PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939734

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939734
Vietnam Foodservice - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
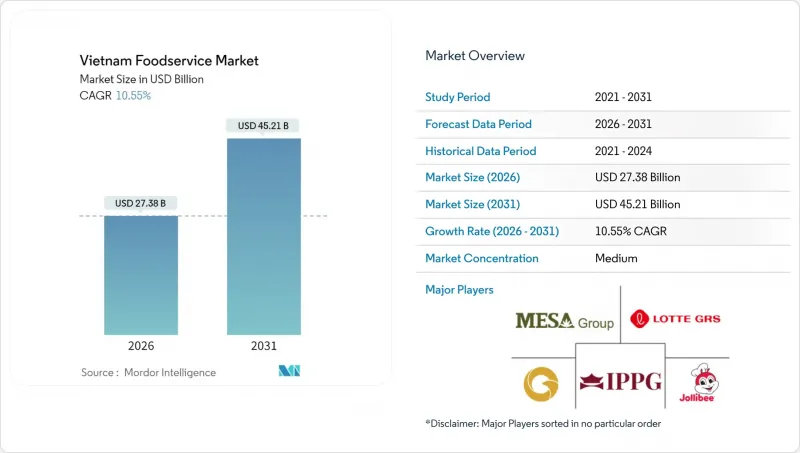
The Vietnam foodservice market was valued at USD 24.77 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 27.38 billion in 2026 to reach USD 45.21 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 10.55% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
The market is experiencing substantial growth as Vietnamese consumers benefit from higher disposable incomes and increased urbanization, while the resurgence in tourism activities drives renewed spending across restaurants, cafes, and food delivery platforms. The digital transformation of the industry has emerged as a significant growth driver, evidenced by cashless payments expanding 26 times faster than the national GDP, while QR code payment systems have become a standard feature across urban establishments. The government's strategic implementation of VAT reductions through Decree 180/2024 and Decree 72/2024 has provided essential financial relief to foodservice operators grappling with increased input costs. Additionally, the robust recovery in tourism, marked by 17.6 million international arrivals in 2024, has reinvigorated revenue streams for foodservice businesses operating within the hospitality sector.
Vietnam Foodservice Market Trends and Insights
Expansion and Modernization of Urban Infrastructure
Vietnam's rapid urbanization is transforming the foodservice landscape by significantly improving market accessibility through enhanced transportation networks and strategic commercial real estate development. The government's substantial infrastructure investments, particularly the ongoing metro system projects in Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi, are systematically reducing delivery times and operational costs while opening untapped markets in previously underserved regions. Urban development initiatives are thoughtfully incorporating mixed-use spaces to establish vibrant food courts and dining districts, naturally concentrating consumer foot traffic and enabling restaurants to optimize their marketing investments. The infrastructure modernization has proven especially valuable for delivery-focused operations, as the expanded road networks and strategically positioned logistics centers enable cloud kitchens to efficiently extend their reach across broader service areas. The ongoing transition toward smart city frameworks, complete with seamless payment systems and robust digital infrastructure, is creating a more conducive operating environment for technology-driven foodservice businesses .
Rapid Digitization and Mobile App Adoption for Ordering
In Vietnam, digital ordering platforms are transforming the foodservice value chain. Users increasingly depend on app-based recommendations for meal selections. This transition has intensified competition, emphasizing algorithm optimization and customer data analysis. The implementation of QR code payments and integrated point of sale (POS) systems has simplified transactions while providing valuable consumer behavior insights. These insights help businesses develop targeted marketing strategies and optimize their menus. Local companies, such as beFood, use AI-powered recommendation engines to compete with international platforms. Similarly, AhaMove demonstrates local innovation by integrating virtual assistants into restaurant Facebook pages. The digital transformation impacts ordering processes, inventory management, supply chain efficiency, and predictive analytics, creating advantages for early technology adopters. The growth in cashless transactions indicates that digital-first operations will likely perform better than traditional cash-based establishments. According to the International Trade Administration, Vietnam's digital economy market is projected to reach USD 45 billion by 2025, with estimates ranging from USD 90 billion to USD 200 billion by 2030 .
Supply Chain Fragility and Ingredient Sourcing Challenges
Vietnam's foodservice sector grapples with persistent supply chain vulnerabilities, as escalating raw material costs continue to erode profit margins across the entire spectrum of food service operators. The unpredictable nature of agricultural prices, compounded by weather pattern changes and worldwide commodity market fluctuations, forces businesses to regularly adjust their menu prices. These constant price revisions strain relationships with regular customers and complicate long-term business planning. International cuisine establishments face additional challenges due to their reliance on imported ingredients, making them susceptible to exchange rate fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. This vulnerability particularly affects high-end restaurants and premium dining venues. The inadequate cold storage infrastructure in smaller cities creates significant obstacles for maintaining fresh ingredient quality, leading to increased food wastage and limiting business growth opportunities for establishments focused on quality dining experiences. The burden of maintaining food safety standards under Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) protocols adds another layer of operational challenges, particularly impacting independent restaurant owners who struggle to distribute compliance-related costs across their operations.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rise of Cloud Kitchens and Virtual-Only Brands
- Increasing Consumer Preference for Convenience and Ready-to-Eat Food
- Pressure from Multinational and Domestic Chains on Smaller Operators
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Full-service restaurants dominate the Vietnamese foodservice market with a 67.74% share in 2025, as diners consistently choose establishments that offer complete dining experiences. These restaurants successfully combine high-quality food offerings with opportunities for social gatherings and pleasant environments. Quick-service restaurants continue to expand through franchising and menu adaptation to local tastes, while cafes and bars thrive within Vietnam's well-established coffee culture
Cloud kitchens are experiencing rapid expansion with a 18.73% CAGR from 2026-2031, as their business model requires lower capital investment and meets the growing demand for food delivery services. The market demonstrates two clear patterns: traditional full-service establishments maintain market leadership by offering distinctive dining experiences, while cloud kitchens gain ground through efficient operations. Within each segment, diverse cuisine options create specialized markets, with Korean and Japanese restaurants showing strong performance in urban locations, while Vietnamese regional dishes remain successful across all restaurant types.
The Vietnamese foodservice market shows a strong preference for independent businesses, which currently control 77.45% of the market share in 2025. This reflects the country's entrepreneurial spirit and consumers' natural inclination toward authentic, local dining experiences. However, chain establishments are gaining momentum, showing an 11.12% CAGR during 2026-2031, as they leverage their advantages in standardized operations, centralized purchasing, and brand recognition.
The franchise business model is becoming increasingly attractive in Vietnam, as it combines the benefits of rapid expansion while preserving local ownership. Local brands like Trung Nguyen E-Coffee have set ambitious targets of 3,000 stores, while international players such as Minor Food Group aim to double their footprint to exceed 200 outlets by 2026. Independent business owners are experiencing mounting challenges, particularly from labor cost increases, with minimum wages set to rise by 6.92% in 2025, alongside regulatory requirements that favor businesses with dedicated administrative teams. The current regulatory environment, governed by Decree 35/2006 and its subsequent modifications, creates favorable conditions for master franchise agreements, enabling local entrepreneurs to access proven business systems while maintaining operational independence.
The Vietnam Foodservice Market Report Segments the Industry Into Foodservice Type (Cafe and Bars, Cloud Kitchen, Full Service Restaurants, Quick Service Restaurants), Outlet (Chained Outlets, Independent Outlets), Location (Leisure, Lodging, Retail, Standalone, Travel), and Service Type (Dine-In, Takeaway, and Delivery). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Golden Gate Group JSC
- Imex Pan Pacific Group
- Jollibee Foods Corporation
- Lotte GRS Co. Ltd.
- Mesa Group
- Restaurant Brands International
- Starbucks Corporation
- The Al Fresco's Group
- Yum! Brands Inc.
- Redsun ITI Corporation
- Viet Thai International JSC
- Trung Nguyen Legend Group
- Masan Group
- Tokyo Deli Vietnam JSC
- McDonald's Corporation
- Huy Vietnam
- Pizza 4P's Holdings
- KIDO Group
- Baemin Vietnam
- Highlands Coffee JSC
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Number of Outlets
- 4.2 Average Order Value
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
5 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 5.1 Market Overview
- 5.2 Market Drivers
- 5.2.1 Expansion and modernization of urban infrastructure
- 5.2.2 Rapid digitization and mobile app adoption for ordering
- 5.2.3 Rise of cloud kitchens and virtual-only brands
- 5.2.4 Increasing consumer preference for convenience and ready-to-eat food
- 5.2.5 Strong coffee and cafe culture
- 5.2.6 Expansion of quick-service and fast-casual restaurant chains
- 5.3 Market Restraints
- 5.3.1 Supply chain fragility and ingredient sourcing challenges
- 5.3.2 Pressure from multinational and domestic chains on smaller operators
- 5.3.3 Quality consistency issues and lack of standardized operating procedures among independents
- 5.3.4 Frequent policy/tax changes on food and beverage products
- 5.4 Porter's Five Forces
- 5.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 5.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 6.1 By Foodservice Type
- 6.1.1 Cafe and Bars
- 6.1.1.1 By Cuisine
- 6.1.1.1.1 Bars and Pubs
- 6.1.1.1.2 Cafe
- 6.1.1.1.3 Juice/Smoothie/Desserts Bars
- 6.1.1.1.4 Specialist Coffee and Tea Shops
- 6.1.1.1 By Cuisine
- 6.1.2 Cloud Kitchen
- 6.1.3 Full Service Restaurants
- 6.1.3.1 By Cuisine
- 6.1.3.1.1 Asian
- 6.1.3.1.2 European
- 6.1.3.1.3 Latin American
- 6.1.3.1.4 Middle Eastern
- 6.1.3.1.5 North American
- 6.1.3.1.6 Other FSR Cuisines
- 6.1.3.1 By Cuisine
- 6.1.4 Quick Service Restaurants
- 6.1.4.1 By Cuisine
- 6.1.4.1.1 Bakeries
- 6.1.4.1.2 Burger
- 6.1.4.1.3 Ice Cream
- 6.1.4.1.4 Meat-based Cuisines
- 6.1.4.1.5 Pizza
- 6.1.4.1.6 Other QSR Cuisines
- 6.1.4.1 By Cuisine
- 6.1.1 Cafe and Bars
- 6.2 By Outlet
- 6.2.1 Chained Outlets
- 6.2.2 Independent Outlets
- 6.3 By Locations
- 6.3.1 Leisure
- 6.3.2 Lodging
- 6.3.3 Retail
- 6.3.4 Sandalone
- 6.3.5 Travel
- 6.4 By Service Type
- 6.4.1 Dine-in
- 6.4.2 Takeaway
- 6.4.3 Delivery
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Market Concentration
- 7.2 Strategic Moves
- 7.3 Market Ranking Analysis
- 7.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials (if available), Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 7.4.1 Golden Gate Group JSC
- 7.4.2 Imex Pan Pacific Group
- 7.4.3 Jollibee Foods Corporation
- 7.4.4 Lotte GRS Co. Ltd.
- 7.4.5 Mesa Group
- 7.4.6 Restaurant Brands International
- 7.4.7 Starbucks Corporation
- 7.4.8 The Al Fresco's Group
- 7.4.9 Yum! Brands Inc.
- 7.4.10 Redsun ITI Corporation
- 7.4.11 Viet Thai International JSC
- 7.4.12 Trung Nguyen Legend Group
- 7.4.13 Masan Group
- 7.4.14 Tokyo Deli Vietnam JSC
- 7.4.15 McDonald's Corporation
- 7.4.16 Huy Vietnam
- 7.4.17 Pizza 4P's Holdings
- 7.4.18 KIDO Group
- 7.4.19 Baemin Vietnam
- 7.4.20 Highlands Coffee JSC
8 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




