PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939641

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939641
Thailand Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Thailand freight and logistics market is expected to grow from USD 53.38 billion in 2025 to USD 56.56 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 75.47 billion by 2031 at 5.95% CAGR over 2026-2031.
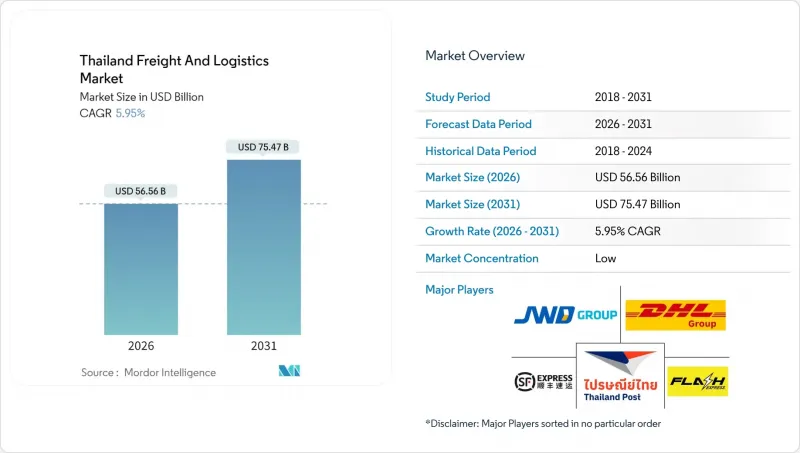
Thailand's position as ASEAN's principal multimodal gateway, combined with sustained manufacturing reshoring and state-led infrastructure investment, underpins this steady expansion. Government mega-projects are compressing transit times, while China+1 investment inflows are reshaping distribution corridors and spurring demand for integrated warehousing. E-commerce continues to lift parcel volumes, prompting operators to modernize last-mile networks and deploy data-driven route optimization. Digitalization-from automated depots to real-time IoT tracking-has become a decisive competitive lever, and sustainability mandates are accelerating modal shifts toward rail and electric truck fleets.
Thailand Freight And Logistics Market Trends and Insights
E-Commerce Boom and Last-Mile Delivery Acceleration
Parcel volumes continue to rise as smartphone penetration surpasses 90% of urban households and online spending migrates from discretionary goods to daily staples. Network densification enables operators to shorten average delivery times to under 24 hours in Bangkok while maintaining nationwide next-day reach. Domestic CEP players have pivoted from aggressive price wars toward yield management, raising unit profitability and freeing cash flow for automation investments. Regional partnerships are unlocking cross-border volumes, with Thai firms leveraging Chinese platforms for seamless fulfillment into CLMV markets. Consumer expectation of real-time visibility is encouraging the rollout of AI-enabled dynamic routing, which cuts fuel costs and shrinks carbon footprints.
Government Mega-Projects (EEC, 2025-2026 Plan, Land Bridge)
The Eastern Economic Corridor anchors USD 16.8 billion of approved investment in 2024 and has catalyzed a new wave of port, airport, and rail link upgrades. The Laem Chabang Terminal F build-out, scheduled to add 4 million TEU capacity by 2027, expands Thailand's container handling headroom by 40%. U-Tapao airport's multi-phase expansion is transforming the province into a tri-modal junction capable of channeling high-value cargo from aircraft to seaport berth within six hours. These assets collectively reduce logistics costs-currently 13-14% of GDP-by lifting multimodal connectivity and alleviating road bottlenecks.
Persistently High Logistics Costs (13-14% of GDP)
Thailand's logistics outlay remains materially higher than the OECD average, largely because 80% of domestic cargo still moves by road. Fragmented trucking fleets lack bargaining power for fuel and equipment, and the median operator runs under five trucks. Port dwell times average 62 hours, adding storage and demurrage expenses. SME carriers face tighter credit as commercial banks prioritize lower-risk segments; SME loan balances fell in 2024 even as corporate lending inched up 1.9%. Policy incentives such as a 10% corporate tax rate in Special Economic Zones should ease the cost burden, yet relocation prerequisites temper uptake.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Manufacturing Re-shoring and China+1 Inflows
- Digitalization (AI/TMS, IoT Visibility, Smart Warehousing)
- Fuel-Price Volatility and Carbon-Pricing Exposure
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Manufacturing accounted for 32.21% of 2025 revenue, anchored by electronics, automotive, and petrochemical clusters in the Eastern Seaboard. High-precision component flows require climate-controlled environments and expedited customs clearance, favoring operators with specialized capabilities. Wholesale and Retail Trade is projected to register the fastest 6.38% CAGR (2026-2031) as omnichannel retailers embrace nationwide fulfillment meshes. Extended cut-off times and same-day delivery windows are pushing demand for micro-fulfillment centers within 5 kilometers of urban shoppers.
Food processors and agribusinesses continue to rely on refrigerated truck lanes linking upcountry farms to Bangkok distribution hubs. Construction logistics remain buoyant thanks to metro rail and airport projects, though they exhibit cyclical demand spikes. The shift toward electric-vehicle assembly is spawning new inbound flows of battery packs and rare-earth magnets, bolstering the Thailand freight and logistics market size for specialized dangerous-goods handling.
Freight Transport contributed 61.12% of Thailand freight and logistics market share in 2025, reflecting sustained bulk cargo flows from industrial estates to ports and border gates. Strong infrastructure links between the Eastern Economic Corridor and Laem Chabang underpin this dominance. At the same time, burgeoning e-commerce demand is propelling CEP revenues, expected to post a 6.92% CAGR between 2026-2031. Traditional road freight firms are integrating real-time telematics and partnering with rail operators to offer quasi-intermodal services that cut transit costs by up to 12%.
Logistics providers are embedding warehouse management systems that feed shipment visibility to shippers, enabling predictive replenishment and smoothing seasonal peaks. As CEP networks densify, "white-glove" two-person deliveries for appliances and electronics are emerging as value-added niches. The government's Land Bridge concept aims to divert trans-Indo-Pacific container flows through southern seaports, which could further expand the Thailand freight and logistics market size for freight transport by mid-decade. In contrast, forwarders expect margin uplift in CEP as operators implement zone-based pricing and fuel surcharge mechanisms.
The Thailand Freight and Logistics Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry, Construction, Manufacturing, Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and Others) and by Logistics Function (Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP), Freight Forwarding, Freight Transport, Warehousing and Storage, and Other Services). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- A.P. Moller - Maersk
- CMA CGM Group (Including CEVA Logistics)
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- FedEx
- Flash Express
- J&T Express
- JWD Group
- Kuehne+Nagel
- LEO Global Logistics Public Co., Ltd.
- Nippon Express Holdings.
- Profreight Group Co., Ltd.
- SCG Logistics, Ltd.
- SF Express (KEX-SF)
- Sub Sri Thai Public Co., Ltd.
- Thailand Post
- Toyota Tsusho (Thailand) Co., Ltd.
- Triple i Logistics Public Co., Ltd.
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- WICE Logistics Public Co., Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.12 Trucking Fleet Size by Type
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Logistics Performance
- 4.15 Modal Share
- 4.16 Maritime Fleet Load Carrying Capacity
- 4.17 Liner Shipping Connectivity
- 4.18 Port Calls and Performance
- 4.19 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.20 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.21 Infrastructure
- 4.22 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.23 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.24 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.25 Market Drivers
- 4.25.1 E-Commerce Boom and Last-Mile Delivery Acceleration
- 4.25.2 Government Mega-Projects (EEC, 2025-26 Plan, Land Bridge)
- 4.25.3 Manufacturing Re-Shoring and China+1 Inflows
- 4.25.4 Digitalisation (AI/TMS, IoT Visibility, Smart Warehousing)
- 4.25.5 Green-Logistics Mandates and Rail Electrification Push
- 4.25.6 Cross-Border CLMV Trade and Trans-Asian Rail Link Uptake
- 4.26 Market Restraints
- 4.26.1 Persistently High Logistics Cost (~13-14 % of GDP)
- 4.26.2 Fuel-Price Volatility and Carbon-Pricing Exposure
- 4.26.3 Parcel-Carrier Margin Squeeze by E-Commerce Platforms
- 4.26.4 U.S. Tariff Risks on Thai Exports (Autos, Electronics)
- 4.27 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.28 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.28.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.28.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.28.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.28.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.28.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 A.P. Moller - Maersk
- 6.4.2 CMA CGM Group (Including CEVA Logistics)
- 6.4.3 DHL Group
- 6.4.4 DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.5 FedEx
- 6.4.6 Flash Express
- 6.4.7 J&T Express
- 6.4.8 JWD Group
- 6.4.9 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.10 LEO Global Logistics Public Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Nippon Express Holdings.
- 6.4.12 Profreight Group Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 SCG Logistics, Ltd.
- 6.4.14 SF Express (KEX-SF)
- 6.4.15 Sub Sri Thai Public Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.16 Thailand Post
- 6.4.17 Toyota Tsusho (Thailand) Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Triple i Logistics Public Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.19 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- 6.4.20 WICE Logistics Public Co., Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment




