PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939591

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939591
United States Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The United States freight and logistics market is expected to grow from USD 1,381.09 billion in 2025 to USD 1,433.58 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 1,724.6 billion by 2031 at 3.8% CAGR over 2026-2031.
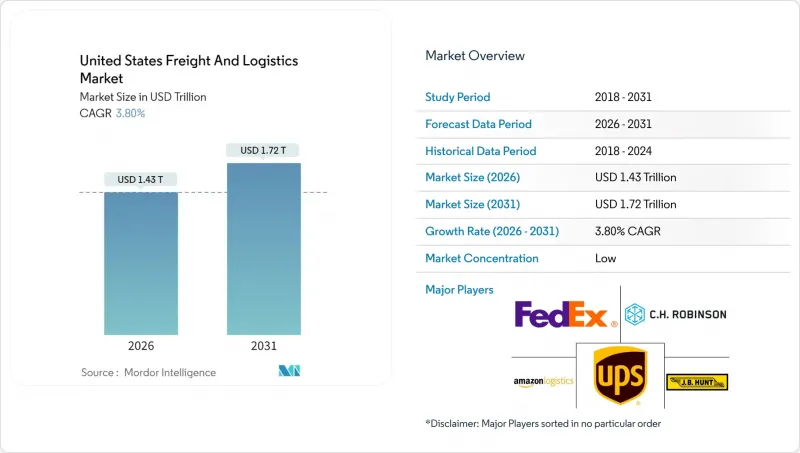
This moderate trajectory reflects a maturing yet resilient landscape shaped by e-commerce fulfillment, nearshoring-driven manufacturing flows, and rapid technology adoption. Shippers shift from asset-heavy to digitally orchestrated networks, unlocking capacity optimization and real-time visibility across modes. Federal Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) funds earmarked for roads, rail, and ports underpin long-term network reliability, while zero-emission truck pilots signal an accelerating transition toward sustainable transport. Competitive intensity tightens as large mergers reshape global forwarding capabilities, even as regional specialists carve niche positions around last-mile and temperature-controlled services.
United States Freight And Logistics Market Trends and Insights
Explosive B2C E-Commerce Parcel Volumes
Domestic parcel shipments increased in 2024, intensifying demand for high-frequency, short-haul movements. Amazon's February 2025 collaboration with FedEx on large packages reinforces distributed fulfillment models that blur lines between retailers and carriers. Consumers expect same-day and next-day delivery, compelling providers to hold reserve capacity during off-peak periods. Regional carriers and last-mile specialists gain share as incumbents manage margin pressure from the groundification of formerly premium air services. The shift toward direct-to-consumer channels reroutes freight from palletized to parcel flows, reshaping lane density and asset utilization requirements.
Reshoring-Driven Domestic Manufacturing Freight Flows
Supply-chain localization accelerates, supported by the CHIPS Act and the Inflation Reduction Act incentives totaling USD 280 billion. Semiconductor, automotive, and pharmaceutical projects concentrate freight demand in the Great Lakes and Southeast corridors. Shorter domestic routes increase reliance on trucking for time-critical components while competing for limited long-haul capacity. Rate premiums emerge on dense manufacturing lanes as reshored volumes stress existing networks, despite ongoing rail and port expansions. State-level incentives amplify regional freight nodes, reinforcing multimodal connectivity priorities.
Acute Long-Haul Driver Shortage and Wage Inflation
Large carriers continued battling elevated turnover in 2024 as an aging workforce and lifestyle concerns deter new entrants. Wage packages climbed as fleets offered signing bonuses, improved home time, and benefit enhancements. Electronic Logging Device mandates and hours-of-service limits reduce effective capacity even when equipment is available. Female and younger worker participation remains low, keeping the labor pool tight. Apprenticeship programs and modernized fleet amenities improve recruitment optics but have yet to close the gap.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Expansion of 3PL/4PL Outsourcing Across Mid-Market Shippers
- Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) Funding
- Port, Rail-Ramp and Urban Congestion Bottlenecks
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Manufacturing contributed 28.54% to the United States freight and logistics market size in 2025 as component inflows and finished-goods distribution multiplied with reshoring incentives. The sector favors multimodal solutions that balance cost and cycle-time, with high-value electronics and pharmaceuticals leaning on expedited services. Wholesale and retail trade, though smaller, posts the fastest 4.05% CAGR (2026-2031) as omnichannel retailing scales micro-fulfillment nodes and parcel density. Construction logistics remain steady on public infrastructure outlays, while oil, gas, mining, and quarrying see volatility tied to commodity pricing and energy policy transitions.
Agriculture, fishing, and forestry maintain a stable baseline of bulk and refrigerated moves, though seasonal variability drives flexible capacity requirements. Emerging verticals, renewable energy components, healthcare devices, and data-center equipment demand specialized handling and regulatory compliance, favoring providers with sector expertise. Across industries, supply-chain localization shifts more volume onto regional trucking lanes, intensifying competition for drivers and warehouse labor in growth corridors.
Freight transport captured 62.85% of the United States freight and logistics market share in 2025, anchored by trucking, rail, and intermodal networks that serve bulk commodities and manufacturing supply chains. CEP, while smaller, posted the strongest 4.38% CAGR (2026-2031) outlook, fueled by e-commerce parcel density clustering around metropolitan fulfillment hubs. Domestic CEP services held 76.05% share, though international small-parcel flows rise on Cross-Border e-commerce demand, supported by simplified de minimis clearance rules. Warehousing and storage demand remains robust, with non-temperature facilities comprising 92.05% of capacity in 2025, yet temperature-controlled square footage expands faster on pharmaceuticals and fresh-food logistics.
Providers blur functional lines as integrated offerings combine transportation, warehousing, and value-added services to capture deeper wallet share. Digital orchestration platforms enable real-time mode selection and inventory balancing across facility networks. CEP operators deploy automated sortation and AI-driven route optimization to offset labor constraints. In freight transport, zero-emission truck pilots and IIJA-funded corridor upgrades will alter fleet mix and regional efficiencies. The convergence of services positions full-stack providers to capitalize on secular shifts while niche specialists succeed by focusing on speed, compliance, or product integrity.
The United States Freight and Logistics Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry, Construction, Manufacturing, Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and Others) and by Logistics Function (Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP), Freight Forwarding, Freight Transport, Warehousing and Storage, and Other Services). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Amazon Logistics
- C.H. Robinson
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- Expeditors International of Washington, Inc.
- FedEx
- GXO Logistics, Inc.
- J.B. Hunt Transport, Inc.
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Landstar System, Inc.
- Lineage, Inc.
- A.P. Moller - Maersk
- NFI Industries
- Old Dominion Freight Line
- Penske Corporation, Inc.
- Ryder System, Inc.
- Schneider National, Inc.
- SEKO Logistics
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- XPO, Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.12 Trucking Fleet Size by Type
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Logistics Performance
- 4.15 Modal Share
- 4.16 Maritime Fleet Load Carrying Capacity
- 4.17 Liner Shipping Connectivity
- 4.18 Port Calls and Performance
- 4.19 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.20 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.21 Infrastructure
- 4.22 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.23 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.24 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.25 Market Drivers
- 4.25.1 Explosive B2C E-Commerce Parcel Volumes
- 4.25.2 Reshoring-Driven Domestic Manufacturing Freight Flows
- 4.25.3 Expansion of 3PL/4PL Outsourcing Across Mid-Market Shippers
- 4.25.4 Federal Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) Funding
- 4.25.5 Digital Freight Marketplaces and API-Based Capacity Aggregation
- 4.25.6 Zero-Emission Truck Corridor Pilots (Hydrogen / BEV)
- 4.26 Market Restraints
- 4.26.1 Acute Long-Haul Driver Shortage and Wage Inflation
- 4.26.2 Port, Rail-Ramp and Urban Congestion Bottlenecks
- 4.26.3 Escalating Cyber-Risk Insurance and Compliance Costs
- 4.26.4 "Nuclear" Jury Verdicts Driving Motor-Carrier Insurance Spikes
- 4.27 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.28 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.28.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.28.2 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.28.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.28.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.28.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Amazon Logistics
- 6.4.2 C.H. Robinson
- 6.4.3 DHL Group
- 6.4.4 DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.5 Expeditors International of Washington, Inc.
- 6.4.6 FedEx
- 6.4.7 GXO Logistics, Inc.
- 6.4.8 J.B. Hunt Transport, Inc.
- 6.4.9 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.10 Landstar System, Inc.
- 6.4.11 Lineage, Inc.
- 6.4.12 A.P. Moller - Maersk
- 6.4.13 NFI Industries
- 6.4.14 Old Dominion Freight Line
- 6.4.15 Penske Corporation, Inc.
- 6.4.16 Ryder System, Inc.
- 6.4.17 Schneider National, Inc.
- 6.4.18 SEKO Logistics
- 6.4.19 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- 6.4.20 XPO, Inc.
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment




