer
- 5.2.1.4 Other Chronic Wounds
- 5.2.2 Acute Wounds
- 5.2.2.1 Surgical/Traumatic Wounds
- 5.2.2.2 Burns
- 5.2.2.3 Other Acute Wounds
- 5.2.1 Chronic Wounds
- 5.3 By End User
- 5.3.1 Hospitals & Specialty Wound Clinics
- 5.3.2 Long-term Care Facilities
- 5.3.3 Home-Healthcare Settings
- 5.4 By Mode of Purchase
- 5.4.1 Institutional Procurement
- 5.4.2 Retail / OTC Channel
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Johnson & Johnson (Ethicon)
- 6.3.2 Solventum
- 6.3.3 Smith & Nephew
- 6.3.4 Medtronic
- 6.3.5 Coloplast
- 6.3.6 Molnlycke Health Care
- 6.3.7 Convatec
- 6.3.8 Beiersdorf
- 6.3.9 Winner Medical
- 6.3.10 Zhende Medical
- 6.3.11 Mindray (Negative-Pressure Therapy)
- 6.3.12 SunMed Medical
- 6.3.13 Acelity/KCI
- 6.3.14 B. Braun
- 6.3.15 Baxter
- 6.3.16 DermaSci
- 6.3.17 Kang Li Medical
- 6.3.18 Lohmann & Rauscher
- 6.3.19 Hartmann
- 6.3.20 United-DS Medical
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




