PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850164

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850164
Wound Care Management Devices - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
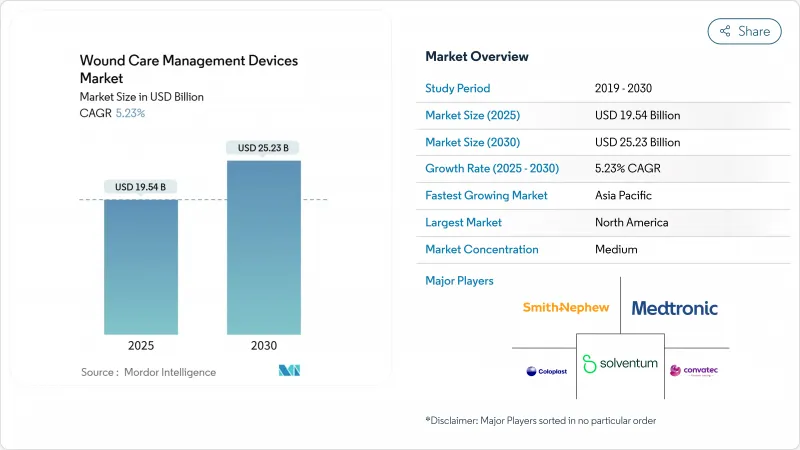
The wound care management devices market size stands at USD 19.54 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 25.23 billion by 2030, advancing at a 5.23% CAGR.
Aging populations, the rising prevalence of diabetes, and steady growth in surgical procedures provide persistent demand tailwinds . Hospitals are investing in negative-pressure wound therapy (NPWT) and smart dressings to curb readmissions, while retailers expand over-the-counter offerings that empower home-based treatment. Breakthroughs such as algae-derived hemostatic gels and bioengineered tissue matrices are shortening healing times and lowering long-term costs. Regulatory pathways in the United States and the European Union now fast-track class-I liquid bandages and other low-risk devices, accelerating commercialization. Market incumbents respond by forging alliances with AI specialists to embed real-time imaging and decision support into dressings and pumps.
Global Wound Care Management Devices Market Trends and Insights
Rising Incidence of Chronic & Diabetic Wounds
Diabetic foot ulcers now affect 15% of patients living with diabetes, driving hospitals to adopt multidisciplinary programs that pair advanced dressings with continuous glucose monitoring. Time-gated mid-infrared optoacoustic sensors enable depth-selective glucose readings, allowing clinicians to adjust therapy before complications arise. Early intervention strategies are shrinking hospitalization days and lowering amputation risks. Payers reward these outcomes with bundled payments that cover dressings, sensors, and telehealth follow-ups. Manufacturers are therefore integrating electronics into dressings to transmit moisture, pH, and temperature data, aligning device design with chronic-care protocols.
Escalating Global Surgical Volumes
Worldwide elective and trauma procedures rebounded in 2025, increasing demand for advanced closure strips, tissue sealants, and NPWT canisters. Mohs micrographic surgery trials on the scalp confirmed that pinch grafting reduces healing times versus second-intention protocols . As ambulatory surgical centers scale throughput, they deploy compact NPWT pumps that fit same-day discharge models. Ultrasound-guided debridement heads off infection risk, and real-time imaging helped cut readmission penalties at high-volume hospitals in the United States. These results encourage procurement teams to refresh closure portfolios despite budget pressures.
Limited Reimbursement in Emerging Markets
Many public insurers in Southeast Asia and Latin America still cover only basic gauze, delaying uptake of NPWT or bioengineered skin substitutes. Rural clinics often face supply-chain gaps that further limit access. Governments are piloting tiered benefit packages that reimburse advanced dressings for diabetic foot ulcers when primary dressings fail, but budget ceilings remain tight. Local assemblers that source polyurethane foams domestically and fill canisters onsite lower price barriers, yet clinician training lags. Public-private partnerships are beginning to bundle devices with outcome-based financing to bridge the affordability gap.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Continuous Product & Material Innovations
- Shift Toward Home-Care & Single-Use NPWT Devices
- High Total Cost of Advanced Therapies
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The wound care segment held 62.43% of 2024 revenue as clinicians favored antimicrobial foams, hydrofibers, and portable NPWT systems for complex cases. This dominance underscores how the wound care management devices market continues pivoting toward products that cut infection risk and support granulation. Wound closure items-including staples, adhesives, and absorbable barbed sutures-recorded a 5.87% CAGR outlook through 2030, buoyed by growing orthopedics and cardiovascular volumes. Traditional gauze retains relevance in low-acuity settings but yields share to dressings imbued with silver or PHMB for postoperative wounds.
Manufacturers integrating AI chips into dressings enable automatic moisture alerts and dosing of embedded antimicrobials, meeting hospital protocols for pressure-injury prevention. Meanwhile, topical biologics migrate from hospital pharmacies to outpatient infusion centers, expanding reach. The wound care management devices market is seeing combination products that pair a smart sensor layer with a hydrogel drug reservoir, supporting reimbursement under newly issued bundled CPT codes. Suppliers that align material science with digital monitoring gain bargaining power in tenders set by group purchasing organizations.
Chronic wounds controlled 58.34% of 2024 revenue, reflecting the resource intensity of diabetic foot ulcers, pressure injuries, and venous leg ulcers. These indications demand prolonged therapy, and payers approve high-end dressings when audits confirm reduced readmissions. Acute wounds, including trauma and post-operative incisions, are expanding at a 5.92% CAGR thanks to rising global surgery rates. Burn centers adopt enzymatic debriders paired with biosynthetic skin substitutes to reduce grafting needs.
Predictive algorithms embedded in electronic health records flag patients at ulcer risk, prompting early application of off-loading shoes and moisture-managing foams. Pressure-injury protocols now employ surface sensors that adjust mattress air cells to redistribute load. Diabetic ulcer management benefits from handheld imaging spectrometers that detect perfusion deficits, steering clinicians toward vascular interventions earlier in the care pathway. Such workflow changes reinforce premium product demand within the wound care management devices market.
The Wound Care Management Devices Market is Segmented by Product (Wound Care [Dressings, Wound-Care Devices, and More] and Wound Closure), Wound Type (Chronic Wounds and Acute Wounds), End User (Hospitals & Specialty Wound Clinics and More), Mode of Purchase (Institutional Procurement and Retail / OTC Channel), and Geography (North America, and More). The Market and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America leads the wound care management devices market, generating 40.12% of the market revenue in 2024. As sophisticated insurance models fund high-end dressings, NPWT, and bioengineered tissues. In the United States, bundled payments under value-based contracts reward quicker closure and fewer complications, encouraging hospitals to trial next-generation hydrogels and sensor-enabled foams. The Food and Drug Administration exempts low-risk liquid bandages from 510(k) clearance, shortening launch times for consumer-oriented products. Canada's single-payer system invests in home-care NPWT pilots that cut outpatient clinic load by 18% in 2025. Mexico continues upgrading surgical facilities, opening bids for mid-priced closure strips and polyurethane films.
Europe remains a mature yet innovation-receptive arena. National health systems fund chronic wound bundles that cover sensor-enabled dressings when evidence shows shorter healing cycles. Germany's hospitals adopt AI-guided imaging to comply with new pressure-injury reporting mandates, stimulating device replacement. The United Kingdom rolls out community nurse-led diabetic foot programs supported by portable imaging tablets. Meanwhile, Southern Europe pursues cost-effective hydrogels that still meet EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) documentation, creating niches for mid-range suppliers.
Asia-Pacific registers the fastest momentum for the wound care management devices market, registering a CAGR of 6.12% through 2030, fueled by healthcare infrastructure expansion and growing elective surgery capacity. China's centralized bulk-procurement schemes now include NPWT pumps, driving local manufacture of canisters and foam dressings to meet price caps. Japan prioritizes aging-in-place policies that reimburse home-care dressings and sensor patches, fostering innovation in ultra-thin silicone adhesives suited to fragile skin. India's state insurance programs begin covering advanced dressings for diabetic foot ulcers in tertiary centers, catalyzing distributor networks that penetrate tier-2 cities. Throughout Southeast Asia, private hospitals differentiate through specialty wound clinics equipped with tele-dermatology portals, widening regional market reach.
- Solventum
- Smiths Group
- Convatec
- Molnlycke Health Care
- Cardinal Health
- Coloplast
- Hartmann Group
- Medtronic
- B. Braun
- Integra LifeSciences
- Essity Medical
- Johnson & Johnson
- Baxter
- Organogenesis
- Kinetic Concepts
- Medela
- Medline Industries
- Lohmann & Rauscher
- Teleflex Medical
- Devon Medical
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising incidence of chronic & diabetic wounds
- 4.2.2 Escalating global surgical volumes
- 4.2.3 Continuous product & material innovations
- 4.2.4 Shift toward home-care & single-use NPWT devices
- 4.2.5 AI-enabled wound imaging & decision support
- 4.2.6 Outcome-based reimbursement reforms
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Limited reimbursement in emerging markets
- 4.3.2 High total cost of advanced therapies
- 4.3.3 Environmental burden of single-use disposables
- 4.3.4 Shortage of skilled wound-care nurses
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porters Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Product
- 5.1.1 Wound Care
- 5.1.1.1 Dressings
- 5.1.1.1.1 Traditional Gauze & Tape Dressings
- 5.1.1.1.2 Advanced Dressings
- 5.1.1.2 Wound-Care Devices
- 5.1.1.2.1 Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT)
- 5.1.1.2.2 Oxygen & Hyperbaric Systems
- 5.1.1.2.3 Electrical Stimulation Devices
- 5.1.1.2.4 Other Wound Care Devices
- 5.1.1.3 Topical Agents
- 5.1.1.4 Other Wound Care Products
- 5.1.2 Wound Closure
- 5.1.2.1 Sutures
- 5.1.2.2 Surgical Staplers
- 5.1.2.3 Tissue Adhesives, Strips, Sealants & Glues
- 5.1.1 Wound Care
- 5.2 By Wound Type
- 5.2.1 Chronic Wounds
- 5.2.1.1 Diabetic Foot Ulcer
- 5.2.1.2 Pressure Ulcer
- 5.2.1.3 Venous Leg Ulcer
- 5.2.1.4 Other Chronic Wounds
- 5.2.2 Acute Wounds
- 5.2.2.1 Surgical/Traumatic Wounds
- 5.2.2.2 Burns
- 5.2.2.3 Other Acute Wounds
- 5.2.1 Chronic Wounds
- 5.3 By End User
- 5.3.1 Hospitals & Specialty Wound Clinics
- 5.3.2 Long-term Care Facilities
- 5.3.3 Home-Healthcare Settings
- 5.4 By Mode of Purchase
- 5.4.1 Institutional Procurement
- 5.4.2 Retail / OTC Channel
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Solventum
- 6.3.2 Smith & Nephew
- 6.3.3 ConvaTec Group
- 6.3.4 Molnlycke Health Care
- 6.3.5 Cardinal Health
- 6.3.6 Coloplast
- 6.3.7 Paul Hartmann AG
- 6.3.8 Medtronic
- 6.3.9 B. Braun SE
- 6.3.10 Integra LifeSciences
- 6.3.11 Essity Medical
- 6.3.12 Johnson & Johnson (Ethicon)
- 6.3.13 Baxter International
- 6.3.14 Organogenesis
- 6.3.15 Kinetic Concepts
- 6.3.16 Medela AG
- 6.3.17 Medline Industries
- 6.3.18 Lohmann & Rauscher
- 6.3.19 Teleflex Medical
- 6.3.20 Devon Medical
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




